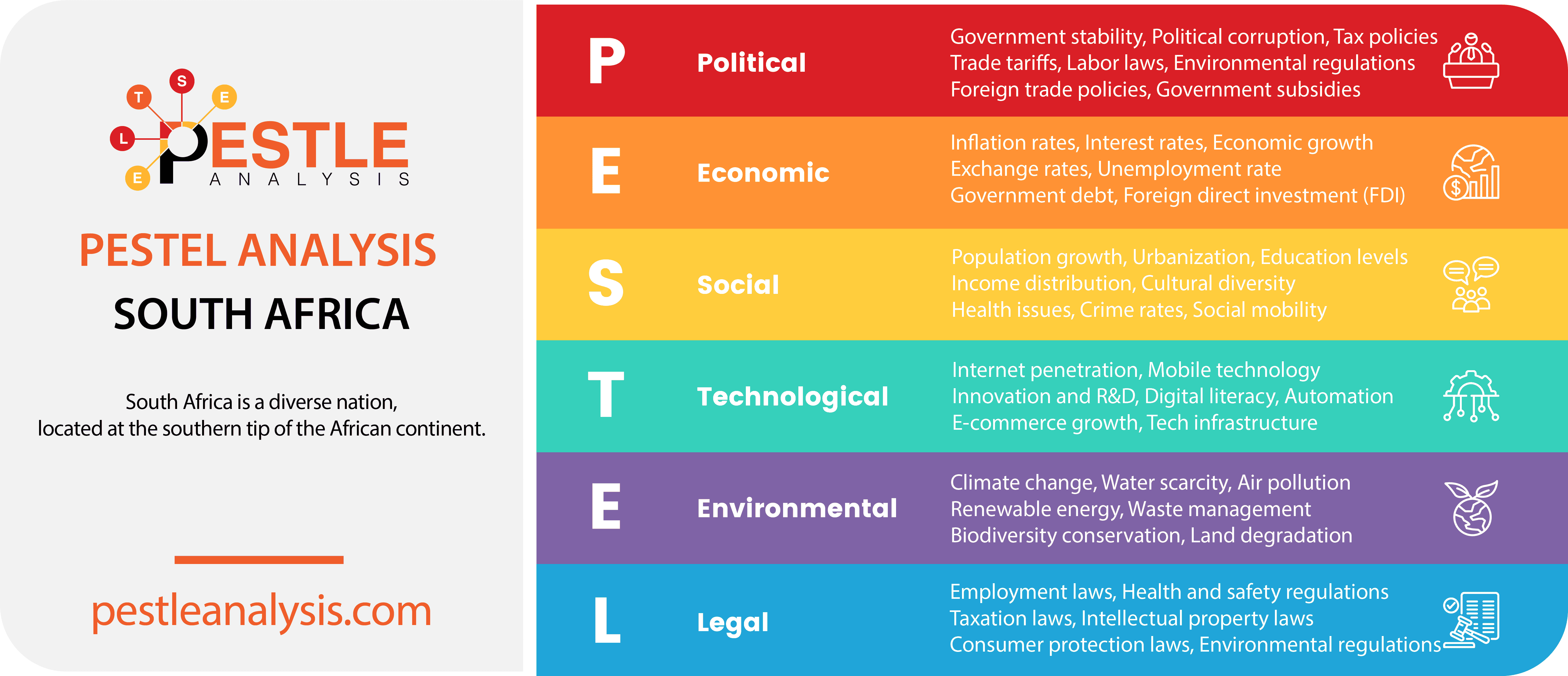
Our PESTLE analysis of South Africa studies the political, economic, social, technological, legal and environmental factors affecting its business environment.
South Africa is improving conditions for budding businesses. But companies outside the country question whether to expand into it due to several issues. This PESTLE analysis will examine the many situations South Africa is currently experiencing that may affect businesses within it.
South Africa PESTLE Analysis
A PESTLE analysis is a strategic tool used to evaluate the external factors that can impact a country or organization. The acronym stands for Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors. Each of these elements is analyzed to understand the broader context in which a business operates, identifying potential opportunities and threats.
