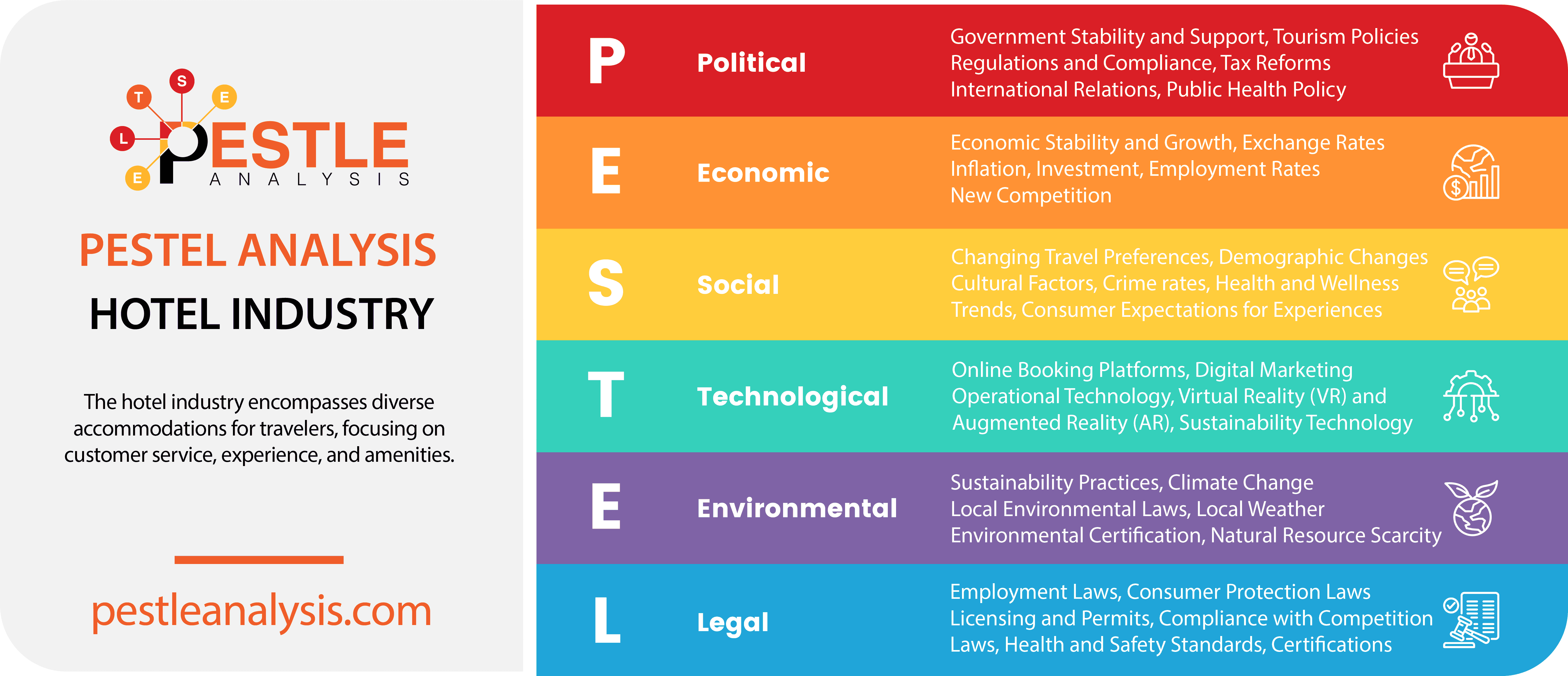
Many factors affect the success and growth of the hotel industry. Everything from governmental changes to high stake competitors and the uncontrollable weather impedes the hospitality industry. In this PESTLE analysis of the hotel industry, we identify the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors that affect the trillion-dollar industry!
Hotel Industry's Political Factors

- Government Stability and Support: The stability of the political environment in a country can significantly influence the hotel industry. Hotels thrive in stable political conditions where policies and governance encourage tourism and investment. Government incentives, grants, or tax relief for tourism-related activities can boost the industry. At the same time, travel bans can kill the hotel and tourism industry. All it takes is one decision and a country loses the vast majority of its economy.
