Airbnb has revolutionized the travel and hospitality industry, offering a more affordable and personal alternative to traditional hotels. With over 4 million hosts worldwide and more than 1 billion guest arrivals to date, the platform has empowered everyday people to generate extra income while providing travelers with unique and local experiences.
Airbnb now operates in over 220 countries and regions, hosting guests in over 100,000 cities globally, making it a formidable force in the sharing economy.
However, Airbnb’s rapid global expansion hasn’t come without its challenges. From dealing with housing regulations to addressing legal compliance and environmental concerns, the company faces significant external factors that could impact its future growth. As consumer behavior shifts and governments impose stricter rules, Airbnb must remain flexible to stay a dominant player.
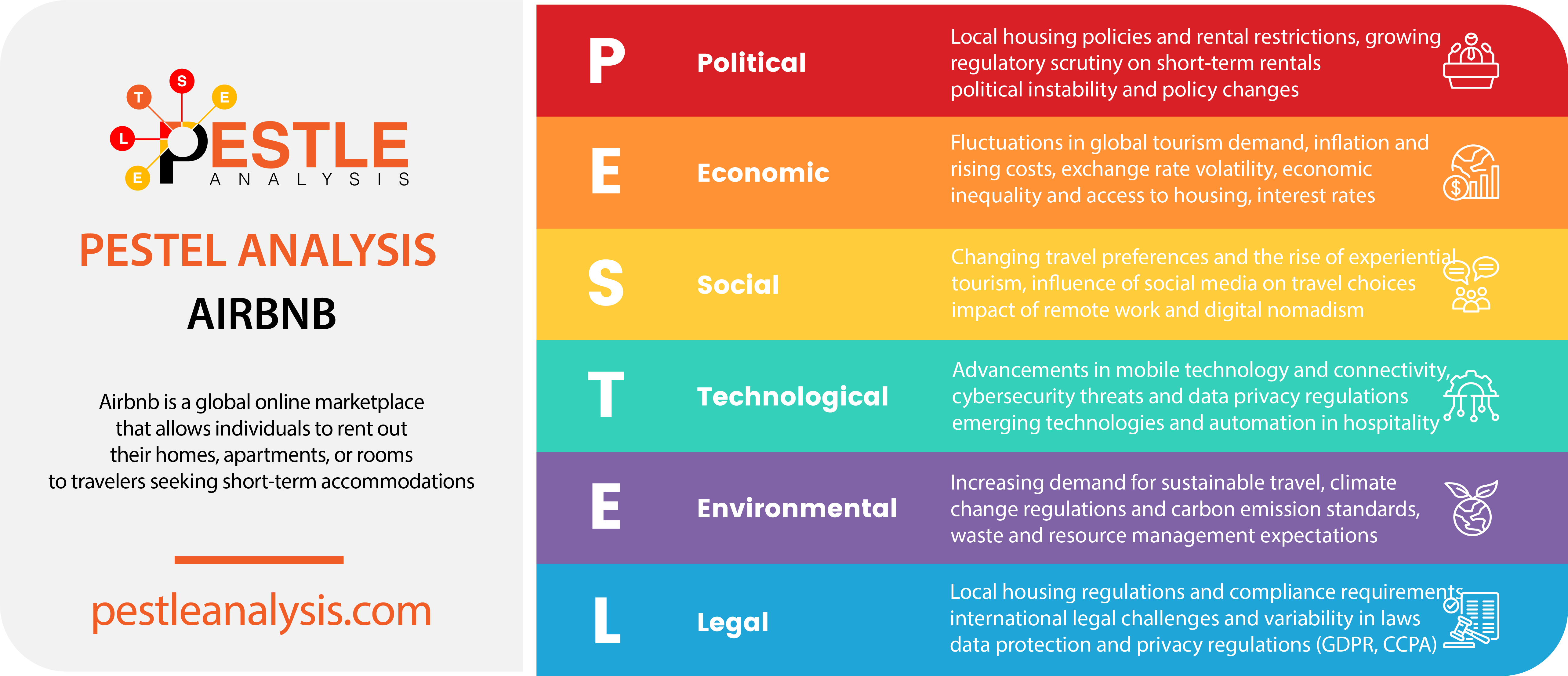
To fully understand these external influences, a PESTLE analysis is essential. This framework breaks down the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors that affect Airbnb’s operations. By exploring each of these categories, you’ll discover the forces driving Airbnb’s success—and the obstacles it must overcome.
