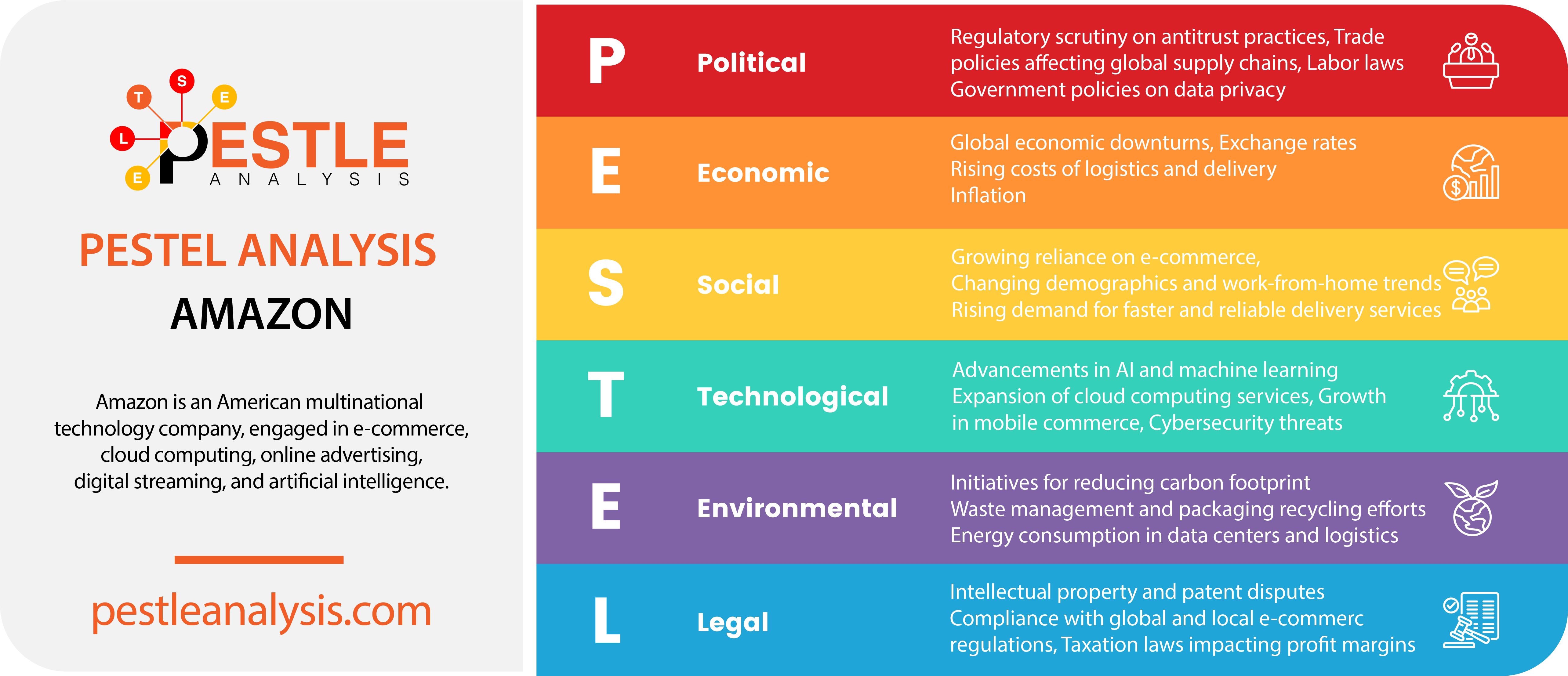
For a global giant like Amazon, a PESTLE analysis is critical to mastering complex international markets, foreseeing challenges, and seizing opportunities—keeping them at the top of a cutthroat game while sharpening their competitive advantage in e-commerce and beyond.
A little-known fact about Amazon's founder: Jeff Bezos initially considered naming Amazon "Cadabra," inspired by "abracadabra," but switched to "Amazon" after his lawyer misheard it as "cadaver". A quirky twist that shaped the name of the world’s largest online retailer.