A PESTLE analysis of South Africa would be of interest to:
- Investors: To assess the risks and opportunities associated with investing in South Africa.
- Businesses: Both local companies and international firms considering expansion into South Africa would benefit from understanding the external factors that could influence their operations.
- Policy Makers: To identify areas that require policy intervention to create a more conducive business environment.
- Academics and Researchers: To study the impact of external factors on South Africa's economic and business landscape.
- Consultants and Advisors: To provide informed advice to clients about the viability and potential of business ventures in South Africa.
By understanding these factors, business managers and operators can make informed decisions about entering or expanding within the South African market. You can find more about PESTLE analysis here.
South Africa's Political Factors

- Government stability: South Africa's political stability influences investor confidence and long-term business planning. Periods of instability can deter investment and disrupt operations.
- Political corruption: Corruption can affect the efficiency of government services and increase the cost of doing business, leading to reduced foreign investment and economic growth. Being mixed up in questionable politics puts a damper on those attempting to build a business and those on the fence about investing in South African businesses.
- Example: The "State Capture" scandal involved extensive corruption where private interests had a significant influence over state institutions, leading to the misallocation of resources, undermining of regulatory bodies, and loss of public trust. High-profile investigations and arrests, including those of former President Jacob Zuma and other senior officials, have brought attention to the pervasive corruption in the country. There is widespread criticism of the ANC (African National Congress) for fostering a corrupt environment and failing to implement necessary reforms. People call for stricter penalties for corruption, better enforcement of laws, and more accountability for public officials. Despite a few optimistic voices recognizing competent individuals within the political system, people's overall tone remains critical and demands significant changes to improve the country’s governance and accountability.
- Tax policies: Tax rates and structures impact business profitability and investment decisions. South Africa's tax policies, including corporate tax rates and VAT, directly affect business costs and pricing strategies.
- Trade tariffs: Import and export tariffs can influence the competitiveness of South African products abroad and the cost of imported goods, impacting supply chains and pricing.
- Example: In 2018, under Section 232 of the Trade Expansion Act, the US implemented a 25% tariff on steel and a 10% tariff on aluminum imports from various countries, including South Africa. The new tariffs increased costs for exporters, reduced their competitiveness in the US market, and forced them to seek alternative markets, thereby impacting the broader South African economy.
- Labor laws: Regulations regarding minimum wage, working conditions, and employment rights affect labor costs and operational flexibility for businesses in South Africa.
- Environmental regulations: Compliance with environmental laws can increase operational costs but also open opportunities for businesses in green technologies and sustainable practices.
- Foreign trade policies: Policies that govern international trade agreements and partnerships impact market access and competitive positioning for South African businesses globally.
- Intellectual property protection: Strong IP laws encourage innovation and investment in research and development, benefiting businesses in technology and creative industries.
- Government subsidies: Subsidies can support specific industries, making them more competitive, but can also lead to market distortions if not managed properly.
- Example: Subsidies for small-scale farmers include grants for purchasing seeds, fertilizers, and equipment, as well as funding for infrastructure improvements like irrigation systems. This support aims to enhance agricultural productivity, ensure food security, and promote economic development in rural areas.
- Regulatory bodies and their efficiency: The effectiveness of regulatory agencies in South Africa affects the ease of doing business, from obtaining licenses to compliance with standards.
- Political conflicts: Internal and external political conflicts can disrupt economic activities, affect consumer confidence, and deter foreign investment.
- International relations: Diplomatic relationships with other countries influence trade opportunities, investment flows, and market access for South African businesses.
- Example: South Africa's membership in the BRICS group, which includes Brazil, Russia, India, and China, has facilitated economic cooperation. This alliance increased trade opportunities and attracted investment from other BRICS countries, bolstering South Africa's economy and enhancing its geopolitical influence on the global stage.
- Public infrastructure policies: Government investment in infrastructure such as transportation, energy, and communication networks is critical for business operations and economic growth.