- Tourism Policies: Governments actively promoting tourism can positively impact the hotel industry by increasing the number of inbound international travelers. Initiatives might include marketing campaigns abroad, visa regime relaxation, and hosting international events.
- Regulations and Compliance: Hotels must comply with numerous regulations, including health and safety standards, labor laws, and building codes. Changes in these regulations can affect operational costs and strategies. For example, stricter immigration laws might complicate hiring foreign labor, which is common in many tourist destinations.
- Tax Reforms: Another thing the government controls is taxes. If there were a tax reform in which hotel owners pay lower taxes, it could improve the industry as a whole. Luxury and high-grade hotels could put that savings towards building more accommodations for guests.
- International Relations: The relationship between the home country and others can influence tourism. For instance, ease of travel and favorable diplomatic relations can lead to increased tourist influxes, whereas conflicts or poor relations can deter travelers.
- Public Health Policy: The recent COVID-19 pandemic highlighted how public health policies can dramatically affect the hotel industry. Travel bans, lockdowns, and quarantine requirements have immediate impacts on hotel occupancy rates and operational capabilities.
- Leadership Change: Since the government affects this industry so intensely, many hotel owners are on edge during election time, as a new President with new ideals can swiftly impact the hotel industry, and overthrow the previous President’s laws.
Political Factors: Examples
- Dubai, part of the United Arab Emirates, demonstrates how political stability and proactive tourism policies can foster growth in the hotel industry. The government's stable rule and significant investments in tourism infrastructure, like the development of landmarks (e.g., Burj Khalifa, Dubai Mall) and world-class airport facilities, have positioned Dubai as a top global destination. This supportive environment has led to a boom in hotel developments, attracting international hotel chains and increasing tourist inflows annually.
- The 2024 budget announcement has been perceived as disappointing by the hospitality industry due to the lack of supportive measures such as a reduction in VAT for hospitality services and the failure to reintroduce VAT-free shopping for overseas tourists. This situation exemplifies a political factor in the PESTLE analysis, demonstrating how government fiscal policies directly affect the operational environment and financial health of the hotel and broader hospitality sectors.
Hotel Industry's Economic factors

- Economic Stability and Growth: Economic conditions greatly influence consumer spending power and travel habits. In thriving economies, both leisure and business travel tend to increase, benefiting hotels. While all businesses are affected by economic changes, the hotel industry is one of the most susceptible to their influence. It goes through economic cycles first and emerges first. Whether it emerges successfully depends on a few primary factors, including unemployment rates, job growth, and travel spending.
- Exchange Rates: The strength of currency can bolster the industry. Fluctuations in currency exchange rates can affect the affordability of traveling to certain destinations, influencing the number of international tourists a country receives. If international currencies are stronger than the American dollar, people outside of the United States will want to visit.
- Inflation Rates: Higher inflation can lead to increased operational costs for hotels, such as utilities, supplies, and wages, potentially reducing profitability unless prices are adjusted.
- Investment: The level of domestic and foreign investment in infrastructure, like roads, airports, and public transport, can enhance accessibility and attractiveness of a destination, benefiting hotels. Hospitality is one of the biggest investment sectors for global investors, especially within the United States. Continued growth is expected into 2020 and beyond.
- Employment Rates: Employment levels also impact the hotel industry. Higher employment rates typically boost business and leisure travel, while lower rates might reduce consumer spending on travel.
- New Competition: Airbnb is the hotel industry’s biggest competition. Travelers, particularly millennials, enjoy the mass selection of rooms Airbnb offers. You can quickly and conveniently book your room through an app — and it’s often less expensive than hotels in the area. Hotels often run out of rooms during peak seasons, and when they don’t, they jack up the room prices. At one time, trying to find a different hotel would be the only option, but now you can check Airbnb and likely find something suitable and cheaper. This is a huge problem for hotels who often see a hike in profit during peak seasons when rooms are scarce. Hotels do offer more than the standard Airbnb room. Many hotels have additional facilities, like pools, a gym, and even massage parlors. You can eat at the many restaurants built within, like Starbucks and iHop, too.