In this Amazon PESTEL analysis, I’m delivering the latest external factors affecting Amazon, breaking down how one of the world’s biggest companies responds to these forces. I’m providing fresh, up-to-date insights into what’s shaping Amazon’s strategies right now!
Amazon's Political Factors

These are like the government's way of saying, "Let's see how we can complicate your business plans today." 😏
Want to dive deeper? Check out my list of all the political factors that can impact a business.
- Regulatory scrutiny on antitrust and monopolistic practices: Alright, so imagine you're playing a game with your friends, and one person keeps winning every single time. After a while, it seems like no one else can win because this one player is just too powerful. That’s kind of what antitrust and monopolistic practices are about, but in the business world. Regulatory scrutiny means that the government, especially from Washington, where U.S. policymakers call the shots, is keeping a close eye on companies to make sure they’re playing fair and not cheating or becoming too powerful. When a company is monopolistic, it means they have so much control over the market that no other companies can compete. This can be bad for customers because it can lead to higher prices and fewer choices.
- Example: In 2019, the European Union (EU) started an antitrust investigation into Amazon. The EU was concerned that Amazon was using data from independent sellers on its platform to figure out which products were selling well. Then, Amazon would start selling those popular products themselves, often at a lower price, which made it really hard for those smaller sellers to compete. The EU's investigation aimed to make sure Amazon wasn't using its power to unfairly push out smaller businesses, ensuring everyone has a fair shot in the market.
- Trade policies affecting global supply chains: Imagine you're trying to get all the ingredients to make your favorite pizza, but each ingredient comes from a different country. If the rules about trading between these countries change, it can make getting those ingredients a lot harder or more expensive. That's what trade policies affecting global supply chains are all about. Trade policies are the rules and agreements set by governments about how goods and services can be traded between countries. These policies can impact how easy or hard it is for companies to get the materials they need from around the world, which can affect prices and availability of products for consumers.
- Example: Starting around 2018, the US imposed tariffs (which are like extra taxes) on a lot of goods coming from China. In response, China did the same thing to US goods. For companies like Amazon that sell a lot of products made in China, these tariffs meant higher costs. If Amazon wanted to import electronics, toys, or clothes from China, they had to pay more because of these tariffs. This affected their global supply chain by making it more expensive and sometimes slower to get products from China to the US.
- Example: On March 25, 2025, India scrapped its 6% digital ad tax, effective April 1, after U.S. threats of tariffs from April 2, per Reuters. This eases costs for Amazon’s advertising services in India, reflecting how trade diplomacy shapes its global strategy.
- Labor laws and unionization efforts: Say you have a part-time job. In that job, there are rules about how many hours you can work, how much you should get paid, and what safety measures your employer needs to take. These rules are labor laws, and they protect workers' rights. Unionization efforts are when workers come together to form a group, called a union, to negotiate better working conditions and pay. Labor laws set the standards for working conditions, wages, and workers' rights, while unionization efforts are about employees banding together to have a stronger voice in negotiating these conditions. Both of these can have a big impact on companies, especially large ones like Amazon.
- Example: In 2021, there was a significant push for Amazon warehouse workers in Bessemer, Alabama, to form a union. The workers wanted to address issues like long working hours, high-performance quotas, and better wages. Amazon, on the other hand, was not in favor of this unionization effort. They argued that they already provided good pay and benefits. The company even launched a campaign to persuade workers to vote against forming a union. Despite the initial vote against unionization, the effort highlighted ongoing concerns about working conditions and labor rights at Amazon.
- Government policies on data privacy and security: Think about all the personal information you share online, like your address, phone number, and even your shopping habits. Government policies on data privacy and security are the rules that protect this information, making sure companies handle it responsibly and keep it safe from hackers. These policies are crucial because they help prevent misuse of personal data and protect people’s privacy. Data privacy policies set guidelines for how companies can collect, store, and use personal information, while data security policies focus on protecting that data from breaches and cyberattacks. For a company like Amazon, which deals with tons of customer data, these policies are incredibly important.
