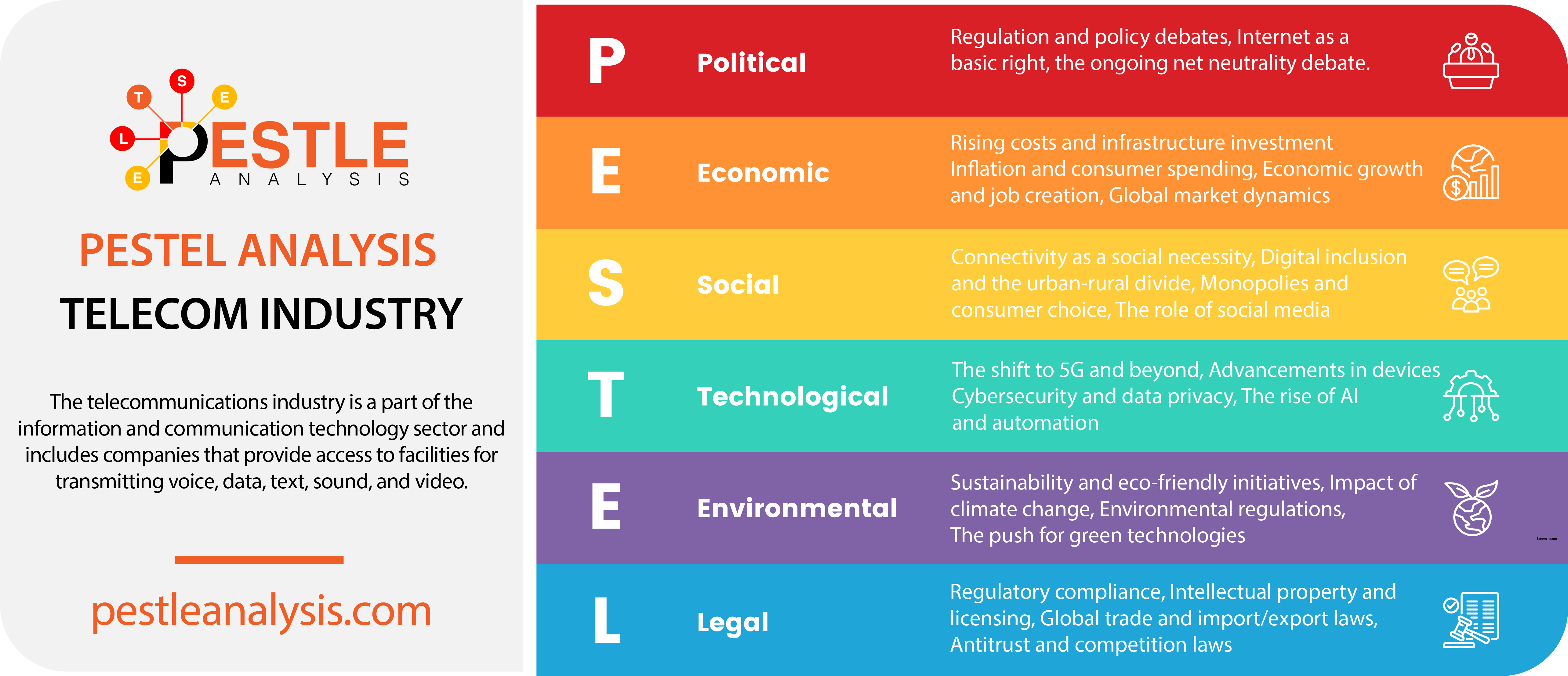
This PESTLE analysis of the telecommunication industry discusses its Political, Economical, Social, Technological, Legal and Environmental factors.
Today, the telecommunication industry is more crucial than ever, as it’s the backbone of how we stay connected in our digital world. From smartphones and high-speed internet to 5G networks and smart devices, this industry keeps our world running smoothly. Whether we’re chatting with friends, streaming videos, playing games online, or even attending virtual classes, we rely on telecommunications every day.
The industry has grown rapidly, with new technologies changing how we communicate and access information. But with all this growth, there are also challenges and debates about how the industry should continue to evolve. Governments, companies, and consumers all have different opinions on the future direction of telecommunications.