Whether you’re a student analyzing the company’s strategy or a business leader seeking insights, this PESTLE analysis offers valuable perspectives.
Airbnb's Political Factors
Politics plays a significant role in the way Airbnb operates across different markets. Governments at local, state, and national levels impose regulations and policies that directly affect Airbnb’s ability to function as a short-term rental platform.
As we begin our PESTLE analysis, we will explore the various political factors, from housing policies to shifts in leadership, that influence Airbnb’s global operations and growth strategies.
- Local Housing Policies and Rental Restrictions: Various cities and jurisdictions have introduced housing policies that directly impact short-term rental platforms like Airbnb. In some regions, short-term rentals are only permitted if the property owner resides on the premises, while others impose strict caps on the number of rental days per year. These policies are designed to control the housing market, limit tourism’s impact on local communities, and ensure proper taxation. Airbnb must adapt to these local laws to continue operating without legal repercussions.
- Example: In Budapest’s sixth district, residents voted to ban short-term rentals starting in 2026, a decision that could set a precedent for other areas. This highlights the increasing political intervention Airbnb faces in key markets, where governments and local councils are responding to community pressures by implementing stricter regulations on short-term rental platforms.
- Example: Greece’s new plan to offer tax breaks to homeowners who switch from short-term to long-term rentals reflects how governments are implementing specific incentives and regulations to address housing shortages caused by platforms like Airbnb. The decision to introduce a tax break, along with increased taxes on short-term rentals and restrictions on new licenses, highlights the political interventions that Airbnb must respond to in various markets.
- Growing Regulatory Scrutiny on Short-Term Rentals: There is increasing political pressure on governments around the world to introduce more stringent regulations on short-term rental platforms like Airbnb. This is often driven by concerns about housing shortages, rising rental prices, and the impact of tourism on local communities. Governments are responding by drafting and enforcing stricter housing laws, which Airbnb must follow to continue operating. The demand for tighter regulation comes from external stakeholders such as policymakers, housing advocates, and local communities, putting pressure on Airbnb to adapt.
- Example: As cities like New York, Los Angeles, and Montreal enact stricter laws to limit short-term rentals, the vacation rental industry is ramping up its efforts to shape policies in their favor. This example highlights how political intervention and advocacy play a crucial role in determining how Airbnb can operate in various markets.
- Political Instability and Policy Changes: Political turmoil, changes in government, or shifts in leadership can have a significant impact on Airbnb’s operations, especially in regions experiencing political unrest. In countries where leadership changes lead to policy shifts, there could be sudden and unpredictable regulations imposed on short-term rental platforms. For instance, political instability in tourist-heavy regions can lead to changes in tourism policies, such as sudden restrictions on rentals, increased taxation, or even bans on non-local property owners renting out homes. Airbnb must stay agile and responsive to these external political forces, as they can disrupt its market presence in certain regions or increase operational risk.
Airbnb's Economic factors
Airbnb’s performance is heavily influenced by global economic conditions and trends. External economic factors such as tourism demand, inflation, and housing market dynamics play a critical role in determining Airbnb’s success.
In our PESTLE analysis second section, we will examine the key economic forces that impact Airbnb’s business, shaping both consumer behavior and the availability of short-term rental properties.