- Example: The European Union implemented the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in 2018. GDPR set strict rules on how companies, including Amazon, could handle the personal data of EU citizens. It required companies to be more transparent about data collection, give users more control over their data, and ensure strong protection measures against data breaches. For Amazon, complying with GDPR meant making significant changes to their data handling practices. They had to update their privacy policies, implement new systems to manage data requests from users, and ensure that their security measures were robust enough to protect user data. And on March 19, 2025, Amazon lost its appeal against a €746 million ($812.4 million) GDPR fine from Luxembourg’s CNPD for data breaches, upheld by a court on March 18 (Reuters). I see this forcing more fixes and costing Amazon big, with its stock at $203.26 against a $2.15 trillion market cap, showing it can take the hit but not without pain.
Amazon's Economic Factors

Economic factors are the financial roller coasters that businesses ride, from booms to busts and everything in between.
Ready for the ride? Check out my complete list of economic factors that can impact a business.
- Global economic downturns impacting consumer spending: Imagine if your parents had less money to spend because of a tough economy; they might cut back on non-essential items like fancy gadgets or extra toys. Global economic downturns are like that on a bigger scale, where people all over the world have less money to spend, impacting businesses. Economic downturns refer to periods when the economy slows down, leading to reduced consumer spending. For a company like Amazon, this means fewer people buying products, which can lead to lower sales and profits.
- Example: During the COVID-19 pandemic, many people lost jobs or saw incomes drop, leading to less spending on non-essentials. While Amazon saw an initial surge in sales for basics, the broader economic uncertainty rattled consumer spending habits across the retail industry, nudging folks toward caution and hitting Amazon’s market for non-essential goods.
- Fluctuations in currency exchange rates affecting international sales: Let's say the value of your country’s money keeps changing compared to other countries' money, making it more expensive or cheaper to buy things from abroad. Fluctuations in exchange rates are about that, and they can impact how businesses trade internationally. Exchange rate fluctuations refer to changes in the value of one currency compared to another, which can affect the cost of importing and exporting goods. For Amazon, these fluctuations can influence the price of products they sell globally and their overall profitability.
- Example: When the UK voted to leave the European Union, the so-called Brexit, it caused significant fluctuations in the British pound’s value. For Amazon, this meant that the cost of importing products into the UK or exporting from the UK became unpredictable. If the pound's value dropped, it made imported goods more expensive, impacting pricing and sales in the UK market.
- Rising costs of logistics and delivery: Imagine if it suddenly cost more for you to get your favorite snack delivered to your house because fuel prices went up or delivery services became more expensive. That’s similar to what businesses face with rising logistics and delivery costs. Logistics and delivery costs include expenses related to transporting goods from suppliers to warehouses and then to customers. For Amazon, higher logistics costs can impact their overall expenses and the final price of products for consumers.
- Example: Throughout 2021, global oil prices saw a significant rise. For instance, the price of Brent crude oil, a major benchmark, increased from around $50 per barrel in January 2021 to over $80 per barrel by October 2021. This surge in fuel prices had a direct impact on shipping costs. For Amazon, this meant spending significantly more on transportation. To put it in perspective, if Amazon spent around $21.7 billion on shipping in the fourth quarter of 2020, a 10% increase in fuel prices could potentially add hundreds of millions of dollars to their shipping costs annually. This increase could lead to higher prices for customers or reduced profit margins for Amazon.
- Unemployment Rates: Higher unemployment rates in 2025, particularly in major markets, mean fewer people with steady income to shop online, though I notice Amazon might benefit from a bigger pool of job seekers for its warehouses—assuming they can dodge union pressure.
- Inflation affecting operational and product costs: Let's assume the price of everything you buy gradually went up, like your favorite snack or school supplies. That’s inflation, and it affects not just consumers but also businesses. Inflation refers to the general increase in prices over time, which can raise the costs of goods and services. For Amazon, inflation can mean higher costs for products they sell and higher operational costs, such as wages and rent.
- Example: As economies started to recover from the COVID-19 pandemic, the demand for goods increased faster than the supply, leading to higher prices. For Amazon, this meant paying more for inventory, shipping, and even wages for their employees. Higher costs could lead to higher prices for customers or reduced profit margins.