Let’s dive into a PESTLE analysis of the telecommunication industry to explore the key factors shaping its development this year.
Telecommunication Industry's Political factors
The telecommunication industry is deeply influenced by political decisions, as regulations and policies play a significant role in shaping how it operates. Governments worldwide are constantly debating how best to manage and oversee this vital industry.
- Regulation and Policy Debates: The government often has its own vision of how telecommunications should be regulated, while consumers and companies have their own ideas. For instance, there’s ongoing debate about the level of government oversight needed to ensure fair practices. Some argue for stricter regulations to protect consumers from unfair pricing and data practices, while others believe that too much government control could stifle innovation.
- Example: In 2024, the European Commission’s decision to extend the roaming agreement between the European Union and Ukraine for another year highlights the political and humanitarian role of telecommunications during crises. This agreement, which allows Ukrainian refugees to stay connected with those back home without incurring additional costs, underscores how political decisions can directly impact the accessibility and affordability of telecom services, especially in times of conflict. It also illustrates the importance of international cooperation in ensuring that communication services remain available to those who need them most.
- Internet as a Basic Right: As the internet becomes more essential for everyday life, many people are pushing for it to be recognized as a basic human right. Today, access to the internet is critical not just for social interactions, but also for education, job opportunities, and accessing government services. The idea is that everyone, regardless of where they live or their financial situation, should have access to affordable and reliable internet. This has led to political pressure on governments to provide or subsidize internet access, especially in underserved areas.
- The Ongoing Net Neutrality Debate: The fight over net neutrality continues to be a major political issue. Net neutrality is the principle that all internet traffic should be treated equally by service providers, without giving preferential treatment to certain websites or services. Supporters of net neutrality argue that it prevents companies from throttling (slowing down) or blocking access to certain content, ensuring a fair and open internet for everyone. On the other hand, some service providers and political leaders argue that relaxing net neutrality rules could encourage investment in infrastructure and innovation.
- Example: In 2024, the Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC) decided to expand the requirement for large telecom companies to share their fiber internet infrastructure with smaller competitors across the entire country by 2025. This regulation aims to lower prices and increase consumer choice, highlighting the government’s role in promoting competition and ensuring affordable access to high-speed internet.
This political tug-of-war between governments, telecom companies, and consumers is crucial because the outcome will determine how free and accessible the internet remains for years to come.
Telecommunication Industry's Economic Factors
The telecommunication industry is heavily influenced by economic conditions, which in turn affect how services are priced and delivered.
- Rising Costs and Infrastructure Investment: Building and maintaining telecom infrastructure, especially in rural or remote areas, remains a significant challenge. Now, the costs associated with deploying 5G networks and upgrading existing infrastructure to keep up with new technology have continued to rise. This often leads to higher prices for consumers, especially in less densely populated areas where it’s more expensive to provide coverage. Despite this, there’s pressure on companies to keep prices competitive, which can squeeze profit margins.
- Inflation and Consumer Spending: With inflation impacting many parts of the economy, consumers may find themselves spending more on essential services, including telecommunications. As the cost of living increases, telecom companies must balance pricing their services fairly while ensuring they can continue to invest in new technology. In some cases, inflation can drive up the cost of telecom equipment, further complicating the situation.
- Economic Growth and Job Creation: The demand for telecommunications services continues to grow as more households are built and more people require access to the internet for work, education, and entertainment. This growth has led to job creation in various areas of the industry, from customer service to technical support and network maintenance. Additionally, the rise of remote work and digital marketing has fueled the demand for telecom services, leading to more opportunities in fields like IT, digital marketing, and cybersecurity.
- Global Market Dynamics: The global nature of the telecommunication industry means that economic conditions in one part of the world can affect the entire industry. For example, supply chain disruptions, trade policies, and international relations can all impact the availability and cost of telecom products and services. Companies that operate globally must navigate these complexities while trying to remain profitable.
Telecommunication Industry's Social Factors
Social trends and behaviors have a significant impact on the telecommunication industry, influencing both how services are used and what services are in demand.
- Connectivity as a Social Necessity: Nowadays, being connected to the internet is not just a convenience; it’s a necessity. People rely on telecommunications for everything from staying in touch with friends and family to working, learning, and even accessing healthcare. As a result, there is growing social pressure on governments and companies to ensure that everyone has access to affordable, high-quality telecom services, regardless of where they live.