- Fluctuations in Global Tourism Demand: The demand for travel and tourism is influenced by global economic conditions. Factors such as economic recessions, pandemics, or geopolitical instability can significantly reduce international travel. Economic slowdowns lower consumer spending on non-essential services like vacation rentals, which in turn negatively impacts Airbnb bookings. Conversely, economic booms tend to increase travel demand, benefiting Airbnb.
- Example: As extreme weather makes traditional summer destinations less attractive, Airbnb is seeing increased demand in regions with cooler climates, such as northern Europe and Alaska, with searches rising by 15% year-over-year. This shift in demand influences Airbnb’s revenue streams and the tourism market in these cooler regions.
- Example: The Paris Olympics proved to be Airbnb’s largest event in terms of guests accommodated. Major events like the Olympics drive significant spikes in demand for short-term rentals, especially in key markets like Paris. This reinforces the economic benefits that Airbnb experiences during global events and the company’s ability to capitalize on such opportunities. Events of this magnitude boost Airbnb’s revenue streams as demand for accommodations surges.
- Example: With U.S. consumers tightening their budgets and delaying vacation bookings due to economic uncertainty and dwindling savings, Airbnb and other travel companies are seeing slower growth in the U.S. market. This trend reflects how external economic conditions, like lower disposable income and rising living costs, can directly impact Airbnb’s bookings and revenue.
- Inflation and Rising Costs: Inflation affects the cost of living and travel expenses globally. As prices for essential goods and services rise, consumers may cut back on discretionary spending, including travel. This can lead to fewer bookings for Airbnb properties, especially among budget-conscious travelers. Additionally, inflation increases costs for Airbnb hosts, who may face higher maintenance, utilities, and property management fees, which can reduce their profitability.
- Exchange Rate Volatility: Airbnb operates globally, and exchange rate fluctuations can impact both travelers and hosts. A strong U.S. dollar, for example, might discourage international travelers from visiting the U.S. due to higher costs while making U.S. travelers more likely to vacation abroad. Exchange rates also affect how much income Airbnb hosts in non-U.S. countries earn when converting payments from foreign guests.
- Economic Inequality and Access to Housing: Growing economic inequality and housing affordability crises in many cities around the world have led to increased scrutiny of platforms like Airbnb. In areas where affordable housing is limited, the presence of short-term rentals can exacerbate housing shortages, driving up rental prices. This dynamic often leads to increased regulatory intervention, influencing Airbnb’s ability to operate freely in certain markets.
- Interest Rates and Property Investments: Interest rates play a key role in property investments, and shifts in interest rates can influence the availability of short-term rental properties. When interest rates are low, individuals are more likely to invest in real estate, potentially increasing the number of Airbnb hosts. Conversely, rising interest rates make borrowing more expensive, which could reduce the number of new property owners or investors entering the short-term rental market.
Airbnb's Social Factors
Social trends and cultural shifts have a profound effect on the travel and hospitality industry, and Airbnb is no exception. Changes in consumer preferences, attitudes towards the sharing economy, and the rise of remote work are just a few of the social factors that impact Airbnb’s market.
In the social part of this PESTLE analysis, we will look at the external social factors driving Airbnb’s success and the challenges it faces in adapting to a rapidly evolving social environment.
- Changing Travel Preferences and the Rise of Experiential Tourism: Travelers, particularly millennials and Gen Z, are increasingly seeking authentic, local, and immersive travel experiences, shifting away from traditional hotel stays. This trend toward experiential tourism benefits platforms like Airbnb, where guests can stay in unique accommodations and book localized experiences. As this social trend grows, Airbnb continues to thrive by catering to changing consumer preferences for personalized and off-the-beaten-path travel.
- Example: Many aspiring expats are now using platforms like Airbnb to “test” living abroad before making long-term retirement decisions. This trend shows how travelers are increasingly seeking authentic, day-to-day experiences in residential neighborhoods rather than staying in traditional hotels. Airbnb benefits from this shift as more people use the platform for extended stays in foreign countries, exploring potential retirement destinations and immersing themselves in local life.