- Interest Rates: Rising interest rates, especially in key markets like the US, are hiking borrowing costs for Amazon’s massive expansion projects—like new warehouses or tech investments—while also making customers think twice about big purchases on credit.
Amazon's Social Factors

These are like the trends and habits of people that can make or break a business—think of it as the market's mood swings!
Curious to know more? Check out my full list of social factors that can impact a business.
- Increasing consumer preferences for sustainable and ethical products: Imagine if everyone in your school started caring a lot more about buying products that are good for the environment and made ethically. This shift in thinking is what businesses are seeing with consumers today. Consumer preference for sustainable and ethical products means that more people want to buy items that don’t harm the environment and are made in fair working conditions. For Amazon, this trend means they need to offer more eco-friendly and ethically produced products to meet customer demands.
- Example: In September 2019, Amazon co-founded The Climate Pledge, committing to reach net-zero carbon by 2040, a decade ahead of the Paris Agreement. They also ordered 100,000 electric delivery vehicles from Rivian to reduce their carbon footprint. This commitment shows how Amazon is adapting to the growing consumer demand for sustainability.
- Growing reliance on e-commerce due to lifestyle changes: Imagine if instead of going to the mall, you and your friends did all your shopping online because your busy lifestyles—school, sports, or just chilling—made it way more convenient. This trend is becoming the norm as more people rely on e-commerce for their daily needs, shaped by lifestyles that prioritize speed, variety, and ease. For Amazon, this shift is a win, but it also means they’ve got to keep leveling up their online shopping experience and delivery game.
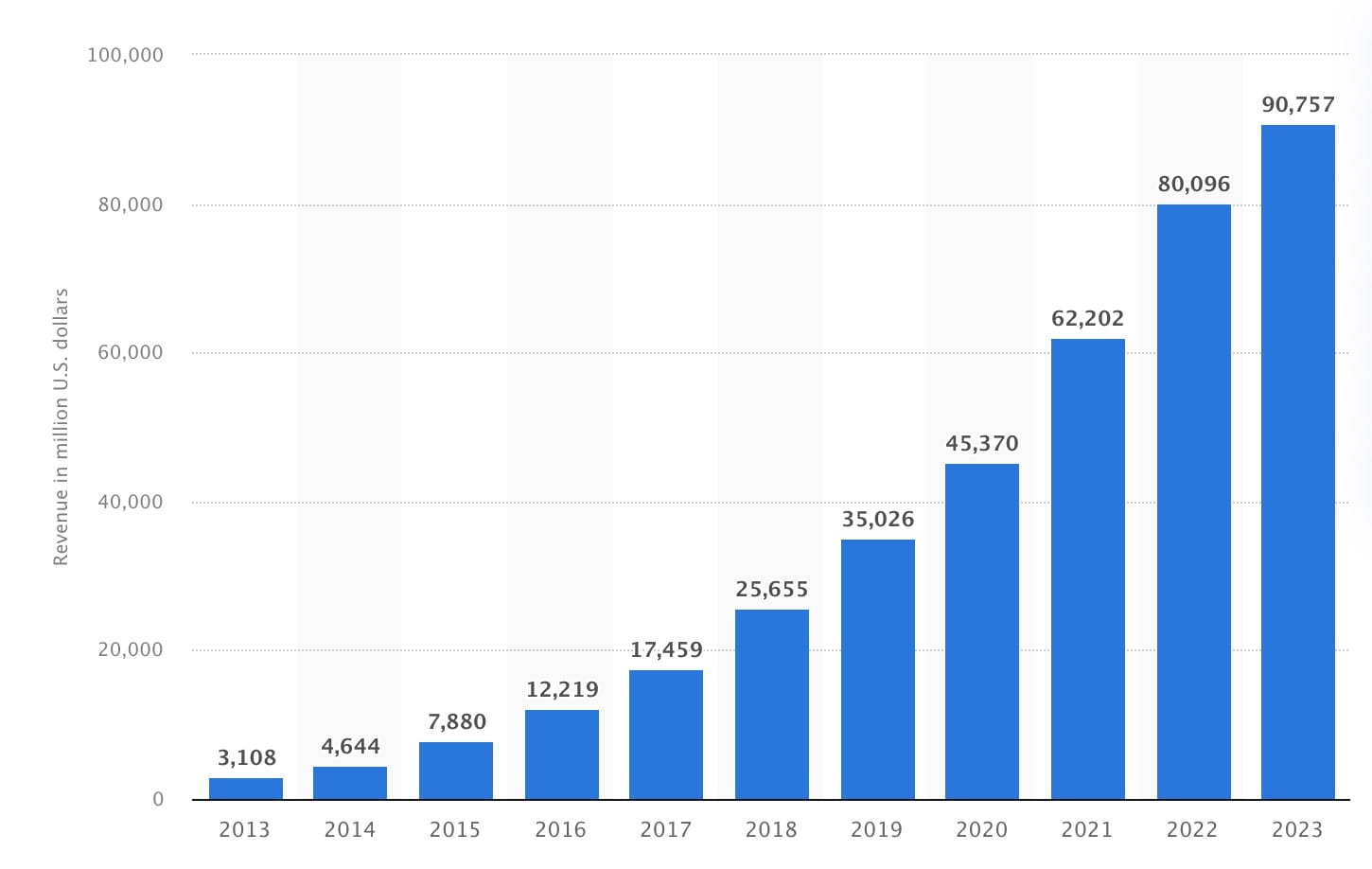
- Example: In 2020, global e-commerce sales grew by over 25%, with Amazon seeing a massive increase in demand. Amazon’s net sales jumped from $280.5 billion in 2019 to $386.1 billion in 2020. This surge showed just how much e-commerce has become a core part of people’s lifestyles.
- Changing workforce demographics and work-from-home trends: Imagine if most parents started working from home and companies had to adapt to this new way of working. That’s what’s happening with changing workforce demographics and work-from-home trends. Changing workforce demographics and work-from-home trends mean that more people are working remotely and the workforce is becoming more diverse. For Amazon, this trend impacts their corporate policies, employee benefits, and even product offerings.
