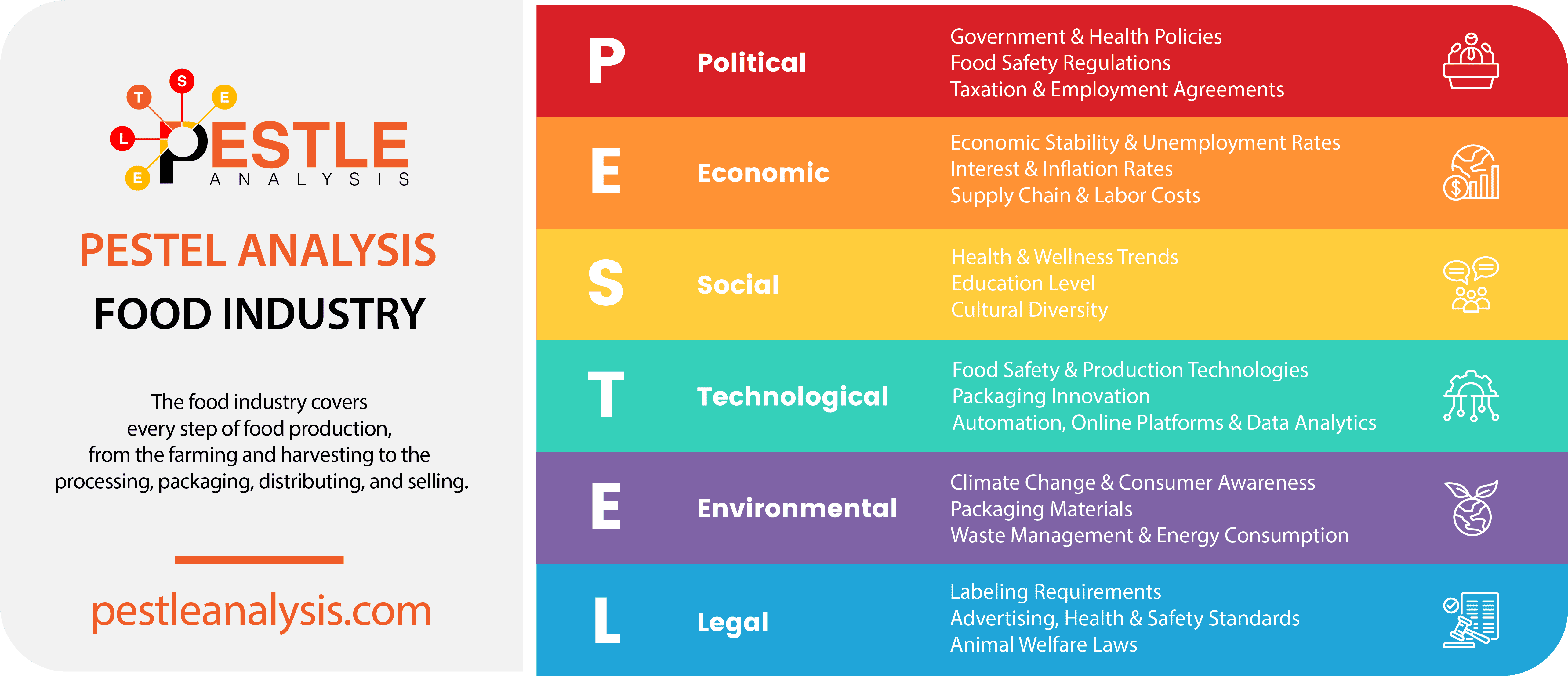
This PESTLE analysis of the food industry looks at its Political, Economic, Sociocultural, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors.
This PESTLE analysis of the food industry identifies the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental external factors affecting the food industry.
In particular, we'll look at how both restaurateurs and food distributors might be affected by current trends. We will use McDonald's as an example throughout the PESTLE analysis.
There's no denying that the food industry is one of the strongest in the world — after all, everyone needs to eat! Indeed, there are some interesting dynamics at play in this space, like rising labor costs, which make it unclear just how profitable food businesses will continue to be.
But...
What is a PESTLE Analysis and How Does it Help the Food Industry Professionals?
PESTLE analysis is a strategic planning tool used by business and project managers. It examines the Political, Economic, Sociocultural, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors that affect a company or an entire industry.
The PESTLE Analysis of the Food industry can help:
- Business Owners and Entrepreneurs: The analysis helps in forming long-term strategies by understanding external factors. It identifies potential risks from external factors, allowing for better risk management plans.