- National security policies: Policies affecting national security can impact the stability of the business environment, including the safety of investments and the movement of goods.
- Political ideology: The ruling party's ideology influences economic policies, regulatory frameworks, and business support programs, impacting the overall business climate.
- Corporate governance standards: High standards in corporate governance promote transparency, reduce corruption, and increase investor confidence in South African businesses.
- Political interference in business: Excessive government interference can stifle innovation and competition, while a supportive environment can foster business growth.
- Example: The controversy surrounding the Gupta family and their influence over state-owned enterprises during former President Jacob Zuma's administration demonstrates this factor. The Guptas allegedly used their political connections to secure lucrative contracts and influence key appointments within companies like Eskom and Transnet. This interference led to widespread corruption, mismanagement, and ultimately significant financial and operational setbacks for these state-owned enterprises, highlighting the detrimental impact of political meddling on business integrity and performance.
- Property rights: Secure property rights are essential for investment, as businesses need assurance that their assets and investments are protected by law.
- Policy continuity: Consistency in government policies ensures a predictable business environment, which is crucial for long-term investment and strategic planning.
- Legal system efficiency: An efficient legal system provides timely resolution of disputes, enforcement of contracts, and protection of business interests, enhancing the overall business climate in South Africa.
South Africa's Economical Factors

- Inflation rates: High inflation erodes purchasing power, increasing costs for consumers and businesses, and can lead to higher interest rates, affecting loans and investments.
- Interest rates: Influences borrowing costs for businesses and consumers; higher rates can reduce spending and investment, while lower rates can stimulate economic activity.
- Economic growth: Affects overall business environment; strong growth provides opportunities for expansion, while slow growth can lead to reduced consumer demand and business contraction. A weak economy will cause new corporations to be cautious when thinking of expanding business into South Africa. It also makes it more difficult for businesses within South Africa to branch out — a high exchange rate makes costs and expenses for South African businessmen difficult.
- Exchange rates: Fluctuations in the rand's value impact import and export competitiveness, affecting trade balances and profitability for businesses engaged in international trade. Right now, the currency is subjected by the market forces. But with such low currency and exchange rate, it’s a wonder how businesses will start or stay in demand with the diminishing Rand. While the Reserve Bank has the ability to influence Rand, it’s staying neutral, except in relation to interest, where the Reserve Bank will respond with interest rate spikes as the rand continues to weaken.
- Unemployment rates: High unemployment reduces consumer spending power and can lead to social instability, while low unemployment boosts economic activity through higher consumption.
- Example: As of May 2024, South Africa's unemployment rate stands at 32.9%, making it one of the highest in the world. This high rate of unemployment reflects ongoing economic challenges, including slow economic growth, structural issues in the labor market, and persistent inequality. The elevated unemployment levels continue to impact consumer spending, social stability, and overall economic performance in the country.
- Government debt: High levels of debt can limit government spending on infrastructure and social programs, potentially leading to higher taxes and reduced public services.
- Foreign direct investment (FDI): Inflows of FDI bring capital, technology, and expertise, boosting economic development and job creation, while low FDI can signal a lack of investor confidence.
- Example: According to UNCTAD’s World Investment Report 2023, FDI flows to Africa reached USD 9 billion in 2022, with South Africa attracting several significant battery storage projects and recording a total FDI stock of USD 173.5 billion, equivalent to 42.8% of its GDP. Despite this potential, South Africa's performance in attracting FDI remains relatively weak compared to other African countries, though there was a notable increase in FDI inflows in 2023, with ZAR 53.8 billion in the second quarter and ZAR 26 billion in the third quarter, primarily from European and other global investors in sectors like financial services, mining, manufacturing, and retail
- Consumer confidence: Reflects the willingness of consumers to spend money; high confidence can drive economic growth, while low confidence can lead to reduced consumption and business revenues.
- Commodity prices: South Africa's economy is heavily reliant on mining; fluctuations in prices of gold, platinum, and other commodities significantly impact export revenues and economic stability.