- Influence of Social Media on Travel Choices: Social media platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and YouTube have a significant influence on travel decisions, with influencers and travelers sharing their Airbnb stays and experiences. The growing culture of sharing travel content online drives more people to seek out unique Airbnb accommodations and book experiences that they see others enjoying. This external trend helps boost Airbnb’s visibility and appeal globally.
- Changing Attitudes Toward Home Sharing and Trust in Peer-to-Peer Services: The growth of the sharing economy has led to a cultural shift in how people perceive home sharing and peer-to-peer services. In many countries, consumers have become more comfortable with the idea of staying in someone else’s home or using a shared service, which has driven Airbnb’s success. However, in some regions, social stigma or privacy concerns still exist, and these attitudes can influence the platform’s adoption in different markets.
- Impact of Remote Work and Digital Nomadism: The rise of remote work and digital nomadism, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, has changed the way people travel and live. Many workers are now able to live and work from anywhere, leading to an increase in long-term Airbnb stays. This external social trend has expanded Airbnb’s customer base, as more people look for flexible, temporary housing options while they work remotely.
- Community Backlash and Gentrification Concerns: In many cities, there is growing social resistance to platforms like Airbnb due to concerns about gentrification, housing affordability, and the displacement of local residents. Some communities feel that short-term rentals increase property prices and reduce the availability of long-term housing, leading to social tensions. This backlash can influence local policies and public opinion, creating challenges for Airbnb in certain markets.
- Example: In Athens, Greece, residents have voiced frustration with the housing crisis, which has been exacerbated by the rise of short-term rentals. This has led the government to impose restrictions on new Airbnb licenses in certain districts. The example from Greece underscores how social dissatisfaction with housing availability and gentrification drives regulatory changes that impact Airbnb’s ability to operate freely.
Airbnb's Technological factors
The technological environment is crucial to Airbnb’s operations, with external technological advancements continuously reshaping the platform and its services. From mobile connectivity to cybersecurity concerns, Airbnb must adapt to a wide array of technological factors.
In the 'T' section of our PESTLE analysis, we will explore how technological trends and challenges, such as emerging technologies and cybersecurity risks, impact Airbnb’s business and its ability to innovate.
- Advancements in Mobile Technology and Connectivity: The global increase in mobile device usage and improved internet connectivity have facilitated Airbnb’s growth. Travelers can easily book accommodations on their smartphones from anywhere in the world, making the platform more accessible. Additionally, the widespread availability of high-speed internet and 5G networks enhances the user experience, allowing for seamless communication between hosts and guests.
- Cybersecurity Threats and Data Privacy Regulations: As a platform that handles sensitive user data, including payment information, Airbnb is vulnerable to external cybersecurity threats. Rising concerns over data breaches and online fraud have led to stricter data privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe. Compliance with these regulations is essential for Airbnb to operate globally, and any failure to protect user data could severely damage its reputation.
- Emerging Technologies and Automation in Hospitality: External technological advancements, such as AI-powered customer service, voice-activated assistants, and smart home technologies, are reshaping the hospitality industry. Airbnb is influenced by these broader tech trends, as hosts adopt smart locks, virtual assistants, and automated check-in systems to improve guest experiences. To remain competitive, Airbnb must adapt to these technologies that are becoming increasingly common in vacation rentals and hotels alike.
- Growing Importance of Online Reviews and Reputation Management Tools: The proliferation of online review platforms and third-party reputation management tools has created an ecosystem where consumer feedback significantly impacts businesses. Airbnb must navigate this external trend, as hosts and properties are rated publicly on platforms beyond its control, such as Google, TripAdvisor, or Yelp. The growing reliance on reviews from external sources can influence bookings, regardless of Airbnb’s internal review system.