- Investors: The analysis provides insights into the stability and growth potential of the food industry, as it helps in assessing the risks involved in investing in food-related businesses.
- Policy Makers and Regulators: PESTLE analysis assists in creating policies that support sustainable growth in the food sector, while it helps understand the impact of new regulations on the industry.
- Marketing Professionals: PESTLE analysis aids in understanding market dynamics and consumer behavior by identifying emerging trends and helps in adapting marketing strategies accordingly.
- Supply Chain Managers: The analysis provides insights into factors that could affect supply chain efficiency. It helps in understanding the impact of political and economic factors on suppliers.
- Academic Researchers: PESTLE serves as a comprehensive framework for studying the food industry, as it helps in identifying and analyzing industry trends for research purposes.
Food Industry Political Factors

We begin our PESTLE analysis of the food industry with political factors.
Government Policies
Governments across the world have expansive regulatory frameworks for every aspect of the food industry.
This includes the cleanliness of commercial kitchens, the standards for storing and transporting produce, and even the requirements for laborers in the food business. Without a doubt, this makes the food industry one of the most tightly-regulated industries of all.
On the plus side, this ensures that consumers aren't exposed to poor quality nutrition, but the complexities of regulation certainly take away from the margins of the food business.
Health Policies
Trends affect the food industry.
Fast food restaurants are adding “healthier options” on their menus as public health policies are pushing for foods with lower sodium and sugar intakes. Current policies push for the public to be more conscious when buying foods.
For example, as part of the Health Menu Choices Act, food services with over 20 locations in Ontario, Canada, must now post the number of calories for food and drinks openly. A change like this could affect food purchases (and the import/exporting of ingredients) in their country.
Fast food chains also show calories, but not as openly. McDonald's reveals calorie and nutritional information on their website.
But they, and other fast food chains, face criticism for their lack of healthy options on their menus. The public health policies encourage consumers to make healthier choices and McDonald's isn’t a necessary (or healthy) choice. Still, with their funds and global power, McDonald’s can strive to include healthier food options to push back against the criticism.
Trade Agreements
These barriers can affect import/export costs.
Subsidies and Support
Having financial help can affect the competitiveness of the industry.
Environmental Regulations
These include policies on sustainable farming and production practices.
Political Stability
Political unrest may impact the supply chain, production, and market access.
Food Safety Regulations
Setting standards for production, packaging, and distribution.
Taxation Policies
Taxes on food products, ingredients, and food-related services can affect the industry.
Employment Laws
These regulations affect labor in agriculture and production.
You can read more about the "P" in PESTLE analysis in our dedicated article on political factors here.
Food Industry Economic Factors

We continue our PESTLE analysis of the food industry with economic factors.
Consumer Spending Power
Fluctuations in disposable income affect demand for various food products. As a general trend, the world's population is only getting richer. That means that individuals in the lower, middle, and upper classes all have more money to spend on luxuries — including restaurant food. As a result, the overall revenue of the food industry is growing, as individuals cook less and eat out more often. This has a positive effect on all corners of the space, including restaurateurs, food distributors, and the individual workers who play a role in these businesses.
Increasing Labor Costs
Disposable incomes are growing for a reason: laborers are earning more money these days. On the whole, the cost of hiring workers is increasing across all industries. This is caused by not only a growing demand for employees, but also higher and higher government expectations for minimum wages. As in many other industries, the effect of increasing labor costs is simple: less margin for the owner of the business, and thus less profit.
Global Commodity Prices
Prices of raw materials like wheat, dairy, and meat can shift production costs.
Exchange Rates
Impact the cost of importing/exporting food products across borders.
Inflation Rates
Affect both the cost of food production and consumer prices.
Economic Stability
Determines consumer confidence and spending habits.
Supply Chain Costs
Logistics, transportation, and energy costs impacting overall expenses.
Technological Advances
Influence on production efficiency and cost reduction.
Interest Rates
Affect investment in the food industry and consumer purchasing power.
Unemployment Rates
Impact consumer spending power and demand for food products.
Market Trends
Consumer preferences shift all the time, influencing the industry's economic state. Healthier alternatives to foods are pricier compared to fast food or easy-to-make meals. Not only that, but the convenience of readily made food — despite the unhealthiness — can outweigh the trial and error of cooking food from scratch. This has allowed greater expansion of fast food restaurants over the last decade.
You can read more about the first "E" in PESTLE analysis in our dedicated article on economic factors here.
Food Industry Social Factors

Fast food trends shift based on what consumers want. As mentioned throughout this analysis, healthiness is the focus in many countries. This is not only pushed by governmental authorities, but by consumers, as well.