- Trade balance: Affects the country's foreign exchange reserves and currency stability; trade deficits can lead to currency devaluation, while surpluses strengthen the economy.
- Example: South Africa continues to have strong trade ties with China, but fluctuations in China's economic performance significantly impact South Africa's business environment. Recently, as China's economy has faced challenges such as slowing growth rates and shifts in economic policies, the effects have been felt in South Africa. In 2015, for instance, China's investment in South Africa fell by 87%, highlighting the vulnerability of South Africa's economy to changes in Chinese economic conditions.
- Industrial output: Levels of production in manufacturing and mining sectors directly influence economic performance and employment rates.
- Infrastructure quality: Adequate infrastructure supports efficient business operations and economic growth, while poor infrastructure can hinder productivity and increase operational costs.
- Labor market conditions: The availability and cost of skilled labor impact business operations and competitiveness, with labor strikes and disputes potentially disrupting economic activity.
- Example: In 2014, South America experienced 88 significant labor strikes, many of which lasted for several months. These strikes involved workers halting their jobs in various industries, including mining, manufacturing, and public services. The prolonged nature of these strikes caused substantial disruptions to production and services, leading to financial losses for companies and economic slowdowns in affected regions.
- Energy availability and costs: Reliable and affordable energy is crucial for industrial operations; energy shortages and high costs can constrain economic growth and lead to production losses.
- Taxation policies: Corporate and personal tax rates influence business investment decisions and disposable income for consumers, affecting overall economic activity.
- Economic policies: Government strategies on fiscal and monetary policies impact economic stability, growth prospects, and investor confidence.
- Global economic conditions: External economic environments, such as recessions or booms in major trading partners, affect South Africa's export demand and overall economic health.
- Availability of credit: Access to affordable credit is essential for business expansion and consumer spending; restricted credit availability can stifle economic growth and entrepreneurship.
South Africa's Social Factors
- Population growth: South Africa's rapidly growing population increases demand for goods and services but also puts pressure on infrastructure, healthcare, and education systems.
- Urbanization: The migration of people from rural to urban areas leads to the expansion of cities, creating opportunities for businesses but also challenges like housing shortages and increased demand for public services.
- Example: In Gauteng, the influx of people has driven economic growth by creating more jobs and enhancing consumer markets, but it has also led to infrastructure bottlenecks and employment challenges. Businesses need to adapt to these changing dynamics by investing in efficient infrastructure and leveraging urban opportunities while managing the risks associated with rapid urbanization
- Education levels: Variations in education quality and access affect workforce skills, impacting productivity and the ability of businesses to find qualified employees. South Africa faces significant challenges, such as poor infrastructure, inadequate facilities, and educational disparities stemming from the apartheid era, which continue to affect current outcomes. Many schools lack basic resources like libraries, laboratories, and internet access, leading to high dropout rates and low literacy levels. Consequently, businesses struggle to find qualified workers, hampering their growth and competitiveness in the global market
- Income distribution: High levels of inequality can lead to social unrest and reduced consumer spending power among the lower-income population, affecting overall economic stability.
- Cultural diversity: South Africa's diverse cultural landscape can enrich the business environment with various perspectives and ideas but may also require businesses to navigate complex social dynamics and preferences.
- Example: Unilever South Africa has leveraged the country's cultural diversity by tailoring its products and marketing strategies to appeal to various ethnic groups. For instance, the company offers a range of personal care products specifically designed for different hair types and skin tones prevalent among South Africa's diverse population.
- Health issues: High prevalence of diseases such as HIV/AIDS and tuberculosis impacts the workforce's health and productivity, increasing healthcare costs for businesses.
- Crime rates: High crime rates can deter investment, increase security costs for businesses, and affect the overall business climate by reducing consumer confidence.
