Renault is a household name in Europe, but internationally, it’s still searching for the GPS coordinates. Maybe a stronger global strategy can help them avoid taking the scenic route.
By identifying these four factors, businesses can gain a clearer understanding of their competitive position and make informed decisions about future strategies. This framework is especially valuable for assessing how a company can leverage its advantages, address its challenges, and respond to market dynamics.
For a global automotive company like Renault, a SWOT analysis is particularly useful in navigating the complexities of the fast-evolving automotive industry.
Renault must balance its traditional internal combustion engine business with the growing demand for electric vehicles (EVs), manage geopolitical risks, and stay ahead of innovation. By understanding its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, Renault can develop strategies to remain competitive and future-proof its business in a dynamic market.

With this in mind, we will now conduct a detailed SWOT analysis of Renault, exploring the key factors that shape its strategic outlook and business decisions. Let’s dive into the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats that impact Renault’s performance.
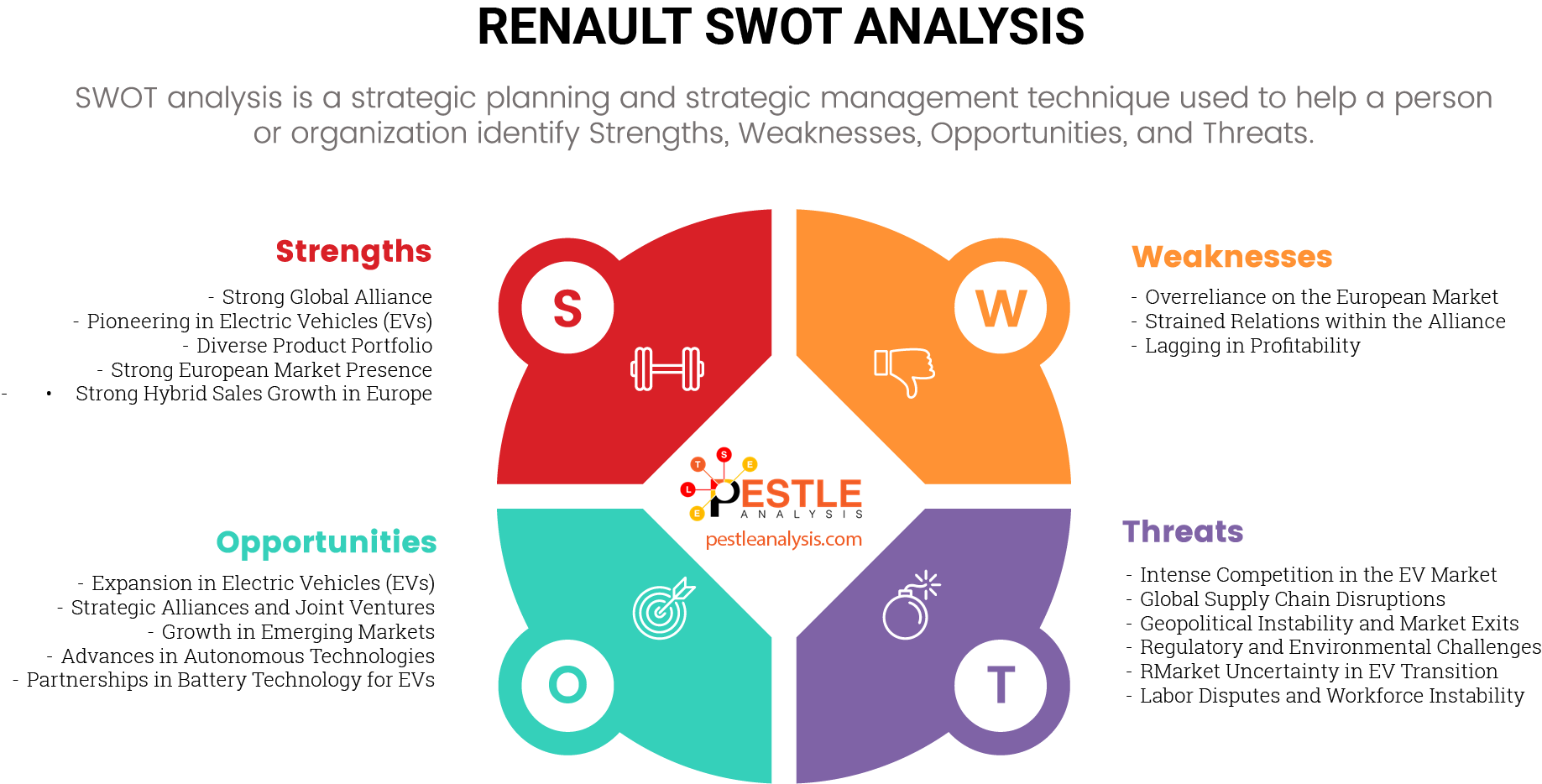
Renault's Strengths
Renault, as a major player in the global automotive industry, has several key strengths.
