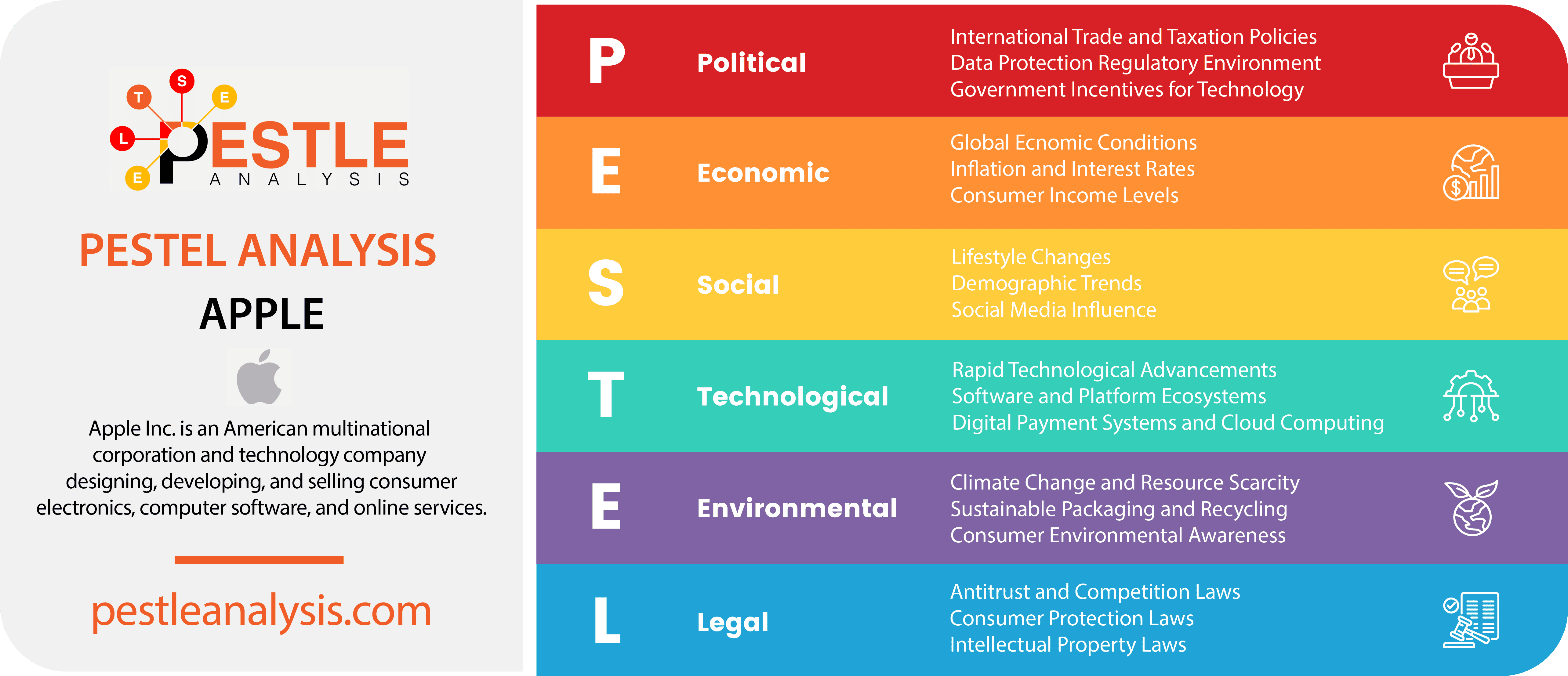
The Apple PESTLE analysis reveals the challenges that the tech company needs to take up to thrive and propel its revenue growth for decades to come.
In today's Apple PESTLE analysis, we look at the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors that matter to Apple's business.
Did you know that before the famous bitten apple logo, Apple's initial logo depicted Sir Isaac Newton sitting under an apple tree, complete with a quotation frame, which was quickly deemed too complicated and was replaced with the iconic simple apple silhouette? Now that you know that, the PESTEL framework checks the external factors that affect the company's business environment.