- Example: Due to high crime rates, particularly armed robberies and burglaries, Shoprite has had to invest significantly in security measures, such as hiring additional security personnel, installing advanced surveillance systems, and implementing stricter loss prevention protocols. By establishing a command center staffed with specialists in investigation, data analysis, and law, Shoprite has significantly reduced armed robberies and burglaries nationwide. Their efforts, which include advanced surveillance, AI, and community tip-offs, have led to numerous arrests and convictions, totaling over 1,384 years in sentences.
- Social mobility: Limited social mobility can entrench inequality, leading to a less dynamic economy and reducing opportunities for businesses to tap into a broader talent pool.
- Consumer behavior: Shifts in consumer preferences and behaviors, driven by changing lifestyles and values, influence market demand and business strategies.
- Demographic shifts: Changes in age distribution, such as a growing youth population or aging workforce, affect labor markets, consumer markets, and social services.
- Public awareness and activism: Increased public awareness and activism around issues like environmental sustainability and corporate responsibility can drive businesses to adopt more ethical practices and transparency.
- Labor force participation: Rates of participation in the labor force, influenced by factors such as gender and age, affect the availability of workers and overall economic productivity.
- Migration patterns: Influxes of immigrants or emigration trends can alter labor markets, consumer bases, and social dynamics, impacting businesses.
- Social cohesion: Levels of social cohesion and community engagement influence the stability and attractiveness of the business environment.
- Technology adoption: The rate at which different social groups adopt new technologies affects market opportunities for businesses in various sectors.
- Poverty levels: High poverty rates limit consumer spending power and can create challenging market conditions for businesses targeting low-income segments.
- Housing availability: The availability and affordability of housing impact the cost of living and labor market dynamics, influencing business costs and employee retention.
- Example: Companies like Anglo American Platinum have had to invest heavily in housing projects for their employees to address the severe shortage of affordable housing in mining regions. This investment not only helps in attracting and retaining workers but also improves employee morale and productivity.
- Transportation infrastructure: Quality and accessibility of public transportation affect employee commute times and business logistics, impacting productivity and operational efficiency.
- Gender equality: Progress towards gender equality in the workplace can enhance workforce diversity and productivity, benefiting business performance.
- Example: The Mining Charter, implemented by mining companies like De Beers, mandates that women must hold at least 10% of mining jobs, which has led companies to actively recruit and promote women within the industry.
- Social media influence: The growing influence of social media shapes consumer trends, brand perception, and marketing strategies for businesses.
South Africa's Technological Factors
Technological advancements within manufacturing and supply chains may be thin. With the government preoccupied with lowering employment rates and removing corrupt politicians from local campaigns, plus the devalued Rand, technology may be more stagnated than in other locations, such as the United States of America.
- Internet penetration: High-speed internet access remains uneven across South Africa, with urban areas having better connectivity than rural regions. This affects business operations, digital transformation, and access to online markets.
- Example: Increased internet penetration has enabled the e-commerce giant Takealot to expand its customer base and streamline its operations through digital platforms. More South Africans accessing the internet have boosted online shopping, driving significant growth for the company.
- Mobile technology: The widespread use of mobile phones, including smartphones, facilitates mobile banking, e-commerce, and communication, enabling businesses to reach a broader audience and streamline operations.
- Innovation and R&D: Limited investment in research and development (R&D) hampers technological innovation. Increasing R&D funding could drive new products and services, enhancing competitiveness.
- Digital literacy: Low levels of digital literacy in certain populations restrict the effective use of technology in business and daily life, limiting the potential for tech-driven economic growth.
- Example: Capitec Bank has leveraged digital literacy initiatives to encourage customers to use their online and mobile banking platforms. By providing digital literacy training and support, Capitec has been able to increase the adoption of its digital services, reduce the strain on physical branches, and enhance customer convenience.
- Cybersecurity: Rising cyber threats necessitate robust cybersecurity measures for businesses. Companies need to invest in secure systems to protect data and maintain consumer trust.
- E-commerce growth: The expansion of e-commerce provides new market opportunities, especially in retail. Businesses need to adapt to online sales platforms to stay competitive.