- Strong Global Alliance (Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi): Renault’s strategic partnership with Nissan and Mitsubishi forms one of the world’s largest automotive alliances. This allows Renault to benefit from shared research and development, technology innovation, and market access across different regions. By pooling resources, Renault can reduce costs, improve production efficiency, and accelerate innovation, especially in areas like electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous driving technologies.
- Pioneering in Electric Vehicles (EVs): Renault has positioned itself as a leader in the EV market, with its ZOE model being one of Europe’s top-selling electric cars (but not without problems). This early commitment to electrification has given Renault a strong competitive edge, especially as global demand for eco-friendly vehicles continues to rise. The company’s dedication to sustainability and green technology helps meet tightening emissions regulations while appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
- Diverse Product Portfolio and Strong European Market Presence: Renault offers a wide range of vehicles, from affordable city cars to commercial vehicles, making it accessible to various consumer segments. Additionally, Renault has a dominant market share in Europe, particularly in France, where it has a strong brand identity. Its ability to cater to different market needs, coupled with its European market strength, allows it to maintain a resilient position against competition.
- Strong Hybrid Sales Growth in Europe: Renault’s robust performance in hybrid vehicle sales demonstrates its ability to meet evolving consumer demands for more affordable and convenient electrified options. As the automotive market shifts toward sustainability, Renault’s focus on hybrids allows it to capitalize on a growing segment while the full transition to electric vehicles continues at a slower pace.
- Example: In the first half of 2024, Renault’s global sales volume rose 1.9%, driven by a 45% increase in hybrid sales in Europe. Hybrids accounted for 34.6% of Renault’s sales, significantly boosting the company’s market share and outperforming market growth. This strong demand for hybrids highlights Renault’s strategic positioning in the electrified vehicle market and its ability to roll out successful new models, ensuring continued growth in its key European market. This example shows how Renault’s strength in hybrid sales positions the company to maintain growth as it navigates the ongoing transition to full electrification.
Renault's Weaknesses
Renault, despite its strengths, also faces some significant weaknesses that impact its competitive position.
- Overreliance on the European Market: Renault generates a significant portion of its revenue from Europe, particularly from France. While this gives it strength in one region, it exposes the company to risks from economic downturns, regulatory changes, or political instability in Europe. Its relatively weaker presence in major growth markets like the U.S. and China limits its ability to diversify revenue streams and tap into faster-growing regions.
- Strained Relations within the Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance: Despite the benefits of its alliance with Nissan and Mitsubishi, tensions between the companies have occasionally surfaced, especially after the arrest of former chairman Carlos Ghosn in 2018. These internal frictions have led to reduced cooperation, misalignment in strategic goals, and operational inefficiencies. The strained relationships could further hinder joint projects, delay innovation, and weaken the alliance’s competitive advantage.
- Lagging in Profitability: Renault has struggled with profitability in recent years, particularly when compared to competitors. Factors such as high production costs, declining sales in key segments, and challenges in maintaining operating margins have contributed to this weakness. Despite strong sales in electric vehicles, the company has faced financial pressure, especially as it continues to invest heavily in new technologies without a clear return on investment in the short term.
Renault's Opportunities
Renault has several opportunities it can leverage to strengthen its position in the evolving automotive industry.
- Expansion in Electric Vehicles (EVs): With the global shift toward sustainable transportation, Renault is well-positioned to expand its electric vehicle offerings. Governments worldwide are implementing stricter emissions regulations and offering incentives for EV adoption. Renault’s early success with the ZOE and its expertise in EV technology provide a platform to launch new models and capitalize on the growing demand for zero-emission vehicles, especially in markets like Europe and China where EV adoption is accelerating.