- Tech Industry Shifts and Digital Ecosystems: Airbnb operates in a broader digital ecosystem dominated by large tech companies like Google, Apple, and Facebook. Changes in these tech giants’ policies—such as updates to app store rules, changes in search engine algorithms, or privacy updates—can directly impact Airbnb’s visibility, user experience, and app performance. For example, new policies on user tracking and targeted advertising may limit Airbnb’s ability to market effectively to potential customers.
Airbnb's Legal Factors
Operating in a highly regulated industry, Airbnb must deal with complex legal requirements across different countries and cities. Legal challenges, including local housing regulations, data protection laws, and taxation issues, directly affect how Airbnb functions globally.
The 'L' section of our PESTLE analysis will examine the legal factors that create external pressure on Airbnb, as it strives to comply with a range of laws and regulations in its various markets.
- Local Housing Regulations and Compliance Requirements: Airbnb operates across diverse legal jurisdictions, each with its own housing regulations. Many cities impose strict requirements on short-term rentals, including zoning laws, the necessity of permits, and limitations on rental durations. These regulations are designed to control the impact of short-term rentals on housing markets, often requiring hosts to pay local taxes, such as hotel or tourist taxes. Airbnb must navigate these complex local laws, which can vary significantly from one city to the next.
- International Legal Challenges and Variability in Laws: Different countries and cities enforce distinct tourism and housing policies that directly affect how Airbnb operates. For example, Barcelona has strict regulations on vacation rentals to protect housing availability for locals, while cities like New York and New Orleans have implemented limits on the number of short-term rental properties to prevent housing shortages. Airbnb faces significant legal risks and operational challenges as it attempts to comply with varying international legal frameworks, often resulting in fines or restrictions.
- Data Protection and Privacy Regulations (GDPR, CCPA): As a global platform, Airbnb must comply with stringent data protection laws, such as Europe’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and California’s Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). These regulations impose strict guidelines on how personal data is collected, stored, and processed. Failure to comply with these laws can result in significant fines and damage to Airbnb’s reputation. As governments around the world continue to strengthen data privacy protections, Airbnb must stay compliant to avoid legal repercussions.
- Litigation and Legal Disputes with Local Governments: Airbnb has faced numerous lawsuits and legal challenges from local governments over issues related to housing, taxation, and public safety. These legal disputes often arise in cities where housing affordability is a concern, and governments aim to regulate the impact of short-term rentals. For instance, Airbnb has been fined in cities like Barcelona and San Francisco for failing to comply with local laws. These external legal conflicts are ongoing and pose a risk to Airbnb’s business model in heavily regulated markets.
- Example: Airbnb’s request for New York City to reconsider its strict regulations on short-term rentals—especially Local Law LL18, which requires hosts to be permanent occupants and register with the city—demonstrates the legal challenges the company faces. Despite Airbnb’s argument that the law has not impacted the housing crisis and has instead reduced the supply of rentals, these local regulations continue to affect Airbnb’s ability to operate in key markets like New York.
- Example: Seville’s enforcement of regulations, including the cutting of essential services like water to illegal rentals, highlights the legal pressure Airbnb and hosts face in complying with local laws. The mayor’s office is reviewing thousands of listings and intends to take action against those that violate regulations, showing how local governments are legally challenging short-term rental platforms to ensure compliance.
- Example: Real estate documents, particularly around short-term rentals, need to be drafted with care to avoid legal loopholes that can result in significant issues for hosts and property managers. The rise of short-term rentals through platforms like Airbnb has led to increased scrutiny over contract terms, zoning laws, and compliance with local real estate regulations, all of which pose legal challenges for Airbnb hosts if not handled properly.
- Taxation Laws and Legal Accountability: Governments worldwide are tightening taxation regulations on short-term rental platforms like Airbnb. Many local governments now require Airbnb to collect and remit taxes on behalf of hosts, including occupancy taxes or value-added taxes (VAT). Airbnb must ensure compliance with these tax laws across its markets, and any failure to do so can result in penalties and legal action. The platform is increasingly being held accountable by governments to ensure hosts meet their tax obligations.