What we’re seeing is a rise in organic and whole foods as diets and lifestyle changes come into play. Vegetarian, vegan and pescetarian eating are becoming less of a fad and more of a lifestyle choice — particularly with the younger generation. How these foods appeal to people is based on their branding look.
As a result, fast food chains are implementing their own branding makeovers.
To input professionals and young adults into their consumer base, McDonald’s is changing their company appearance. The restaurant interior was initially “grab and go”. Now they have a much cleaner and modern look with wood, softer lighting, menu screens, and wifi.
To market to the younger generation, they had to change their branding and look. They even changed their slogan to “Lovin’ Beats Hatin’” but that hasn’t gone over too well. And they’re adding healthier options to their menu still.
Having said that, it's time for sociocultural factors in our PESTLE analysis of the food industry.
Health and Wellness Trends
Increasing demand for organic, natural, and healthier food options. Nowadays, scientists know more about the relationship between food and our bodies than ever before. There's a clear relationship between the food we eat and our personal health, and consumers are conscious of this. As a result, many individuals are looking for healthier ways to fuel their bodies. This doesn't necessarily have a positive or negative effect on the food industry, but it means that businesses will have to adapt to stay relevant. For example, fast food businesses will likely have to move away from traditional, high-calorie fried foods towards healthier alternatives like salads.
Cultural Diversity
Influence on food variety, ethnic cuisines, and dietary preferences.
Demographic Changes
Aging populations, urbanization, and family size impacting food consumption patterns.
Lifestyle Changes
Busy lifestyles boosting demand for convenience foods and delivery services. Aside from having a better grasp of what kinds of food are and aren't healthy, consumers are also more knowledgeable about their individual dietary restrictions. For example, many individuals now understand the negative impact of gluten in those with Celiac disease. This has led to consumers expecting greater understanding on behalf of those who work in the food industry. Once again, this isn't necessarily a bad thing, but it means that the food industry will have to make changes to keep clients happy.
Consumer Attitudes
Growing environmental and ethical concerns influencing food choices (e.g., veganism, locally sourced).
Social Media Influence
Trends and viral food products shaped by online communities and influencers.
Education Level
Higher awareness of food safety, nutrition, and sustainability issues.
Income Distribution
Affects access to various types of food products, including premium options.
Traditions and Beliefs
Religious dietary laws and traditional practices shaping food consumption.
Consumer Activism
Demand for corporate responsibility, fair trade, and ethical sourcing practices.
You can read more about the "S" in PESTLE analysis in our dedicated article on economic factors here.
Food Industry Technological Factors

Technology can give a competitive edge in every industry. Technology is necessary to create packaging, food labels, and the production of food. Newer corporations may be lacking in technology power compared to veteran food-based companies.
McDonald’s moved big screens into their restaurants to showcase their menu. Additionally, they show footage of new promotional drinks and foods, as a method of marketing. They also use their website to provide allergy notices, calorie information, and promotions.
With technology advancing, it helps food corporations reach consumers in new and easier methods. We even have online groceries which deliver fresh produce to customers quickly.
But startups or smaller businesses will have a hard time with outreach compared to global giants like McDonald’s.
We continue our PESTLE analysis of the food industry with technological factors.
Food Production Technologies
Advances in biotechnology, hydroponics, and aquaponics enhancing yield and sustainability.
Supply Chain Innovation
Blockchain for transparency, drones for delivery, and IoT for inventory management.
Food Safety Technologies
Improved methods for detecting contaminants and ensuring product safety.
Packaging Innovations
Smart packaging that extends shelf life and provides consumer interaction via QR codes.
Alternative Foods Development
Lab-grown meat, plant-based proteins, and other sustainable food alternatives.
Automation and Robotics
Automation in food processing, packaging, and even in restaurants for efficiency. We're seeing various types of automation more and more in the food industry. Perhaps the best example is the use of self-checkout screens at fast food venues such as McDonalds, but it's not the only one! Just recently, social media platforms went crazy as viral footage of a hotel's robot cooking up omelettes began to spread. As we find more ways to use technology — including robots — in the food industry, there will be less need for laborers. Overall, this is a good thing for the industry, as it will allow businesses to improve profitability and reduce the likelihood of human error.
Data Analytics
Big data and AI for market trend analysis, consumer behavior prediction, and personalized marketing.
Mobile and Online Platforms
E-commerce growth, food delivery apps, and online reservation systems.