Economic Factors: Examples
- UK's decision to leave the European Union, known as Brexit, had mixed effects on the British hotel industry. On one hand, the weakened British pound made the UK an attractive destination for foreign tourists. On the other hand, Brexit raised operational costs and uncertainty when it comes to labor since many hotel staff come from EU countries.
- The 2024 Global Hotels Outlook report by CBRE forecasts a 3% growth in Revenue Per Available Room (RevPAR), driven by a rebound in international travel and robust demand in the meetings and events sector.
Hotel Industry's Social Factors

- Changing Travel Preferences: Trends such as eco-tourism, solo travel, staycations, or preference for boutique over chain hotels can shift market dynamics.
- Demographic Changes: Aging populations might prefer different accommodations than younger travelers, influencing service offerings.
- Cultural Factors: Cultural events and festivals can significantly boost demand for temporary accommodations. Understanding cultural dynamics and seasonal peaks is crucial for strategic planning in hospitality.
- Crime rates: Crime rates can significantly influence both the perception and reality of safety for tourists and business travelers, thereby impacting their decision to visit a particular destination. Everyone wants to stay somewhere safe. If a hotel is near an area with high crime rates, it’ll struggle to survive. Choosing a spot with low crime is crucial for all hotel owners, otherwise, customers won’t stay at their locations.
- Health and Wellness Trends: Growing interest in health and wellness can lead hotels to offer specialized services like spa treatments, wellness programs, and healthy food options.
- Consumer Expectations for Authentic Experiences: There's an increasing demand for authentic and personalized travel experiences, driving hotels to offer unique, locally-inspired services and amenities.
Social Factors: Examples
- The Lapa Rios Lodge in Costa Rica is an example where the hotel's operations are deeply integrated with conservation efforts and community engagement. This approach attracts travelers who are conscious of their environmental impact. At the same time, it helps preserve the local ecosystem, promoting sustainable tourism.
Hotel Industry's Technological Factors

- Online Booking Platforms: The rise of platforms like Booking.com, Airbnb, and others has changed how customers find and book hotels, increasing competition but also expanding market reach.
- Digital Marketing: Social media and online marketing play a crucial role in attracting tourists. Hotels need robust strategies to engage potential customers online. Years ago, hotels only used traditional media (print and broadcast), but now there are new media brought forth via the internet to consider. Social media, like Facebook and mobile apps, are the most prominent tools hotel owners can use but they must also be wary of. Reviews on blogs can make or break a hotel’s reputation. Anyone can write a review and post it on a blog or share it on social media. People who stay at hotels will take photos and write up an honest post about their experience. This is a good and bad thing for the hotel industry. Hotel owners who are confident that their hotels are worthy will pay social media influencers to write about it. Hopefully, this will grab attention and the hotel chain will gain new customers. However, it only takes one scathing review to destroy a reputation.
- Operational Technology: Innovations in management software and Internet of Things (IoT) can improve operational efficiency, customer service, and data management. Think of smart room features controlled by apps or voice, such as lighting, temperature, and entertainment systems.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): VR for virtual tours during booking and AR for enhancing in-stay experiences.
- Sustainability Technology: Systems designed to monitor and reduce energy usage, part of the broader trend towards greener operations.
Technological Factors: Examples
- The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of contactless technologies in hotels globally. As a result, Hilton Hotels introduced "Digital Key" technology, allowing guests to check-in, choose their room, and unlock their hotel room door, all from their mobile devices. This technology enhanced guest safety by reducing physical contact and provided convenience, improving the overall customer experience during a critical time.
- The implementation of customer service chatbots, AI-supported pricing algorithms, advanced mobile technologies, data-driven customer insights, service robots, and integrated payment solutions are six significant technological trends transforming the hospitality industry in 2024. These technologies are enhancing guest experiences, improving operational efficiency, and enabling better data utilization within hotels.
Hotel Industry's Legal Factors

- Employment Law: Compliance with local and international labor laws is critical in avoiding legal issues and ensuring fair work practices.
- Consumer Protection Laws: These regulate services provided and impact how hotels interact with customers, manage complaints, and protect customer data. Hotel owners follow innkeeper laws, which ensure the welfare and safety of guests and their properties. In some locations, the innkeeper law must be posted inside the door of every guest room of the hotel. In most cases, the innkeeper law will state how much compensation the innkeeper will pay guests if their property is stolen or damaged.