- Tech infrastructure: Insufficient technological infrastructure, such as reliable power supply and internet bandwidth, hinders the efficiency and scalability of businesses.
- Government support: Government initiatives and policies supporting tech startups and innovation hubs can spur technological advancement and entrepreneurship.
- Automation and AI: Adoption of automation and artificial intelligence (AI) in industries can increase productivity and efficiency but may also lead to job displacement, requiring workforce reskilling.
- Example: The agricultural technology company Aerobotics uses drones equipped with AI-driven software to monitor crop health and analyze data. This technology allows farmers to detect problems such as pest infestations and water stress early, leading to more precise and efficient farming practices. The implementation of AI and automation in agriculture helps improve yields, reduce costs, and enhance sustainability, showcasing the transformative potential of these technologies in traditional industries.
- Fintech developments: The growth of financial technology (fintech) solutions enhances financial inclusion and offers innovative services, improving access to banking and financial services for individuals and businesses.
- Example: Yoco is a prominent fintech company in South Africa that provides point-of-sale (POS) solutions for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). By offering affordable card payment systems and financial services, Yoco has enabled many businesses to accept digital payments, improving their revenue streams and operational efficiency. Their mobile app and POS devices cater to the increasing need for cashless transactions, driven by higher digital literacy and internet penetration in the country.
- Renewable energy technology: Investment in renewable energy technologies can address power shortages, reduce operational costs, and promote sustainable business practices.
- Blockchain technology: Implementing blockchain in various sectors can improve transparency, reduce fraud, and streamline operations, especially in finance and supply chain management.
- Example: Bankymoon is a South African blockchain consultancy that focuses on integrating blockchain technology into various sectors. One notable project involves using blockchain to manage electricity usage in schools through smart meters. These meters allow donors to purchase electricity for schools directly via blockchain, ensuring transparency and efficient use of funds.
- Educational technology (EdTech): The rise of EdTech platforms supports education and training, helping to address skills gaps and prepare a tech-savvy workforce.
- Health technology: Advances in health technology improve healthcare delivery and efficiency, benefiting public health and productivity.
- Agritech: Agricultural technology innovations can enhance productivity, efficiency, and sustainability in the agriculture sector, vital for food security and economic stability.
- Telecommunications: The quality and affordability of telecommunications services influence business communication and remote work capabilities, essential in the modern economy.
- Smart cities: Development of smart city initiatives can improve urban living standards, infrastructure management, and environmental sustainability, making cities more attractive for business investment.
- Example: Cape Town is an example of a city embracing smart city technologies. The city has implemented several smart initiatives, such as advanced traffic management systems, smart street lighting, and improved waste management solutions. These technologies help reduce energy consumption, improve public services, and enhance the overall quality of life for residents. The integration of IoT and data analytics in managing city infrastructure exemplifies Cape Town's commitment to becoming a more efficient and sustainable urban environment.
- Biotechnology: Growth in biotechnology can drive advancements in healthcare, agriculture, and environmental sustainability, offering new business opportunities and solutions to societal challenges.
- Example: CapeBio Technologies, a South African biotech firm, focuses on producing molecular biology reagents and diagnostic kits. Their work is crucial for advancing healthcare solutions in the country, particularly in the field of infectious diseases. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CapeBio developed rapid test kits, showcasing the importance of local biotech innovation in addressing public health challenges.
South Africa's Legal Factors

- Employment laws: Regulations around minimum wage, working hours, and employee rights impact labor costs and operational flexibility for businesses, requiring compliance to avoid legal penalties.
- Health and safety regulations: Strict health and safety standards ensure worker protection but can increase operational costs for businesses in terms of compliance and equipment upgrades.
- Taxation laws: Corporate tax rates, VAT, and other tax regulations influence business profitability and financial planning, affecting overall economic activity.
- Intellectual property laws: Strong IP protections encourage innovation and investment in research and development by ensuring businesses can protect their inventions and creative works.
- Consumer protection laws: Regulations that safeguard consumer rights influence business practices, ensuring fair treatment of customers but also requiring compliance efforts.