Sustainability Tech
Technologies aimed at reducing waste, improving water usage, and lowering carbon footprints in food production.
Nutritional Science Advances
Enhanced food fortification and the development of functional foods to meet health needs.
You can read more about the "T" in PESTLE analysis in our dedicated article on technological factors here.
Food Industry Legal Factors

Our PESTLE analysis of the food industry includes the following legal factors:
Food Safety Regulations
Laws governing the handling, preparation, and storage of food to ensure it's safe for consumption. As touched upon in the Political section of this PESTLE analysis, the food industry has high standards for safety matters. In particular, there are scores of rules in every country on how food should be transported, stored, and prepared — including directions on what temperatures various food types can reach, how they should be cleaned, and so on. While this is indeed largely a Political issue, it becomes a Legal matter if any of these regulations are ever breached. As such, those in the food business need to be extremely careful to ensure that they stay within the bounds of these rules to prevent costly lawsuits.
Labeling Requirements
Mandatory disclosure of ingredients, nutritional information, allergens, and origins.
Employment Laws
Regulations affecting labor practices, worker safety, and rights within the food industry.
Environmental Legislation
Laws aimed at reducing the environmental impact of food production, such as waste management and emissions controls.
Import/Export Regulations
Compliance with international standards and tariffs affecting global trade in food products.
Health and Safety Standards
Guidelines to ensure the physical safety of food and the work environment in which it is produced.
Intellectual Property Rights
Protection of proprietary recipes, processes, and branding in the food industry.
Advertising Standards
Regulations controlling how food products can be marketed, especially those targeting children and health claims.
Data Protection Laws
Safeguarding consumer information collected through loyalty programs, online sales, and marketing activities.
Animal Welfare Laws
Standards for the ethical treatment of animals used in food production.
You can read more about the "L" in PESTLE analysis in our dedicated article on legal factors here.
Food Industry Environmental Factors

In this final part of our PESTLE Analysis of the food industry, we will examine environmental factors.
Climate Change
Impact on crop yields, availability of raw materials, and food production costs.
Water Scarcity
Challenges in sourcing water for agriculture and processing, affecting sustainability and operational costs.
Land Use
The balance between agricultural production and the preservation of natural habitats, biodiversity, and carbon sequestration capacities.
Pollution Control
Regulations and practices aimed at minimizing waste and emissions from food production and packaging.
Sustainable Farming Practices
Adoption of methods that reduce environmental impact, such as organic farming, crop rotation, and reduced use of chemical pesticides.
Energy Consumption
The shift towards renewable energy sources in food production and transportation to reduce carbon footprint.
Waste Management
Strategies for reducing food waste along the supply chain and innovative recycling of by-products.
Packaging Materials
Development and use of biodegradable, compostable, or recyclable packaging solutions to reduce environmental impact.
Ecosystem Health
The impact of food production on local ecosystems and biodiversity, including pollinators and soil health.
Consumer Awareness
Growing demand for environmentally friendly and ethically produced food products, influencing market trends and production methods. Not only is there growing awareness for the health repercussions of the food we eat, but also for the environmental repercussions of the food we eat. One particularly problematic food group from an environmental point of view is meat. The production of meat — especially red meats — uses huge amounts of water and creates a significant carbon footprint. No less, the meat industry is tearing down large amounts of forest to create new space for farms. The result of this is that more and more individuals are switching to plant-based diets, and governments are slowly taking interest. Once again, this isn't necessarily a negative for food businesses, but they will have to recognize the impact of this shift in the long term.
You can read more about the second "E" in PESTLE analysis in our dedicated article on environmental factors here.
Summary and Recommendations Based on the Food Industry PESTLE Analysis
This PESTLE analysis of the food industry is certainly an interesting one. It's a mix of positives, negatives, and uncertainties. The food industry is seeing a large shift due to consumer consciousness.
Fast food chains, such as McDonald’s, are expanding overseas as sales in western countries have been slowing down. To appeal to new (and younger) demographics McDonald’s utilize their website and have completely repackaged their brand and restaurant look.
It’s clear, now more than ever, how much say consumers have in the development of the food industry.
On the one hand, consumers have more to spend on food and robots can reduce expenses. On the other hand, the space is carefully regulated and labor prices are increasing. What's more, eaters' diets are becoming increasingly more specific. Of course, the food industry is here to stay, but it seems those who prevail will have to understand what consumers really want to be eating in the 21st century.
Now, you can check out our SWOT analysis of the food industry to find out more about this major industry, more PESTLE analysis examples or find everything you need to know about PESTLE analysis here.