These factors can be good or bad for Apple. They really impact its performance compared to its rivals. And Apple has many competitors in the tech world, like Google, and Microsoft.
Apple has always been a top player in the high-end electronics market. However, this PESTLE analysis of Apple Inc. shows that Apple needs to keep updating its strategies to stay on top. Handling these outside factors well is crucial.
So, let's begin with the first part of our PESTLE analysis of Apple.
Apple Political Factors

Did you know that the name 'iMac' wouldn't exist if it wasn't for Steve Jobs' persistence with the "i" prefix, symbolizing the internet, the individual and innovation, and we would call it "Macman"?
Now that you know that it’s time to look at the political factors in our Apple PESTLE analysis.
International Trade Policies
Apple's global operations are heavily influenced by trade policies, tariffs, and import/export regulations.
Changes in these policies, such as the US-China trade tensions, can impact Apple's supply chain and product pricing. Apple is heavily dependent on lower-cost manufacturing in China. Social and political unrest in China could disrupt manufacturing or increase manufacturing costs in that country. There have also been calls to restrict Chinese imports into the United States in an effort to boost American manufacturing.
The cost of finding alternatives to Chinese manufacturing could be high for Apple. This could lead to increased prices for Apple products.
Regulatory Environment
Apple operates in a highly regulated industry, with various laws and regulations governing data privacy, consumer protection, and intellectual property rights. Compliance with these regulations is crucial for Apple's operations and reputation.
Example: As Apple integrates AI in 2024, it may face regulatory scrutiny over data privacy and AI ethics, impacting its global operations and compliance costs.
Taxation Policies
Changes in corporate tax rates and tax laws in different countries can significantly affect Apple's financial performance.
For example, Apple has faced scrutiny over its tax practices in Europe and the United States. Apple is one of a number of American technology companies that has accumulated a large amount of cash. This is generating calls for higher corporate taxation in the United States, where income inequality has become a major political issue.
Political Stability
Apple's presence in various global markets requires navigating different political climates. Political instability in key markets can disrupt Apple's supply chain, sales, and overall business operations.
For example, Apple’s dependence on Chinese manufacturing and markets makes it vulnerable to political unrest in that country. Apple could become the target of growing nationalism and anti-Americanism in China, which could reduce its market share. Apple’s close association with China could also become a political issue in countries like the United States and Japan if China were to be perceived as a threat.
Government Support for Technology
Governments promoting technological innovation and digital infrastructure can create favorable conditions for Apple's growth. That is especially true in emerging markets.
Environmental Regulations
Political pressure to address environmental concerns has led to stricter regulations on electronic waste, energy efficiency, and carbon emissions. Apple has responded by emphasizing its commitment to sustainability and renewable energy.
Data Protection Policies
With the increasing importance of cybersecurity, governments are implementing stricter regulations to protect consumer data and national security. Apple needs to comply with these regulations while maintaining user privacy and security.
Intellectual Property Protection
Strong intellectual property laws are essential for Apple to protect its innovations and brand. Changes in these laws or enforcement practices can impact Apple's competitive advantage. Apple’s dominant position in fields like music could lead to antitrust concerns and political pressure to break the company up or limit its market share.
By understanding and adapting to these political factors, Apple can continue to thrive as a leading technology company.
Apple Economic Factors

Did you know that Apple tried to extend its brand into fashion back in the 1980s, when they released a collection of Apple-branded clothing and accessories, only for the attempt to be a short-lived one?
Now that you know that it’s time to look at the economic factors in our Apple PESTLE analysis.
Global Economic Conditions
Fluctuations in global economic growth rates, such as recessions or booms, can influence consumer spending and demand for Apple products. Increased labor costs in China could take away the cost advantage of some Apple products.
Exchange Rate Volatility
As a global company, Apple is exposed to currency exchange rate fluctuations. Changes in exchange rates can impact the cost of production, pricing of products, and overall profitability. A strong U.S. dollar could increase exchange rates, making it more expensive for Apple to do business in key markets like Europe and China.
Inflation Rates
High inflation rates can lead to increased production costs and reduced purchasing power of consumers, which may affect Apple's sales and profit margins. Stagnating middle-class incomes in some developed countries, including the United States, could shrink the potential market for higher-end consumer goods such as those marketed by Apple.
Interest Rates
Changes in interest rates can influence Apple's financing costs for its operations and investments, as well as consumer spending on credit.
Consumer Income Levels
The disposable income levels of consumers directly impact their ability to purchase Apple's premium products. Economic downturns or income inequality can affect sales.
Market Competition
Economic factors also influence the competitive landscape. For example, economic downturns can intensify price competition among tech companies, impacting Apple's market share and profitability.
Supply Chain Costs
Economic conditions, such as fluctuations in the prices of raw materials and labor costs, can affect Apple's supply chain expenses and overall cost structure.
Technological Investment
Economic stability and growth enable Apple to invest in research and development, leading to innovation and maintaining a competitive edge in the market.
Apple has to stay attuned to these economic factors and adapt its strategies accordingly, if they want to stay on top.
Apple Social Factors

Did you know that in the mid-2000s, Apple reportedly worked with the U.S. Department of Energy to develop a special iPod that could secretly record and store data?
Now that you know that it’s time to look at the social factors in our Apple PESTLE analysis.
Consumer Preferences
Changes in consumer preferences, such as a growing demand for sustainable products or a shift towards mobile computing, can significantly impact Apple's product development and marketing strategies.
Demographic Trends
Age distribution, income levels, and urbanization trends can influence the demand for Apple's products.
For example, younger populations may be more inclined towards the latest technology, affecting sales of new devices. At the same time, the biggest growth in consumer spending in coming decades will be in areas of the world such as Africa where people are unfamiliar with Apple products. Consumers in those markets and younger people in Apple’s established markets, such as the United States, lack the strong emotional attachment to Apple products that drive sales.
Lifestyle Changes
The increasing importance of technology in everyday life, such as remote work and online entertainment, can drive demand for Apple's products and services.
Brand Perception
Apple's brand image and reputation play a crucial role in its success. Social factors like public opinion, media coverage, and celebrity endorsements can affect consumer perception and loyalty. For instance, there is a backlash against expensive and stylish products among some customers in the United States and Europe. Meanwhile, Apple’s close association with China could offend some potential customers in other regions, such as North America and Europe, particularly if tensions with China rise.
Cultural Differences
As a global company, Apple needs to consider cultural differences in product design, marketing, and customer service to cater to diverse markets effectively.
Health and Safety Concerns
Social concerns about health and safety, such as those related to electromagnetic radiation or device addiction, can influence consumer choices and regulatory requirements for Apple's products.
Social Media Influence
The impact of social media on consumer behavior, including product reviews, influencer endorsements, and viral trends, can affect the popularity and sales of Apple's products.
For example, Apple’s music marketing strategy has created resentment and led to public criticism from major recording stars that could tarnish the brand’s image.
Ethical and Social Responsibility
Increasing awareness of ethical issues and social responsibility, such as labor practices and environmental sustainability, can impact Apple's brand image and consumer loyalty. Concerns about Apple’s manufacturing in China could limit its products’ appeal among socially-conscious consumers.
By understanding and responding to these social factors, Apple can continue to align its products and strategies with consumer preferences and societal trends.
Apple Technological Factors

Did you know that the iPhone could have had a physical keyboard, similar to competitors like BlackBerry, but Jobs pushed for a touchscreen-only interface?
Now that you know that, it’s time to look at the technological factors in our Apple PESTLE analysis.
Rapid Technological Advancements
The fast pace of technological innovation requires Apple to continuously invest in research and development to stay ahead of competitors and meet consumer expectations.
Competitors such as Google and Samsung have demonstrated a strong ability to duplicate Apple’s products and services. It took less than a year for Google to roll out a payment app; Android Pay, with the same capabilities as Apple Pay. This means that many of Apple’s signature services and products are no longer unique.
Emerging Technologies
Technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), augmented reality (AR), 5G connectivity, and the Internet of Things (IoT) present opportunities for Apple to develop new products and enhance existing ones. At the same time the number of new consumer products Apple can bring out is limited. Many of its new offerings, such as Apple TV, will have a limited market.Growing use of smartphones and tablets will lower demand for Apple’s popular personal computers.
Cybersecurity Threats
The growing capabilities of cyber criminals make Apple’s systems less secure and take away one of its strongest competitive advantages: its reputation for high levels of security and safety. As cyber threats become more sophisticated, Apple needs to invest in advanced security measures to protect user data and maintain trust in its ecosystem.
Software and Platform Ecosystems
The development and integration of software platforms, such as iOS, macOS, and the App Store, are crucial for creating a seamless user experience and driving customer loyalty. Apple’s proprietary operating system can limit the variety of applications available to smartphone users.
Supply Chain Automation
Technological advancements in automation and robotics can improve the efficiency of Apple's supply chain and reduce production costs.
Sustainability and Green Technologies
Innovations in energy-efficient technologies and sustainable materials are increasingly important for reducing Apple's environmental impact and appealing to eco-conscious consumers.
Digital Payment Systems
The evolution of digital payment technologies, such as Apple Pay, is transforming consumer payment habits and expanding Apple's presence in the financial services sector.
Cloud Computing
The growth of cloud computing services, such as iCloud, enables Apple to offer seamless data storage and synchronization across devices, enhancing user convenience and data accessibility.
By staying at the forefront of technological innovation and adapting to these factors, Apple can continue to lead the industry and deliver cutting-edge products and services to its customers.
Apple Legal Factors

Did you know that the original voice of Siri in the U.S., provided by voice actor Susan Bennett, was recorded in 2005 for an unrelated project, and she herself didn't know her voice was being used for Siri until after the feature was released on iPhones in 2011?
Now that you know that it’s time to look at the legal factors in our Apple PESTLE analysis.
Intellectual Property Laws
Apple relies heavily on patents, trademarks, and copyrights to protect its innovations and brand. Legal battles over intellectual property rights can impact its competitive advantage and financial performance. Apple depends on a variety of products covered by intellectual property laws, such as software and music, for much of its income. This leaves the company highly vulnerable to both piracy and litigation.
Data Privacy Regulations
Laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the US affect how Apple collects, stores, and uses consumer data. Compliance is crucial to maintain customer trust and avoid hefty fines.
Antitrust and Competition Laws
Apple is scrutinized by regulators worldwide for its market dominance and business practices. Legal challenges and antitrust investigations can lead to regulatory penalties and impact its market position.
By offering financial services, Apple could face increased levels of litigation. News reports indicated that Apple was planning to enter another highly regulated sector: automobile manufacturing. Entering the auto business could increase regulatory, insurance and litigation costs at Apple.
Consumer Protection Laws
Regulations aimed at ensuring product safety, quality, and transparency require Apple to adhere to strict standards in its product design, manufacturing, and marketing practices.
Employment Laws
As a global employer, Apple must comply with various labor laws and regulations related to wages, working conditions, and employee rights in different countries.
Environmental Regulations
Legal requirements for electronic waste disposal, energy efficiency, and hazardous materials management affect Apple's product design and manufacturing processes.
Tax Laws
Changes in corporate tax laws and international tax regulations can significantly impact Apple's financial planning and tax obligations.
Export/Import Regulations
Apple's global supply chain and distribution network are subject to various international trade laws, including export controls and import tariffs, which can affect its cost structure and pricing strategies.
By effectively navigating these legal factors, Apple can mitigate risks and ensure compliance, which is essential for maintaining its reputation and operational stability.
Apple Environmental Factors

Did you know that in macOS, the Digital Color Meter utility, used for measuring and displaying color values on the screen, contains a quirky Easter egg, allowing users to switch the readout to display colors as "Apple RGB?"
Now that you know that, it’s time to look at the environmental factors in our Apple PESTLE analysis.
Climate Change
The increasing focus on climate change and carbon emissions requires Apple to adopt sustainable practices, such as using renewable energy sources and reducing its carbon footprint across operations and products. Pollution and other environmental side effects from manufacturing facilities in China are a growing concern. This could lead to increased regulation and higher manufacturing costs at some point in the future.
Resource Scarcity
The scarcity of critical raw materials used in electronics manufacturing, such as rare earth metals, can affect Apple's supply chain and production costs.
Waste Management and Recycling
Regulations and consumer expectations regarding electronic waste disposal and recycling necessitate Apple to invest in responsible waste management practices and promote recycling of its products. The biggest environmental issue facing Apple is the disposal of used or nonworking electronic devices.
The expense of disposing of devices, particularly those containing lithium batteries, could be high. Apple could be forced to assume that expense because of concerns about such devices in landfills.
Energy Efficiency
Consumer and regulatory demand for energy-efficient products drives Apple to design and develop devices that consume less power, contributing to environmental sustainability. Concern about energy use and other side effects from data centers could lead to increased regulation and costs. Apple is highly vulnerable to electricity cost increases because of its dependence on data centers and other Internet infrastructure.
Sustainable Packaging
The push for reducing plastic waste and using eco-friendly packaging materials influences Apple's packaging design choices and materials selection.
Environmental Regulations
Compliance with environmental regulations, such as those governing hazardous substances in electronics, impacts Apple's product design and manufacturing processes. China’s efforts to cut greenhouse gases and limit fossil fuel use could increase electricity rates and manufacturing costs for Apple in that country.
Consumer Environmental Awareness
Growing consumer awareness and concern about environmental issues can influence purchasing decisions, prompting Apple to highlight its environmental initiatives and credentials.
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Impact
As Apple expands its operations and supply chain, it must consider the impact on biodiversity and ecosystems, particularly in regions with sensitive environments.
By addressing these environmental factors, Apple can enhance its sustainability efforts, reduce its environmental impact, and meet the expectations of stakeholders and consumers.
Recommendations: Taking action based on the Apple PESTLE Analysis
Based on this Apple PESTLE analysis, here are a few strategic recommendations to ensure the company continues to thrive and maintain its market leadership in the face of evolving external factors:
- Enhance Global Supply Chain Resilience: Apple should further diversify its supply chain. This could involve exploring new geographic locations for manufacturing and assembly to mitigate risks from trade tensions and tariffs.
- Invest in Sustainable Technologies: Apple should continue to invest in green technologies. This includes using renewable energy sources, sustainable materials, and advancing recycling efforts to meet consumer expectations and regulatory requirements.
- Expand Services Portfolio: The analysis indicates a growing importance of digital services. Apple should capitalize on this trend by expanding its services division, including Apple Music, Apple TV+, and financial services.
- Focus on Emerging Markets: Apple could tailor its products and marketing strategies to meet the unique needs and preferences of these regions, enhancing its global footprint and market share.
- Enhance Privacy and Data Protection: Apple should continue to lead in privacy enhancements and security features. This strengthens brand loyalty and aligns with global regulatory trends.
- Leverage AI and Machine Learning: Apple should intensify its efforts in these areas, both to improve product offerings and to optimize operational efficiencies across its business model.
Apple operates in a very competitive industry. While these factors affect Apple's business, they are surely having an impact on Apple's fiercest competitors. So, it makes sense to check the PESTLE analysis of each of their competitors to understand how these external factors influence each brand in a different way:
- PESTLE Analysis of Google
- PESTLE Analysis of Microsoft
- PESTLE Analysis of Samsung
- PESTLE Analysis of Xiaomi
- PESTLE Analysis of Nokia
But these are just a few of the many PESTLE analysis examples you can find here, along with everything you need to know about PESTLE analysis!