- Environmental regulations: Laws aimed at protecting the environment require businesses to adopt sustainable practices, which can lead to increased costs but also promote long-term ecological benefits.
- Competition laws: Antitrust regulations prevent monopolistic practices and promote fair competition, impacting how businesses operate and strategize within the market.
- Contract law: The legal framework governing contracts ensures that agreements are enforceable, providing businesses with the confidence to enter into transactions and partnerships.
- Property rights: Clear and enforceable property laws are essential for business investment and development, providing security for assets and real estate investments.
- Immigration laws: Policies regarding work visas and immigration affect the ability of businesses to attract and retain skilled foreign workers, influencing labor market dynamics.
- Example: In early 2024, the South African government introduced several amendments to its immigration regulations, including the introduction of a Digital Nomad Visa, which allows remote workers to stay in the country for up to three years. This visa aims to attract high-earning individuals who can contribute to the local economy without competing for local jobs. Additionally, the amendments include a point-based system for work visas, simplifying the application process and ensuring that the country attracts skilled workers essential for economic growth.
- Corporate governance: Regulations on corporate governance standards ensure transparency and accountability in business operations, fostering investor confidence and ethical management.
- Licensing and permits: The need to obtain various licenses and permits can be a barrier to entry for new businesses, affecting the ease of starting and operating a business.
- Data protection laws: Legislation like the Protection of Personal Information Act (POPIA) requires businesses to safeguard personal data, impacting how they collect, store, and use information.
- Bankruptcy laws: Clear bankruptcy regulations provide a legal framework for businesses to resolve insolvency issues, protecting both creditors and debtors and enabling economic restructuring.
- Example: In 2020, Edcon filed for business rescue, a process under South African bankruptcy law designed to rehabilitate financially distressed companies. The business rescue plan allowed Edcon to restructure its debt, renegotiate terms with creditors, and seek new investment, ultimately leading to parts of the business being sold off to new owners.
- Trade regulations: Compliance with international and local trade laws affects how businesses engage in import and export activities, influencing their market reach and operational strategies.
- Labor union laws: Regulations governing labor unions and collective bargaining impact labor relations and can influence wage structures, working conditions, and dispute resolutions.
- Judicial efficiency: The effectiveness and speed of the judicial system affect the resolution of business disputes, contract enforcement, and overall legal certainty for businesses.
- Anti-corruption laws: Stringent anti-corruption regulations aim to create a transparent business environment, reducing the risk of bribery and fostering fair competition.
- Foreign investment laws: Policies regulating foreign direct investment (FDI) influence the attractiveness of South Africa as a destination for international investors, affecting capital inflows and economic growth.
- Public procurement laws: Regulations on government procurement processes ensure transparency and fairness in how public contracts are awarded, impacting opportunities for businesses to engage in public sector projects.
South Africa's Environmental Factors
- Climate change: South Africa is vulnerable to climate change impacts such as droughts, extreme weather events, and rising temperatures, which can disrupt agriculture, water supply, and overall economic stability.
- Water scarcity: Frequent droughts and water shortages affect agricultural productivity, industrial processes, and daily life, necessitating investments in water management and conservation technologies.
- Example: In 2018, Cape Town faced a severe water crisis, famously known as "Day Zero," when the city came close to shutting off its water supply due to prolonged drought. This crisis forced businesses to implement stringent water-saving measures and invest in water-efficient technologies. The tourism industry, a significant contributor to the local economy, was particularly affected as hotels and restaurants had to find ways to reduce water usage while maintaining operations.
- Air pollution: High levels of air pollution, particularly from industries and mining activities, pose health risks to the population and can lead to regulatory pressures on businesses to adopt cleaner technologies.
- Renewable energy: The push for renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power is transforming the energy sector, offering opportunities for green businesses and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Example: South Africa's Renewable Energy Independent Power Producer Procurement Programme (REIPPPP) has attracted significant foreign and domestic investment, driving the development of renewable energy projects such as wind and solar farms across South Africa. One notable project is the Khi Solar One plant, a 50 MW concentrated solar power (CSP) facility near Upington. This project not only contributes to the country’s renewable energy goals but also creates jobs and stimulates local economies.