- Digital Inclusion and the Urban-Rural Divide: While urban areas generally have access to the latest telecom technologies, rural areas still struggle with limited options. This urban-rural divide creates significant social challenges, as people in rural areas may find themselves at a disadvantage when it comes to education, job opportunities, and social connections. The industry is under pressure to find ways to bridge this gap, but doing so is often expensive and logistically challenging.
- Monopolies and Consumer Choice: In many regions, a few large companies dominate the telecommunication market, limiting consumer choice. This lack of competition can lead to higher prices and fewer options for consumers, which is a growing concern today. Social media and public opinion are increasingly influencing these companies to offer better services, lower prices, and more transparency about their practices.
- The Role of Social Media: Social media platforms have become deeply integrated into daily life, and telecom companies play a crucial role in supporting these networks. The demand for constant connectivity has driven innovation in mobile data plans and Wi-Fi access, as people expect to be online wherever they go. This trend has also led to new business opportunities for telecom companies in the form of partnerships with social media platforms and other digital services.
Telecommunication Industry's Technological Factors
Technological advancements are at the heart of the telecommunication industry, driving both opportunities and challenges.
- The Shift to 5G and Beyond: Nowadays 5G networks have become widely available, offering faster speeds, lower latency, and more reliable connections. This has opened up new possibilities for the internet of things (IoT), smart cities, autonomous vehicles, and other innovations. Telecom companies are heavily investing in 5G infrastructure, while also starting to explore the potential of 6G, which promises even more revolutionary changes in the future.
- Example: In 2024, Lumen Technologies secured $5 billion in deals with cloud and tech companies, including Microsoft, to provide networking and cybersecurity solutions tailored for AI workloads. This surge in AI adoption has led to increased investment in high-capacity fiber networks, highlighting the critical role of advanced telecom infrastructure in supporting the next wave of technological innovation. Lumen’s strategic focus on AI-ready infrastructure demonstrates how telecom companies are positioning themselves at the forefront of this technological shift.
- Advancements in Devices: Smartphones, tablets, and other connected devices have continued to evolve, becoming more powerful and versatile. These advancements have driven demand for better network capabilities, pushing telecom companies to innovate continuously. For instance, the shift from copper to fiber optic cables for faster internet speeds and the widespread adoption of eSIM technology have transformed the way we use and interact with telecom services.
- Cybersecurity and Data Privacy: As the world becomes more connected, cybersecurity has become a top priority for the telecommunication industry. With more devices connected to the internet and more personal data being transmitted, the risk of cyberattacks has increased. Telecom companies must invest in robust security measures to protect their networks and customers, while also complying with increasingly strict data privacy regulations.
- The Rise of AI and Automation: Artificial intelligence (AI) and automation are playing an increasingly important role in the telecommunication industry. From chatbots that handle customer service inquiries to AI-driven network management systems, these technologies are helping companies improve efficiency and reduce costs. However, they also raise questions about job displacement and the need for a workforce that can adapt to new technologies.
Telecommunication Industry's Legal Factors
Legal considerations are critical in the telecommunication industry, as laws and regulations can shape everything from business practices to consumer rights.
- Regulatory Compliance: Telecommunication companies must navigate a complex web of regulations, including those related to data privacy, consumer protection, and fair competition. Today, these regulations are becoming more stringent, particularly regarding how companies collect, store, and use customer data. Compliance is not only a legal requirement but also crucial for maintaining consumer trust.
- Example: The controversy in Greece, where the former head of the EYP intelligence service was accused of using illegal spyware to monitor targets, underscores the legal challenges related to privacy and surveillance in telecommunications. Although the EYP denied using the Predator malware, the scandal led to resignations and judicial investigations, raising serious concerns about the protection of private communications. This case highlights the importance of strict legal frameworks and oversight in preventing abuses of surveillance technology within the telecom industry, especially as such issues gain increasing attention within the European Union.
- Intellectual Property and Licensing: The industry also faces legal challenges related to intellectual property, particularly with the rapid pace of technological innovation. Companies must ensure that they have the necessary licenses to use patented technologies, and disputes over intellectual property rights can lead to costly legal battles. This is especially relevant as new technologies like 5G and AI become more prevalent.