- Example: Renault’s 2024 memorandum of understanding (MoU) with the Slovenian government to produce a new electric version of the Twingo at the Revoz plant in Novo Mesto. Production is set to begin in 2026, with an initial annual output of 150,000 vehicles. This strategic investment not only helps Renault secure its EV future but also supports job retention and long-term growth at the plant, highlighting the potential benefits of expanding EV production capabilities.
- Strategic Alliances and Joint Ventures: Renault has the opportunity to leverage strategic alliances and joint ventures to strengthen its position in the global automotive market. Collaborating with industry leaders allows Renault to pool resources, access new technologies, and share risks in the development of future mobility solutions.
- Example: Due to Renault’s joint venture with Geely and Aramco, called Horse Powertrain, in 2024, Aramco acquired a 10% stake in this venture, which focuses on producing hybrid systems and internal combustion engines compatible with advanced fuels like e-fuels. This partnership not only supports Renault’s continued involvement in fuel-based engines but also positions it to adapt to future sustainability trends, such as the shift toward e-fuels and cleaner hybrid technologies. Strategic alliances like this enable Renault to remain competitive and innovative while addressing future regulatory and consumer demands for greener automotive solutions.
- Growth in Emerging Markets: Renault has the opportunity to increase its presence in rapidly growing markets like India, Southeast Asia, and Africa, where demand for affordable vehicles is rising. Expanding its product lines tailored to the needs of these regions—such as small, fuel-efficient cars and entry-level electric models—could help Renault diversify its revenue streams and reduce its overreliance on Europe. Additionally, growth in these markets presents new revenue potential for both conventional and electric vehicles.
- Example: A key example is Renault’s backing of BeyonCa, an EV startup that plans to establish Hong Kong’s first car brand. In 2024, BeyonCa announced it would set up a final assembly plant and its international headquarters in Hong Kong, aiming to produce 100,000 EVs annually by a few years after 2025. While much of the manufacturing will take place in mainland China, the move highlights Renault’s strategy to support emerging EV brands in new markets, providing access to growing regions like the Middle East and ASEAN countries.
- Advances in Autonomous and Connected Car Technologies: The automotive industry is moving towards smarter and more autonomous vehicles. Renault’s partnership within the Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance offers opportunities to share resources and develop cutting-edge autonomous driving, connectivity, and smart vehicle technologies. By investing in autonomous vehicle R&D and integrating advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) into its vehicles, Renault can position itself as a leader in the next generation of automotive technology, which is likely to attract tech-savvy consumers and businesses.
- Partnerships in Battery Technology for Electric Vehicles: Renault has the opportunity to strengthen its electric vehicle (EV) lineup through strategic partnerships in battery technology, which are crucial for improving performance and reducing costs. By collaborating with top battery manufacturers, Renault can enhance its EV capabilities and remain competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
- Example: A notable example is Renault’s EV unit, Ampere, teaming up with LG Energy Solution (LGES) and CATL in 2024 to develop and supply lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries. These partnerships will help Renault mass-produce more affordable EVs and expand its range of models. The inclusion of LFP technology, known for its cost-effectiveness and safety, allows Renault to better compete with cheaper Chinese rivals while addressing supply chain challenges for critical materials like cobalt. The agreement with LGES alone aims to power around 590,000 vehicles by 2030, positioning Renault to scale its EV production significantly.
Renault's Threats
Renault faces several external threats that could impact its long-term success.
- Intense Competition in the EV Market: The global electric vehicle (EV) market is becoming increasingly competitive, with established automakers like Tesla, Volkswagen, and new entrants from China (such as NIO and BYD) rapidly expanding their EV offerings. Renault, despite its early success, risks losing market share to these competitors, who are often better funded and can push innovation faster. Additionally, many competitors are expanding aggressively in key markets where Renault has a limited presence, which could diminish Renault’s position as a leader in the EV space.
- Economic Uncertainty and Global Supply Chain Disruptions: Economic downturns, particularly in Europe, could negatively affect Renault’s sales and profitability. Inflation, rising energy prices, and changes in consumer spending patterns could lower demand for new vehicles, especially in Renault’s core European market. Moreover, global supply chain disruptions—such as semiconductor shortages, rising material costs, and logistical delays—pose a significant threat to Renault’s production capacity and ability to deliver vehicles on time, further straining financial performance.
- Geopolitical Instability and Market Exits: Renault faces significant risks from geopolitical instability, particularly in regions where political conflicts or sanctions impact business operations. When countries impose sanctions or political tensions escalate, companies like Renault may be forced to exit key markets, losing valuable revenue streams and production capacity.
- Example: Renault’s 2022 sale of its majority stake in Avtovaz, Russia’s largest carmaker, to the Russian state for a symbolic one rouble was in response to international sanctions following the war in Ukraine, highlighting how external political factors can disrupt business operations. Such exits not only result in immediate financial losses but also weaken Renault’s global footprint, making it vulnerable to future geopolitical changes.
- Regulatory and Environmental Challenges: As governments impose stricter emissions regulations, including bans on internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles in the coming decades, Renault will need to transition its product line towards full electrification. While this shift presents opportunities, it also brings financial and operational risks. Compliance with ever-evolving environmental regulations requires substantial investment in new technologies and manufacturing capabilities. Additionally, failure to meet these regulatory requirements could result in fines, restricted market access, or damage to the company’s reputation.
- Regulatory Pressure and Market Uncertainty in EV Transition: Renault faces the challenge of aligning with strict regulatory timelines for electric vehicle (EV) adoption in Europe, which could create financial strain and market uncertainty. As governments push for rapid EV adoption to meet environmental goals, automakers like Renault must balance compliance with regulations while managing production costs and market demand.
- Example: Renault CEO Luca De Meo’s call for more flexibility in the European Union’s 2035 ban on diesel and petrol cars is an example. In July 2024, De Meo highlighted that while Renault supports the shift to electric vehicles, the current market slowdown and high production costs pose significant challenges. He emphasized that without cost reductions and stronger consumer demand, Renault, and the industry at large, may struggle to meet the ambitious timeline.
- Labor Disputes and Workforce Instability: Labor disputes pose a significant threat to Renault’s operations, as they can disrupt production, affect employee morale, and damage the company’s reputation. In industries like automotive manufacturing, where skilled labor is critical to innovation and quality, conflicts with the workforce can lead to operational inefficiencies and delays in key projects.
- Example: In 2024, employees at Renault’s Viry-Chatillon facility, responsible for building the Formula 1 engines, staged a peaceful protest during the Italian Grand Prix. The protest was in response to reports that Renault plans to cease engine production at the plant by 2026 and shift to Mercedes engines, threatening hundreds of jobs. While the protest was peaceful, it reflects potential unrest within the workforce that could escalate if management decisions negatively impact employees. Such disputes could disrupt Renault’s F1 operations and tarnish its image, especially in a high-visibility sector like motorsports.
Recommendations based on Renault's SWOT Analysis
To wrap up this SWOT analysis of Renault, here are three key recommendations based on the findings:
- Diversify Market Presence Beyond Europe: While Renault is a dominant force in Europe, its overreliance on this region makes it vulnerable to economic and regulatory changes. Expanding aggressively into high-growth markets like Asia, particularly China and India, could mitigate this risk and tap into new revenue streams.
- Capitalize on the Growing Hybrid and EV Market: Renault has a strong foundation in electric vehicles and hybrids, but with increasing competition, it’s crucial to continue innovating and lowering production costs. Strategic partnerships, like those with LGES and CATL, should be expanded to maintain a competitive edge in battery technology and EV affordability.
- Strengthen Internal Stability and Global Alliances: The strained relations within the Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance and labor disputes could hinder growth. Addressing these internal challenges by fostering better cooperation and ensuring workforce satisfaction will help Renault operate more efficiently and stay agile in a rapidly evolving market.
If you’re curious how Renault stacks up against other major carmakers, check out the SWOT analyses I’ve previously conducted on companies like Volkswagen, Tesla, and Toyota to see how they’re handling similar challenges and opportunities in the automotive industry.
- SWOT Analysis of Volkswagen
- SWOT Analysis of Tesla
- SWOT Analysis of Toyota
- SWOT Analysis of Mercedes
- SWOT Analysis of BMW