- Waste management: Inefficient waste management practices can lead to environmental degradation and health issues, prompting businesses to adopt sustainable waste disposal and recycling practices.
- Biodiversity conservation: South Africa's rich biodiversity requires protection, and businesses operating in sensitive areas must ensure their activities do not harm ecosystems, often leading to stricter environmental regulations.
- Land degradation: Soil erosion and desertification affect agricultural productivity and land use, requiring sustainable land management practices to prevent further environmental damage.
- Example: In South Africa's Eastern Cape, land degradation due to overgrazing, deforestation, and poor land management practices has led to soil erosion and reduced agricultural productivity. Initiatives like the Working for Water program aim to combat this issue by removing invasive alien plants, which consume large amounts of water and contribute to soil erosion. This program not only helps restore degraded land but also provides employment opportunities for local communities, demonstrating a sustainable approach to land management that benefits both the environment and the economy.
- Carbon emissions: Regulatory measures to reduce carbon emissions, such as carbon taxes and emission caps, impact industries reliant on fossil fuels, encouraging the adoption of cleaner technologies.
- Regulatory compliance: Businesses must comply with national and international environmental regulations, which can involve significant costs for monitoring, reporting, and implementing environmentally friendly practices.
- Public awareness: Growing public awareness and activism around environmental issues influence consumer preferences and demand for sustainable products, prompting businesses to adopt eco-friendly practices.
- Sustainable agriculture: There is a growing need for sustainable agricultural practices to ensure food security and environmental protection, affecting the agribusiness sector.
- Mining regulations: Environmental regulations in the mining sector aim to mitigate the ecological impact of mining activities, requiring companies to invest in rehabilitation and sustainable practices.
- Deforestation: Efforts to combat deforestation impact industries reliant on timber and related products, pushing them towards sustainable sourcing and reforestation initiatives.
- Marine conservation: Protecting marine ecosystems affects fisheries and related industries, promoting sustainable fishing practices and the preservation of marine biodiversity.
- Energy efficiency: Regulations and incentives for energy efficiency encourage businesses to reduce energy consumption, leading to cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
- Green building standards: The adoption of green building practices and standards affects the construction industry, promoting energy-efficient, sustainable building designs.
- Environmental litigation: Increased environmental litigation risks for businesses that fail to comply with environmental laws can lead to financial penalties and reputational damage.
- Sustainable tourism: The tourism industry is increasingly focusing on sustainable practices to protect natural attractions and promote eco-friendly tourism, impacting business strategies in this sector.
- Example: Grootbos Private Nature Reserve, located in the Western Cape, is a leading example of sustainable tourism in South Africa. The reserve integrates conservation, community development, and eco-friendly tourism practices. It focuses on preserving the unique fynbos biome and supports local communities through job creation and educational programs. Grootbos has received international recognition for its sustainable practices, showing how tourism can be conducted in a way that benefits both the environment and local populations, setting a standard for other tourism ventures in the region.
- Ecosystem services: Businesses are recognizing the value of ecosystem services such as pollination, water purification, and climate regulation, incorporating these considerations into their operational planning.
- Environmental education: Initiatives to educate the public and businesses about environmental sustainability help drive a culture of conservation and responsible resource use, influencing corporate practices and policies.
Recommendations based on the PESTLE Analysis of South Africa
Having concluded the PESTLE analysis, it is evident that South Africa offers a complex but potentially rewarding business environment. The country boasts a robust infrastructure, a diverse economy, and significant investment opportunities, particularly in renewable energy, technology, and the mining sector. However, challenges such as high crime rates, regulatory hurdles, and socio-economic disparities persist.
For a comprehensive understanding of South Africa's business landscape, exploring our SWOT analysis of South Africa is recommended. This will provide deeper insights into the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats that shape the current and future business climate in the country.