- Licensing and Permits: Operating a hotel requires various licenses and permits that can be subject to local governmental changes and bureaucracy.
- Compliance with Competition Laws: Hotels must adhere to antitrust and competition laws to avoid legal risks and fines. These laws prevent unfair business practices like price-fixing or monopolistic behaviors. Ensuring compliance not only avoids legal challenges but also fosters a fair competitive market, benefiting both consumers and the industry's integrity.
- Health and Safety Standards: Hotels must comply with national and local health and safety regulations concerning food handling, preparation, and storage. This includes employee hygiene, kitchen cleanliness, and proper food storage conditions to prevent contamination and foodborne illnesses.
- Training and Certification: Staff involved in food preparation and service often need specific training and certifications in food safety practices. This involves additional costs for the hotel for training programs and ensuring certifications are up to date.
- Inspections and Audits: Regular health inspections by local authorities can affect how hotels manage their dining facilities. Failing an inspection can lead to fines, temporary closures, or in severe cases, permanent closure of the facility, affecting the hotel's reputation and financial performance.
Legal Factors: Examples
- In 2023, MGM's Aria Resort & Casino faced a lawsuit for racial discrimination after allegedly detaining an African-American attorney staying at the property. This case underscores the legal factor in the PESTLE analysis, demonstrating how non-compliance with discrimination laws and inadequate handling of guest relations can lead to significant legal challenges, impact public perception, and incur potential financial penalties. It highlights the critical need for hotels to ensure all staff are trained on anti-discrimination policies and that these policies are rigorously enforced to maintain a respectful and inclusive environment for all guests.
- In 2024, benchmarking company STR, along with 10 hotel companies, faced a lawsuit claiming that the 'exchange of competitively sensitive information' allows operators to set high prices. Such legal challenges highlight critical issues within the hotel industry regarding compliance with competition laws.
Hotel Industry's Environmental factors

- Sustainability Practices: Increasing awareness and regulations around environmental sustainability affect how hotels manage their waste, energy, and water resources.
- Climate Change: Changes in climate can affect tourism patterns and destinations, necessitating adaptive strategies in hotel operations and offerings.
- Local Environmental Laws: Compliance with environmental regulations is not just legally necessary but can also serve as a marketing tool for eco-conscious travelers.
- Local Weather: When vacationing, customers want to stay somewhere warm and relaxing. The weather in the local area is the deciding factor for whether someone chooses to stay at a certain hotel. This isn’t something hotel owners can control, but they must understand the seasonal differences before pricing their rooms — and adjust accordingly.
- Environmental Certification: Certifications like LEED or Green Seal can attract environmentally conscious consumers.
- Carbon Footprint Concerns: Pressure to reduce carbon emissions leads to innovations in building design and operational efficiencies.
- Natural Resource Scarcity: Scarcity of water and other natural resources can influence operational costs and sustainability efforts.
Environmental Factors: Examples
- In 2024, the new EU Directive on environmental advertising, which impacts how hotels communicate their sustainability credentials, is an example of a legal and environmental factor in our PESTLE analysis. This directive imposes strict rules on "green advertising," requiring specific substantiation for environmental claims such as "eco-friendly" or "energy efficient." Hotels must now meet high standards for environmental performance to use such claims, influencing how they market their sustainability efforts and comply with new legal standards.
Recommendations based on the Hotel Industry's PESTLE analysis
The hotel industry is experiencing major competition with corporations like Airbnb, which offers a variety of rooms for cheaper than the average hotel room. The industry is also overly reliant on the government; everything from potential tax reform to travel bans can cause the industry to crumble.
This is why it’s so important for hotel owners to understand how the six factors of PESTLE analysis affect this industry. If they don’t, they may find themselves on the receiving end of harsh online reviews and customer loss due to environmental issues and legal challenges.
If you’re curious about the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats this industry faces, read our SWOT Analysis of the Hotel Industry here to learn more and check out our PESTLE Analysis of the Tourism Industry. Finally, here's the PESTLE analysis of well-renowned hotels around the world:









