India, officially known as the Republic of India, is the seventh-largest country by area and the second-most populous in the world, with more than 1.44 billion people as of 2024. Attaining independence in 1947, the South Asian country is known for its cultural diversity and is also among the world’s leading democratic countries.
For the past decade or so, India has been experiencing constant GDP growth and continuous liberalization from 1991 to the present. The country has also been opening its doors to attract investors and foreign companies to further promote growth. To get a better understanding of the business environment in India, read on as we analyze it through the PESTLE analysis of India.
The strategic planning tool is usually used for companies. When it comes to country analysis, PESTLE is used to understand the broader macroeconomic environment, evaluate national policies and their impact on economic stability, identify potential opportunities and threats for foreign investors, and assess the overall attractiveness of the country for international trade and investment.
This comprehensive overview helps policymakers, businesses, and analysts to make informed decisions regarding economic policies, market entry strategies, and investment plans. You can read more about PESTLE analysis here.
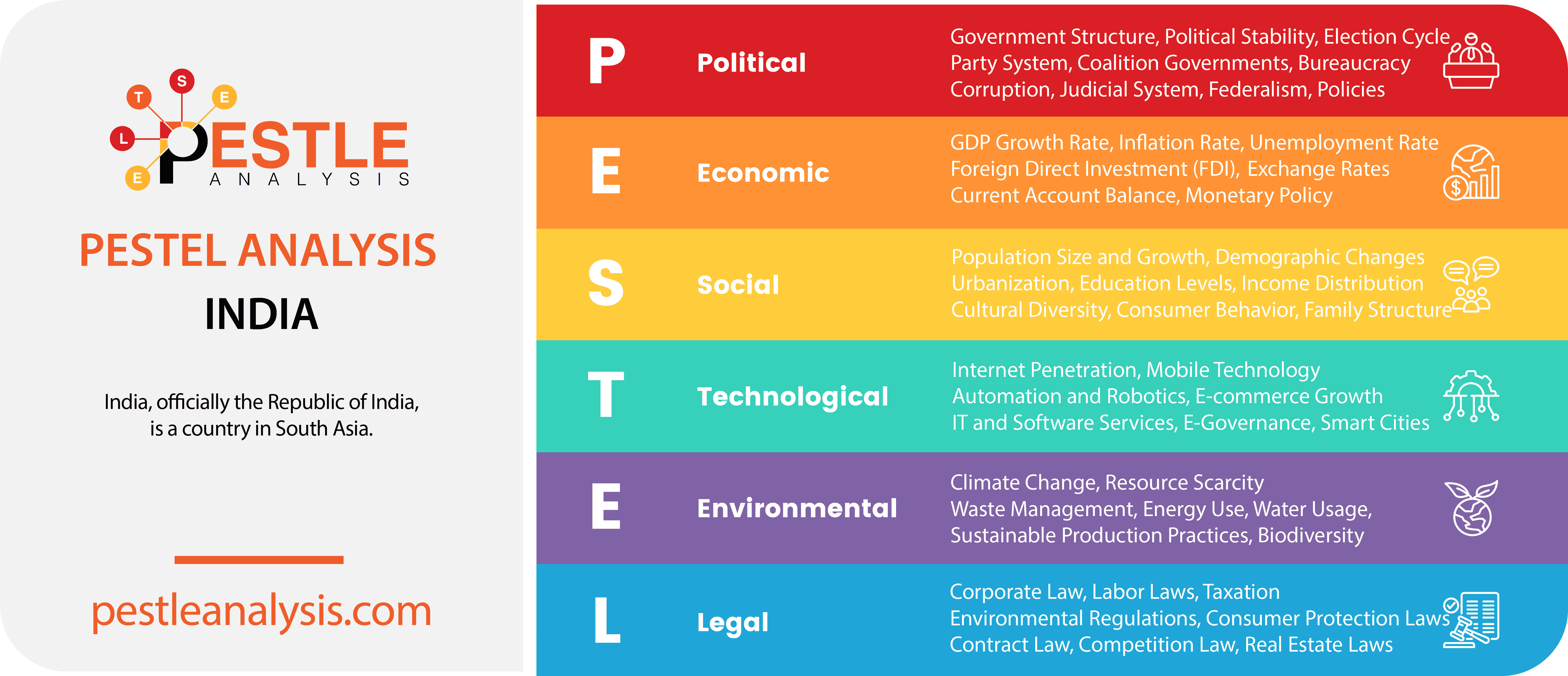
India's Political Factors
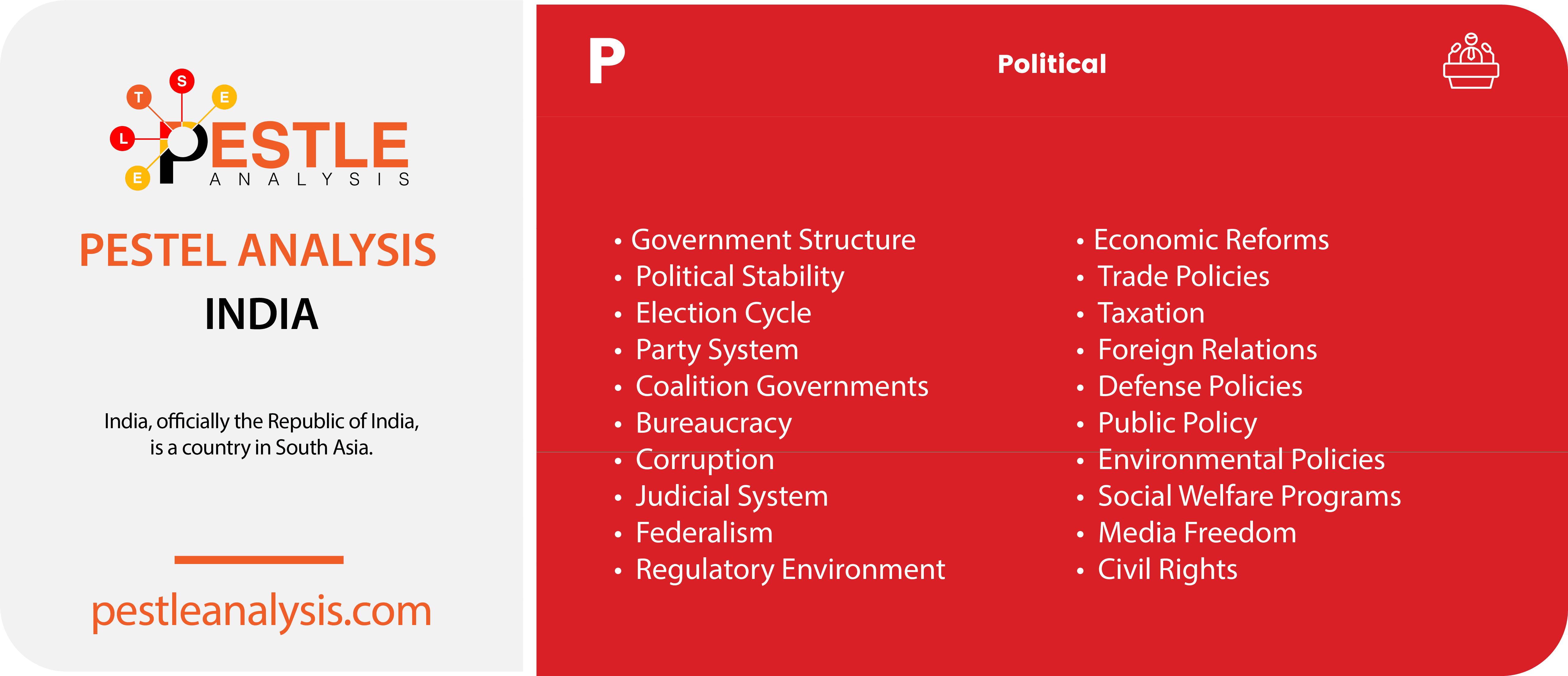
As one of the largest democracies in the world, India operates under a federal system of government. The political environment is heavily influenced by various factors, including government policies, political interests, and the ideologies of numerous political parties. Consequently, the business environment in India is shaped by a wide range of political factors. The country’s well-developed taxation system includes multiple taxes imposed by the Union Government, such as income tax, service tax, and sales tax. Additionally, local bodies manage other taxes, like octroi and utility taxes. Privatization is also significant, with the government promoting free enterprise through various programs and initiatives.
Here are 20 political factors influencing India and how each may affect a business operating in the country:
- Government Structure: India’s federal parliamentary system requires businesses to comply with both national and state-level regulations, which can vary widely. This necessitates a detailed understanding of multiple regulatory frameworks for businesses operating across different states .
- Political Stability: Political stability in India is generally strong, but regional tensions, such as those in Jammu and Kashmir, can disrupt operations and supply chains for businesses in those areas .
- Election Cycle: Regular elections can lead to policy uncertainty and changes in regulations, which can impact business strategies and long-term planning.
- Party System: The policies of major political parties, such as the BJP’s focus on economic reform and the INC’s emphasis on social welfare, can significantly impact the business environment, influencing regulations and economic policies .
- Coalition Governments: Coalition governments often lead to compromises in policy-making, which can result in inconsistent regulatory environments and uncertainty for businesses.
- Bureaucracy: India’s bureaucratic processes can be slow and complex, leading to delays in obtaining necessary permits and approvals, which increases the time and cost for businesses to start and operate .
- Corruption: Corruption remains a significant issue, affecting various levels of government. This can result in increased costs for businesses and create an uneven playing field, where companies may need to navigate through unofficial payments to expedite processes .
- Judicial System: While India’s judiciary is independent, legal processes can be slow, impacting the resolution of business disputes and enforcement of contracts. This can delay projects and increase legal costs .
- Federalism: The autonomy of state governments means businesses must adapt to different local regulations and policies, which can complicate operations across multiple states. This includes varying labor laws, taxation rates, and environmental regulations .
- Regulatory Environment: India has a comprehensive regulatory framework that businesses must comply with, impacting ease of doing business. For example, introducing the Goods and Services Tax (GST) aimed to simplify taxation but required businesses to overhaul their accounting systems .
- Economic Reforms: Economic liberalization since 1991 has aimed to attract foreign investment and boost economic growth, providing opportunities for businesses. Recent reforms include labor law changes and efforts to improve the ease of doing business .
- Trade Policies: Policies affecting international trade, such as tariffs and trade agreements, can impact import/export businesses and their competitiveness in the global market.
- Taxation: Tax reforms like GST simplify the tax structure but require businesses to adapt to new compliance requirements, impacting their financial planning.
- Foreign Relations: Diplomatic relations with other countries influence trade agreements and foreign investment. For instance, improved ties with the United States and European Union can enhance market access for Indian businesses
- Defense Policies: National security and defense policies can affect business continuity, particularly in border areas. Increased defense spending can also lead to opportunities for defense-related industries .
- Public Policy: Policies related to infrastructure, education, and healthcare impact the business environment by improving workforce quality and operational efficiency. Government initiatives like Digital India aim to boost technological infrastructure.
- Environmental Policies: Stringent environmental regulations can increase compliance costs for businesses but also promote sustainable practices. Initiatives like the Swachh Bharat (Clean India) Mission aim to improve environmental standards.
- Social Welfare Programs: Government programs aimed at poverty alleviation and social justice can affect labor markets and consumer spending, influencing business costs and demand for products.
- Media Freedom: A free press can shape public opinion and consumer behavior, impacting brand reputation and market dynamics. Media scrutiny can also influence business practices and corporate governance.
- Civil Rights: Policies protecting civil liberties and human rights ensure ethical business operations. Adherence to these policies can enhance a company’s reputation and employee relations.
Check out our complete list of political factors to include in a PESTLE analysis.
India's Economic Factors
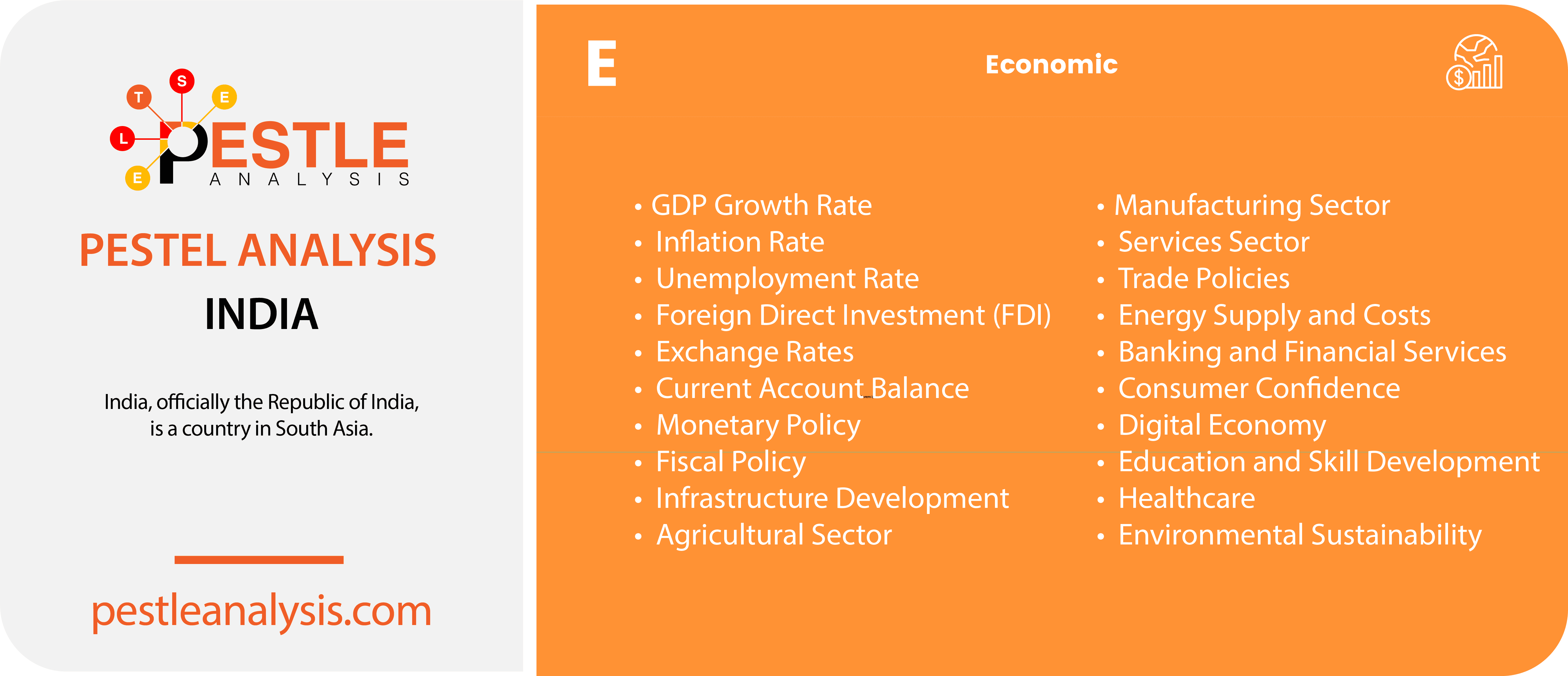
The economy of India has been significantly stable since the introduction of the industrial reform policies in 1991. As per the policy, reductions in industrial licensing, liberalization of foreign capital, formation of FIBP, and so on have resulted in a constant improvement of India’s economic environment.
As of 2024, India’s nominal GDP is approximately $3.94 trillion, making it the fifth-largest economy globally. The GDP growth rate for the fiscal year 2023-2024 is projected to be around 6.7%, driven by robust private consumption and investment supported by government policies aimed at improving infrastructure and the business ecosystem.
Here are 20 economic factors specific to India and how each can affect a business operating in the country:
- GDP Growth Rate: A high GDP growth rate indicates a robust economy, which can lead to increased consumer spending and business opportunities. Conversely, a slowdown can affect sales and profitability.
- Inflation Rate: High inflation can increase the cost of raw materials and reduce consumer purchasing power, impacting sales and profit margins. Low inflation provides a more stable economic environment for planning.
- As of May 2024, the current inflation rate in India is approximately 5.6%. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has projected that inflation will stabilize around 4.5% to 5% throughout the year.
- Unemployment Rate: High unemployment can reduce consumer spending power but may also lead to a larger labor pool with potentially lower wage demands. Low unemployment suggests strong consumer spending but may lead to higher labor costs.
- The unemployment rate stands at 7.4% in 2024.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): High levels of FDI can lead to increased competition but also signal a healthy economic environment attracting international businesses and partnerships.
- India continues to attract substantial FDI, with inflows exceeding $70 billion annually, signaling a healthy economic environment and increased competition.
- Significant foreign investment inflows from the inclusion in JPMorgan's EM debt index in 2024 indicate strong economic prospects and increased liquidity in the bond market.
- Exchange Rates: Fluctuating exchange rates can affect the cost of imports and exports, impacting profitability for businesses involved in international trade.
- In May 2024, the Indian Rupee fluctuates around 82-83 INR per USD.
- Current Account Balance: A deficit can lead to tighter monetary policies and affect interest rates, impacting borrowing costs for businesses. A surplus indicates a strong export sector and foreign exchange reserves.
- India has a current account deficit of around 2% of GDP, leading to tighter monetary policies and higher borrowing costs.
- Monetary Policy: Policies set by the Reserve Bank of India, such as interest rate adjustments, affect borrowing costs and investment levels for businesses.
- As of 2024, the Reserve Bank of India’s repo rate is 6.5%.
- Fiscal Policy: Government spending on infrastructure and social programs can create business opportunities, while taxation policies directly impact business profits and consumer spending.
- Infrastructure Development: Investments in infrastructure, such as transportation and logistics, can reduce operational costs and improve market access for businesses.
- Agricultural Sector: Performance of the agricultural sector affects rural incomes and consumer spending. It also impacts businesses dependent on agricultural raw materials.
- The sector is contributing around 16% to GDP in 2024.
- Manufacturing Sector: Growth in manufacturing boosts industrial demand and creates supply chain opportunities, while a slowdown can affect industrial suppliers and related businesses.
- The sector is growing, driven by initiatives like “Make in India,” boosting industrial demand and supply chain opportunities.
- Services Sector: The performance of the services sector, including IT, finance, and tourism, influences overall economic health and provides numerous business opportunities in these industries.
- Trade Policies: Tariffs, trade agreements, and import-export regulations affect the cost of doing business and the competitiveness of Indian goods in the global market.
- Energy Supply and Costs: Reliable and affordable energy is crucial for business operations. Fluctuating energy prices can impact production costs and profitability.
- Banking and Financial Services: The health of the banking sector affects access to credit and financing for businesses. Reforms and stability in the sector enhance financial services availability.
- Consumer Confidence: High consumer confidence boosts spending on goods and services, benefiting businesses. Low confidence can reduce sales and impact growth strategies.
- Digital Economy: Growth in digital infrastructure and e-commerce creates new business models and revenue streams but also increases competition and the need for technological adaptation.
- Education and Skill Development: Investment in education improves labor quality and productivity, benefiting businesses by providing a skilled workforce.
- Healthcare: Access to quality healthcare affects labor productivity and can influence business costs related to employee health benefits.
- Environmental Sustainability: Regulations and initiatives promoting sustainability can increase compliance costs but also open up new markets for green products and enhance brand reputation.
India's Social Factors
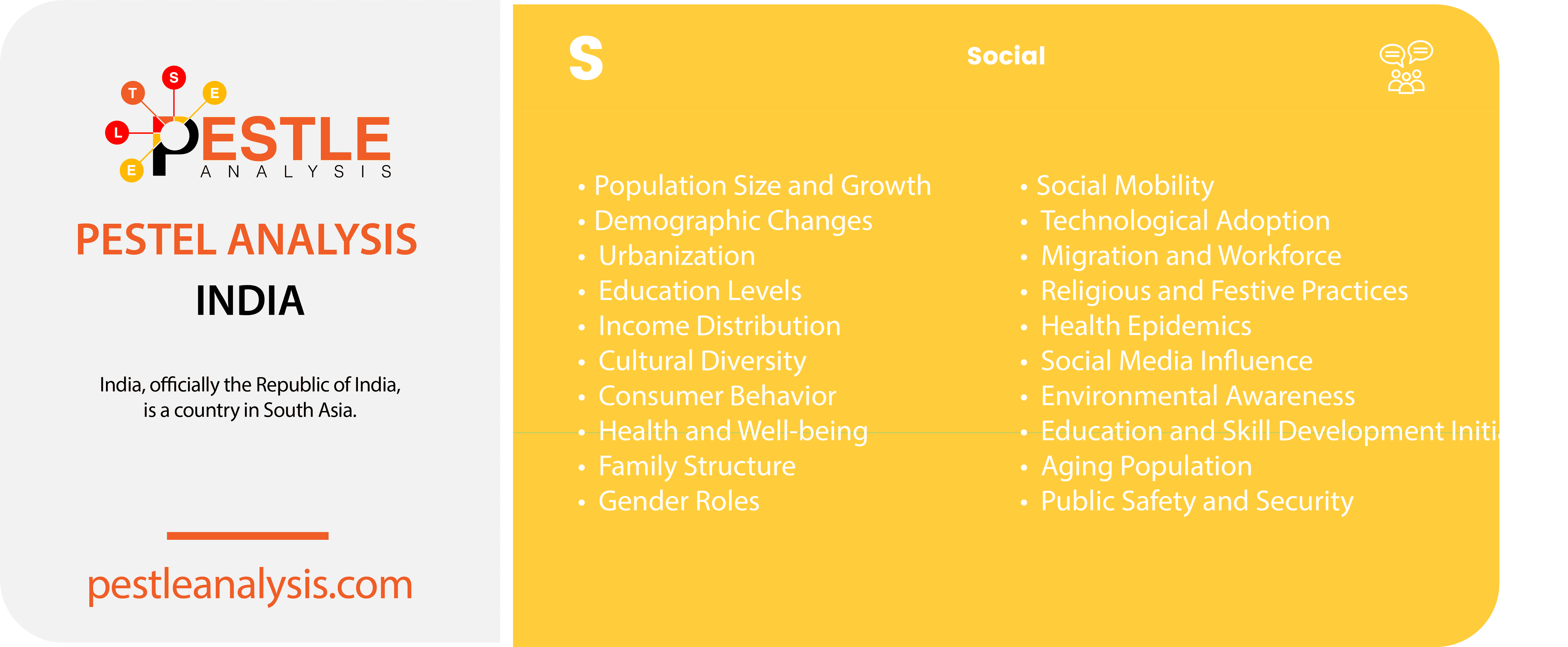
Social factors refer to changes in societal trends that impact the business environment. For instance, India’s aging population is leading to higher pension costs and an increase in the employment of older workers. With a population of more than 1.4 billion, about 68% of Indians are between the ages of 15 and 64. This demographic distribution brings diverse flexibility in education, work attitudes, income distribution, and more.
Here are 20 social factors specific to India and how each can affect a business operating in the country:
- Population Size and Growth: With over 1.4 billion people, India offers a vast consumer base. Rapid population growth can lead to increased demand for goods and services but also necessitates robust infrastructure and services.
- India has a population of approximately 1.44 billion people, with a growth rate of 0.83% in 2024.
- Demographic Changes: A young population with a median age of around 28 years and over 40% of its population under the age of 25, means a significant proportion of the population is entering the workforce, driving consumption and innovation but also requiring investment in education and job creation.
- Urbanization: Rapid urbanization is creating new markets and increasing demand for housing, infrastructure, and services. Businesses need to adapt to urban consumer preferences and logistical challenges.
- As of 2024, approximately 34% of the population lives in urban areas.
- Education Levels: Increasing literacy rates and higher education levels are leading to a more skilled workforce, enhancing productivity and innovation. However, regional disparities in education require businesses to invest in training and development.
- Literacy rates are rising, with overall literacy at about 77.7% in 2024.
- Income Distribution: The growing middle class boosts demand for a wide range of products and services. However, income inequality means businesses must also consider the needs of lower-income segments.
- Cultural Diversity: India’s diverse cultures, languages, and traditions require businesses to tailor their products and marketing strategies to different regional markets.
- Consumer Behavior: Changing lifestyles and consumer preferences, influenced by rising incomes and exposure to global trends, impact product demand and marketing strategies.
- Health and Well-being: Increasing awareness of health and wellness is driving demand for healthcare products, fitness services, and healthier food options.
- Family Structure: Traditional joint family systems are gradually giving way to nuclear families, influencing housing demand, consumer spending patterns, and product preferences.
- Gender Roles: Increasing female workforce participation is impacting household incomes and spending patterns, creating opportunities for businesses targeting women consumers.
- Social Mobility: Rising social mobility allows more individuals to improve their economic status, increasing the potential customer base for various goods and services.
- Technological Adoption: Widespread adoption of smartphones and internet services is driving e-commerce and digital marketing, necessitating businesses to invest in online platforms.
- Migration and Workforce: Internal migration from rural to urban areas affects labor availability and consumer markets, influencing business operations and strategy.
- Religious and Festive Practices: Festivals and religious practices significantly influence consumer spending patterns, creating seasonal demand spikes that businesses can leverage.
- Health Epidemics: Health crises like COVID-19 impact consumer behavior, supply chains, and business operations, necessitating adaptability and crisis management strategies.
- Social Media Influence: The growing influence of social media shapes consumer opinions and behaviors, requiring businesses to actively manage their online presence and engagement.
- Environmental Awareness: Increasing environmental consciousness among consumers is driving demand for sustainable and eco-friendly products, impacting product development and marketing.
- Education and Skill Development Initiatives: Government and private initiatives to improve education and skills impact workforce quality and availability, affecting business productivity and growth.
- Aging Population: While India has a young population, the number of elderly is also increasing, creating demand for healthcare, senior living, and related services.
- Public Safety and Security: Perceptions of safety and security impact consumer behavior, business operations, and investment decisions, particularly in regions with higher crime rates.
Explore our comprehensive list of social factors to include in a PESTLE analysis.
India's Technological Factors
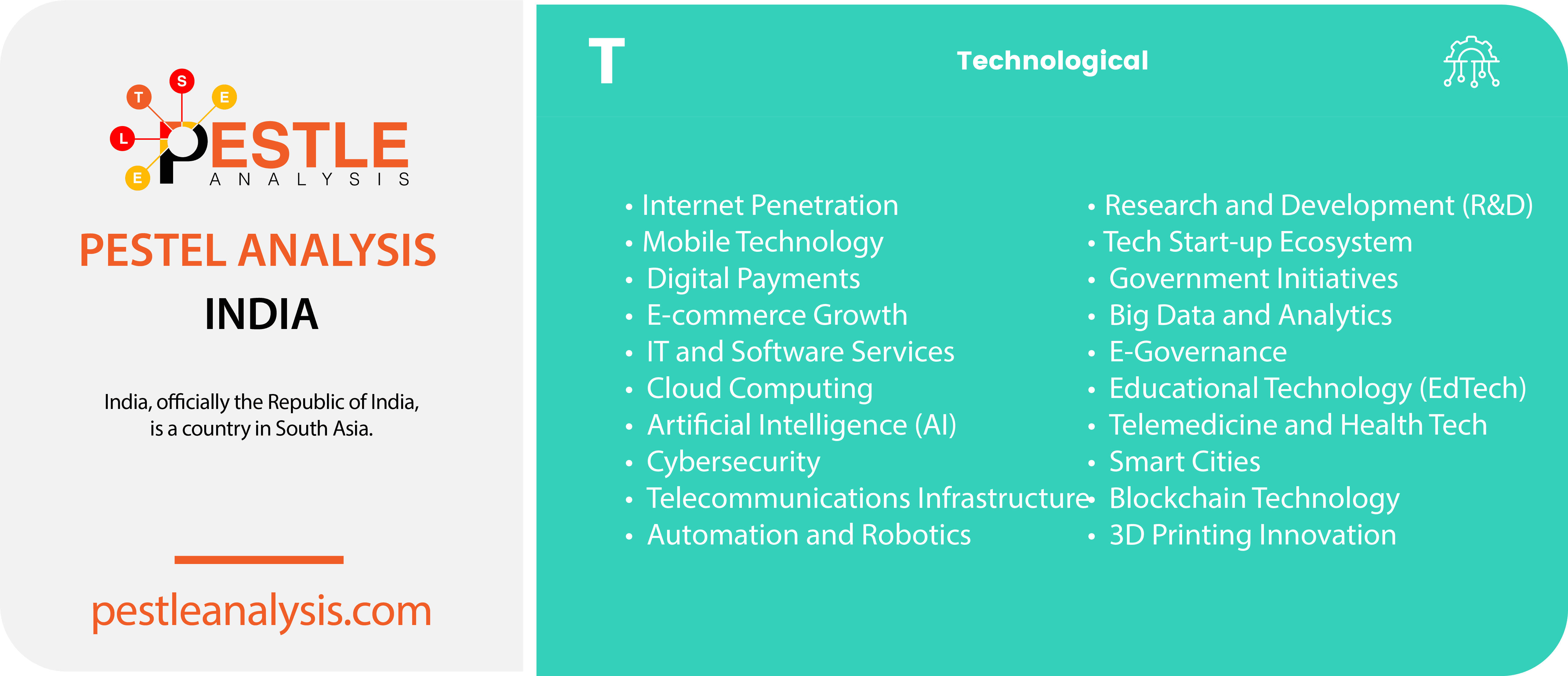
Technology plays a pivotal role in shaping product development and streamlining cost-efficient processes. As of 2024, India is well-equipped with 4G technology and is rapidly expanding its 5G infrastructure, which is driving numerous technological initiatives across the country. India boasts one of the world’s strongest IT sectors, consistently pushing forward with IT development, software innovations, and technological advancements. Additionally, India has made significant strides in space technology, successfully launching multiple satellites and missions, further cementing its position as a global technology leader.
Here are 20 technological factors in India and how each can affect businesses operating in the country:
- Internet Penetration: Increasing internet access, especially with the growth of affordable smartphones, is driving e-commerce and digital marketing opportunities for businesses.
- Jio’s affordable data plans have significantly increased internet access across India, enabling e-commerce platforms like Flipkart and Amazon to reach more customers.
- Mobile Technology: The widespread use of mobile phones, with a significant percentage of the population using smartphones, is influencing consumer behavior and enabling mobile-based business models.
- Paytm, a leading digital wallet, has capitalized on the widespread use of smartphones to provide mobile payment solutions to millions of users across urban and rural India.
- Digital Payments: The rise of digital payment platforms like UPI (Unified Payments Interface) is facilitating cashless transactions and enabling smoother e-commerce experiences.
- The Unified Payments Interface (UPI) processed over 8 billion transactions monthly as of early 2024, making cashless transactions more accessible and boosting online retail sales
- E-commerce Growth: The rapid expansion of the e-commerce sector provides businesses with new sales channels and opportunities to reach a broader audience.
- IT and Software Services: India’s robust IT and software services industry supports business operations, offering solutions for everything from customer relationship management to enterprise resource planning.
- Cloud Computing: Increasing adoption of cloud services allows businesses to scale operations efficiently and cost-effectively, enhancing flexibility and data accessibility.
- Startups like Zoho are leveraging cloud services to offer scalable business solutions, enhancing operational efficiency for SMEs across different sectors.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): Advancements in AI and ML are enabling businesses to enhance customer experiences, improve operational efficiencies, and drive innovation.
- Haptik, an AI-based conversational commerce platform, uses AI to enhance customer support and automate interactions, improving user experiences for businesses like Jio and Kotak Mahindra Bank.
- Cybersecurity: As businesses digitize, the need for robust cybersecurity measures grows to protect against data breaches and cyber-attacks.
- Companies like Quick Heal provide cybersecurity solutions to protect businesses from cyber threats, ensuring safe online transactions and data security for enterprises.
- Telecommunications Infrastructure: Improvements in telecom infrastructure, including 4G and upcoming 5G networks, enhance connectivity and enable more sophisticated digital services.
- The rollout of 5G networks by companies like Airtel is set to enhance connectivity, enabling businesses to offer more advanced digital services and improve operational efficiency.
- Automation and Robotics: Adoption of automation and robotics in manufacturing and other sectors is improving productivity, reducing costs, and increasing precision.
- Bajaj Auto’s use of robotics in manufacturing processes has improved productivity and precision, reducing production costs and increasing output.
- Research and Development (R&D): Investment in R&D, supported by both government and private sector initiatives, is fostering innovation and technological advancement.
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) invests heavily in R&D, leading to technological advancements like the Mars Orbiter Mission, which showcases India’s capability in space technology.
- Tech Start-up Ecosystem: India’s vibrant start-up ecosystem, supported by incubators, accelerators, and venture capital, drives innovation and offers collaboration opportunities for established businesses.
- Bengaluru’s startup ecosystem, supported by incubators like NASSCOM and accelerators like Y Combinator, fosters innovation and collaboration, leading to the growth of successful startups like Ola and Swiggy.
- Government Initiatives: Programs like Digital India and Make in India are promoting digital literacy, tech adoption, and manufacturing, creating a conducive environment for technology-driven businesses.
- The Digital India initiative, mentioned before, has promoted digital literacy and tech adoption, helping small businesses go online and improving access to government services through e-governance.
- Big Data and Analytics: Utilization of big data and analytics helps businesses gain insights into consumer behavior, optimize operations, and make data-driven decisions.
- Reliance Retail uses big data analytics to optimize supply chain management and personalize customer experiences, driving efficiency and sales growth.
- E-Governance: Implementation of e-governance initiatives improves transparency, reduces red tape, and enhances business-government interactions.
- Educational Technology (EdTech): Growth in EdTech is enhancing skills and education, leading to a more qualified workforce.
- Byju’s, an EdTech giant, leverages digital platforms to enhance learning experiences for millions of students, improving educational outcomes and skill development.
- Telemedicine and Health Tech: Advancements in telemedicine and health technology are improving healthcare access and quality, impacting businesses in the healthcare sector.
- Practo, a health tech startup, provides telemedicine services, improving healthcare access and quality for patients across India.
- Smart Cities: Development of smart cities with integrated technology solutions improves urban infrastructure and living standards, benefiting businesses operating in these areas.
- Blockchain Technology: Adoption of blockchain technology in various sectors, including finance and supply chain, enhances transparency, security, and efficiency.
- Signzy, a fintech startup, uses blockchain technology to enhance security and efficiency in digital transactions for banking and financial services.
- 3D Printing Innovation: The growing use of 3D printing technology in manufacturing and prototyping offers cost-effective and rapid production solutions.
- Brahmavarta 3D, an Indian startup, utilizes 3D printing technology to provide rapid prototyping and production solutions for industries like automotive and healthcare, reducing costs and turnaround times.
Discover the full range of technological factors to consider in a PESTLE analysis.
India's Legal Factors

In recent years, several legal changes have been implemented in India, impacting businesses significantly. These include stricter recycling regulations, an increase in the minimum wage, and enhanced protections against disability discrimination. These legal reforms have directly influenced business operations, requiring adjustments in compliance, labor costs, and workplace accessibility standards.
Here are 20 legal factors in India and how each can affect businesses operating in the country:
- Corporate Law: Regulations under the Companies Act govern the formation, operation, and dissolution of companies. Compliance is necessary to avoid legal penalties and ensure smooth operations.
- Labor Laws: Various labor laws, including the Industrial Disputes Act and the Shops and Establishments Act, regulate employment conditions, wages, and workers’ rights. Businesses must adhere to these to avoid disputes and ensure a motivated workforce.
- Taxation: Tax laws, including the Goods and Services Tax (GST), income tax, and corporate tax regulations, affect financial planning and profitability. Compliance with tax regulations is crucial to avoid legal issues and penalties.
- Environmental Regulations: Laws such as the Environment Protection Act and regulations on pollution control require businesses to adopt sustainable practices. Non-compliance can lead to fines and legal action.
- Intellectual Property Rights (IPR): Laws protecting patents, trademarks, copyrights, and designs are critical for businesses to safeguard their innovations and branding. Violations can lead to legal disputes and loss of competitive advantage.
- Foreign Exchange Regulations: The Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) governs foreign investments and transactions. Compliance is necessary for businesses engaged in international trade and investment.
- Consumer Protection Laws: The Consumer Protection Act ensures that businesses provide safe and reliable products and services. Non-compliance can lead to legal action and damage to reputation.
- Contract Law: The Indian Contract Act regulates contractual agreements. Businesses must ensure that contracts are legally sound to avoid disputes and enforce agreements effectively.
- Competition Law: The Competition Act aims to prevent anti-competitive practices. Businesses must avoid monopolistic behavior and unfair trade practices to comply with this law.
- Data Protection Laws: Emerging data protection regulations, including the Personal Data Protection Bill, require businesses to secure personal data and ensure privacy. Non-compliance can lead to significant penalties.
- Real Estate Laws: Laws such as the Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act (RERA) regulate property transactions. Compliance is essential for businesses in the real estate sector to ensure transparency and legal validity of transactions.
- Import-Export Regulations: Laws governing import-export activities, including customs regulations and export incentives, affect businesses engaged in international trade. Compliance ensures smooth operations and benefits from trade incentives.
- Health and Safety Regulations: Laws such as the Factories Act mandate safety standards in workplaces. Compliance ensures the safety of employees and avoids legal liabilities.
- Licensing and Permits: Various industries require specific licenses and permits to operate legally. Ensuring all necessary approvals are obtained is crucial for business continuity.
- Bankruptcy and Insolvency Law: The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) provides a framework for resolving insolvency. Understanding these laws helps businesses manage financial distress and restructure effectively.
- E-commerce Regulations: Specific laws and guidelines govern e-commerce operations, including those related to consumer rights, data protection, and electronic transactions. Compliance ensures legality and consumer trust.
- Anti-bribery and Corruption Laws: Laws like the Prevention of Corruption Act aim to curb corruption. Businesses must adopt ethical practices and ensure compliance to avoid legal consequences.
- Sector-specific Regulations: Certain industries, such as banking, pharmaceuticals, and telecommunications, have specific regulatory bodies and laws. Compliance with these sector-specific regulations is essential for legal operations.
- Land Acquisition Laws: Laws governing land acquisition, such as the Land Acquisition Act, affect businesses involved in infrastructure projects. Understanding and complying with these laws is crucial for project development.
- Dispute Resolution Mechanisms: Availability of arbitration and other alternative dispute resolution mechanisms provides businesses with options to resolve disputes efficiently and avoid lengthy litigation.
View our detailed list of legal factors to include in a PESTLE analysis.
India's Environmental Factors

When it comes to the environment, the quality of air in India has been severely impacted by industrialization and urbanization, leading to significant health problems. In response, the country has seen the establishment of environmental pressure groups and the implementation of stringent noise controls, waste management regulations, and pollution control measures. These efforts aim to mitigate the environmental damage and improve public health outcomes.
Here are 20 environmental factors in India and how each can affect businesses operating in the country:
- Air Pollution: High levels of air pollution in many cities can lead to health problems for employees, increase healthcare costs, and affect productivity. It may also lead to stricter regulations on emissions for businesses.
- The Delhi administration has launched antipollution campaigns, focusing on reducing emissions from power plants, vehicles, and agricultural practices like stubble burning.
- Water Scarcity: Limited access to clean water can affect industrial operations, particularly in manufacturing and agriculture sectors. Businesses may face increased costs for water procurement and treatment.
- Waste Management: Inefficient waste management systems can lead to increased costs for waste disposal and compliance with regulations, impacting business operations and reputation.
- Climate Change: Changing climate patterns can affect agricultural productivity, supply chains, and infrastructure. Businesses need to adapt to these changes to ensure continuity and resilience.
- The severe heatwaves and droughts in northern India have disrupted agricultural productivity, affecting businesses reliant on stable crop yields. Farmers have struggled to maintain their crops, which impacts the food supply chain and related businesses.
- Energy Supply: Dependence on fossil fuels and the push for renewable energy sources can affect energy costs and availability. Businesses may need to invest in sustainable energy solutions.
- Companies like Tata Power are investing heavily in renewable energy projects, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and benefiting from government incentives.
- Biodiversity: Regulations aimed at protecting biodiversity can impact land use and development projects. Businesses in sectors like real estate and mining need to consider environmental conservation measures.
- Environmental Regulations: Compliance with laws such as the Environment Protection Act and specific state regulations is mandatory, affecting operational costs and practices.
- Carbon Footprint: Increasing focus on reducing carbon emissions can lead to additional costs for businesses to implement eco-friendly technologies and practices.
- Natural Disasters: Frequent natural disasters like floods, cyclones, and droughts can disrupt business operations, supply chains, and logistics. Disaster preparedness and resilience planning are essential.
- Deforestation: Deforestation policies and their enforcement can impact industries like logging, agriculture, and real estate development, necessitating sustainable practices.
- Public Health: Environmental health issues, such as pollution-related diseases, can affect the workforce’s health and productivity, leading to higher healthcare costs and potential legal liabilities.
- Green Building Standards: Adoption of green building standards and certifications can influence construction costs and practices but can also lead to long-term savings and market differentiation.
- Infosys has adopted green building standards across its campuses, including the use of LEED certification for its buildings. This initiative has led to long-term savings on energy and water consumption and has helped Infosys differentiate itself in the market as a leader in sustainability.
- Sustainable Practices: Growing consumer preference for sustainable products and practices can influence business strategies, product development, and marketing.
- ITC Limited has implemented comprehensive sustainable practices, including water stewardship and solid waste management programs. These initiatives have not only improved ITC’s environmental footprint but also enhanced its brand reputation and attracted environmentally conscious consumers
- Renewable Energy Initiatives: Government incentives for renewable energy adoption can create opportunities for businesses to reduce energy costs and environmental impact.
- Soil Degradation: Soil erosion and degradation can impact agricultural productivity, affecting businesses in the agriculture and food sectors.
- Plastic Waste Regulations: Increasing regulations on plastic use and waste management can affect packaging and production processes, requiring businesses to find sustainable alternatives.
- Hindustan Unilever has responded to increasing regulations on plastic use by implementing sustainable packaging solutions and enhancing its recycling programs. This shift not only ensures compliance with regulatory standards but also aligns with growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products.
- Environmental Awareness: Rising environmental awareness among consumers can drive demand for green products and influence corporate social responsibility initiatives.
- Mahindra & Mahindra has leveraged rising environmental awareness by launching a range of electric vehicles (EVs) and investing in green manufacturing practices. These initiatives cater to the growing market for sustainable products and position the company as a pioneer in green technology
- Recycling Infrastructure: Availability and efficiency of recycling infrastructure can impact waste management practices and costs for businesses.
- Marine Pollution: Regulations to combat marine pollution can affect industries like shipping and fisheries, requiring compliance and adoption of sustainable practices.
- Environmental Litigation: Potential for environmental lawsuits and legal actions can affect business operations and financial stability, necessitating proactive compliance and risk management strategies.
Examine our complete list of environmental factors to include in a PESTLE analysis.
More research following the PESTLE analysis of India
And that's a wrap. Our PESTLE analysis of India shows how different factors like politics, economy, society, technology, law, and the environment affect the country. To get a full understanding, make sure to check out our SWOT analysis of India too. This will help you see India’s strengths and weaknesses, as well as opportunities and threats from outside.
Using both PESTLE and SWOT together helps you understand how things like India’s strong tech sector and stable government can create great chances for businesses. At the same time, you’ll learn about challenges, like strict environmental laws and infrastructure issues. This combined approach gives you a clear picture of how to succeed in India’s busy and exciting business world!

![PESTLE Analysis of India [2024 Updated]](/content/images/size/w30/2024/05/india-pestle-analysis-template.png)