- Global Trade and Import/Export Laws: As telecom companies operate on a global scale, they must comply with international trade laws and import/export regulations. These laws can affect the availability of telecom products, particularly when it comes to sourcing components for devices and infrastructure. Changes in trade policies or tariffs can have significant impacts on the industry, influencing everything from pricing to product availability.
- Antitrust and Competition Laws: In many regions, governments are becoming more vigilant about preventing monopolies and ensuring fair competition in the telecommunication industry. Antitrust laws are being enforced more strictly to prevent large companies from unfairly dominating the market. This has led to increased scrutiny of mergers and acquisitions, as regulators aim to protect consumer interests.
- Example: In 2024, The Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC) initiated an informal review of the network-sharing deal between TPG Telecom and Optus, reflecting ongoing regulatory scrutiny in the telecommunications industry. This deal, which would significantly expand TPG’s mobile network coverage in regional Australia, is being examined for its potential impact on competition and pricing. The ACCC’s involvement underscores the importance of adhering to competition laws, as previous deals between TPG and other telecom giants have been blocked due to concerns about market dominance and reduced consumer choice. This example illustrates the critical role of regulatory bodies in shaping industry dynamics and ensuring fair competition.
Telecommunication Industry's Environmental Factors
Environmental considerations increasingly impact the telecommunication industry, as both consumers and regulators demand more sustainable practices.
- Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Initiatives: There is growing awareness of the environmental impact of the telecommunication industry, particularly regarding the energy consumption of data centers, the production of electronic devices, and the disposal of e-waste. Companies are under pressure to adopt more sustainable practices, such as using renewable energy sources, reducing their carbon footprint, and promoting recycling programs for old devices.
- Impact of Climate Change: Climate change poses a significant challenge for the industry, particularly in terms of infrastructure resilience. Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, floods, and wildfires, can damage telecom infrastructure, leading to service disruptions. Companies must invest in building more resilient networks and developing contingency plans to ensure that services remain operational during and after such events.
- Environmental Regulations: Governments are increasingly implementing regulations aimed at reducing the environmental impact of the telecommunication industry. These regulations may include requirements for energy efficiency, limits on carbon emissions, and rules governing the disposal of electronic waste. Compliance with these regulations can be costly, but it is essential for companies that want to maintain their reputation and avoid legal penalties.
- The Push for Green Technologies: There is a growing demand for “green” technologies in the telecom industry, such as energy-efficient network equipment and environmentally friendly devices. Companies that invest in these technologies can differentiate themselves in the market and attract environmentally conscious consumers. However, the development and deployment of green technologies can also require significant investment, which may be challenging for some companies.
Further Reading
The telecommunication industry is a complex and dynamic field shaped by various political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors. As we’ve seen, these factors can have a profound impact on how companies operate, how services are delivered, and how consumers interact with the world around them.
If you’re interested in diving deeper into how specific companies are navigating these challenges, I encourage you to check out SWOT and PESTLE analyses of some of the most influential players in the industry. Here are 10 of the most important ones:
- AT&T – A major American telecommunications company with a significant presence in mobile, broadband, and media services.
- Verizon – Another leading U.S. telecom giant, known for its extensive wireless network and broadband services.
- T-Mobile – A key player in the wireless communications market, particularly noted for its aggressive expansion and customer-friendly policies.
- Vodafone – A global telecom leader based in the UK, with a strong presence across Europe, Asia, and Africa.
- China Mobile – The world’s largest mobile telecommunications company by number of subscribers, dominating the Chinese market.
- Deutsche Telekom – A German-based multinational telecom company, known for its T-Mobile brand and extensive European network.
- Orange S.A. – A major French multinational telecommunications corporation, providing mobile, landline, and internet services across Europe and Africa.
- British Telecom (BT) – The leading telecommunications and network provider in the UK, also offering services in other parts of the world.
- Telefonica – A Spanish multinational with a strong presence in Europe and Latin America, particularly through its Movistar brand.
- Samsung, – Although primarily known for its electronics, Samsung is a significant player in telecom, particularly in the development of 5G technology and network equipment.
Exploring these analyses will give you a deeper understanding of how each company addresses the challenges and opportunities in today’s telecommunication landscape.