Airbnb's Environmental Factors
As environmental concerns become increasingly important to consumers and governments alike, Airbnb is influenced by a growing demand for sustainable practices. From climate change regulations to the rise of eco-conscious travel, external environmental forces shape Airbnb’s strategy and reputation.
As we conclude our PESTLE analysis, we will explore the key environmental factors that impact Airbnb, and how the platform is responding to the global push for more sustainable travel solutions.
- Increasing Demand for Sustainable Travel: There is growing consumer awareness and demand for eco-friendly and sustainable travel options. Travelers are increasingly looking for accommodations and experiences that minimize environmental impact, favoring companies that prioritize sustainability. This trend encourages Airbnb to promote local stays and unique accommodations that have a lower carbon footprint compared to large hotel chains, positioning the platform as a greener alternative in the hospitality sector.
- Climate Change Regulations and Carbon Emission Standards: Governments around the world are implementing stricter environmental regulations aimed at reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable practices. These policies affect all sectors, including hospitality. In some regions, governments may impose additional requirements on businesses like Airbnb to reduce their carbon footprint or comply with new environmental standards. Airbnb must adapt to these regulations, particularly in markets where climate policies are more aggressive.
- Waste and Resource Management Expectations: As sustainability becomes a priority for governments and consumers, Airbnb is influenced by external pressures to promote responsible resource management among its hosts. This includes encouraging hosts to adopt energy-efficient appliances, reduce water consumption, and manage waste sustainably. Local regulations may also mandate certain environmental practices, pushing Airbnb to promote eco-friendly accommodations on its platform to align with these external expectations.
- Impact of Natural Disasters and Climate Events on Travel Patterns: Climate change has led to an increase in natural disasters such as hurricanes, wildfires, and floods, which can disrupt travel plans and affect short-term rental markets. Regions that are heavily impacted by climate-related events may see a decrease in tourism, directly affecting Airbnb bookings. Moreover, Airbnb must adapt to changing travel patterns as more travelers seek eco-conscious or disaster-resilient destinations, and certain areas become less viable for travel due to environmental degradation.
- Pressure from Environmental Advocacy Groups: Airbnb faces increasing scrutiny from environmental advocacy groups who challenge the impact of short-term rentals on urban development, local ecosystems, and over-tourism in sensitive areas. These groups often call for more stringent regulations on short-term rentals to protect local environments and communities from the negative effects of tourism. Airbnb must balance growth with environmental sustainability to mitigate reputational risks posed by advocacy groups.
Recommendations based on our PESTLE Analysis of Airbnb
Airbnb continues to lead the sharing economy by providing an affordable and accessible alternative to traditional hotels.
However, the company faces persistent external challenges, including navigating complex housing regulations, ensuring legal compliance, and addressing evolving social and environmental expectations. Its success depends on its ability to stay adaptive to political, legal, and technological shifts while maintaining its appeal to both budget-conscious travelers and local economies.
Recommendations for the Airbnb company operations:
- Stay proactive with regulations: Engage with local governments and policymakers to anticipate regulatory changes and adjust business strategies to align with evolving housing and taxation laws.
- Enhance sustainability efforts: As environmental concerns grow, expanding partnerships with eco-friendly hosts and promoting greener practices can strengthen Airbnb’s reputation among environmentally conscious travelers.
- Leverage technology and data: Continue investing in data-driven insights and automation to streamline operations, enhance guest experiences, and respond quickly to changing market conditions.
For students studying Airbnb, it’s essential to understand how the company’s internal strengths and weaknesses interact with external opportunities and threats. We highly recommend checking out our Airbnb SWOT analysis to gain deeper insights into these dynamics.
The SWOT analysis provides a clear view of Airbnb’s competitive advantages and risks, especially how the company’s internal factors align with the external environment outlined in this PESTLE analysis.