- Example: In early 2021, Amazon announced that corporate employees could work from home until at least mid-2021, later extending it to January 2022. This change required Amazon to invest in new technologies and support systems to maintain productivity and employee satisfaction.
- Rising demand for faster and more reliable delivery services: Imagine if everyone started expecting their online orders to arrive the next day, no exceptions. This growing expectation is what businesses face today. Rising demand for faster and more reliable delivery services means that consumers want their products delivered quickly and without issues. For Amazon, this trend requires continuous investment in their logistics and delivery network.
- Example: A real-life example is Amazon Prime’s expansion of one-day delivery services. In 2019, Amazon announced a $800 million investment to make one-day shipping the standard for Prime members in the US. By mid-2020, Amazon had expanded one-day delivery to over 10 million products, responding to the increased demand for faster delivery.
Amazon's Technological Factors

These factors are like the ever-changing gadgets and gizmos that businesses need to keep up with or risk becoming obsolete.
Excited to geek out? Check out my list of technological factors that can impact a business.
- Technological Advancements in AI and machine learning for operations and customer service: Imagine having a smart assistant that helps with homework, predicts what you need, and answers questions instantly. That’s how businesses harness technological advancements like Artificial Intelligence and machine learning—building systems that learn from data, automate tasks, and deliver sharp insights. For Amazon, these advancements supercharge everything from warehouse efficiency to personalized customer recommendations, keeping them ahead in the tech race.
- Example: Amazon uses AI to analyze consumer behavior and suggest products they might like. In 2013, these recommendations were responsible for approximately 35% of Amazon’s total sales. This AI system learns from each user's preferences to provide personalized shopping experiences, making it easier for customers to find what they need.
- Expansion of cloud computing services: Imagine having access to a super powerful computer you can use anytime from your own laptop. That’s what cloud computing offers businesses, and in this PESTEL analysis of Amazon, it’s a standout technological factor. Expanding cloud computing services through Amazon Web Services (AWS) means delivering scalable, powerful resources over the internet, boosting Amazon’s revenue and reach.
- Example: In 2021, AWS generated $90 billion in revenue, accounting for about 16% of Amazon’s total revenue. AWS provides cloud services to millions of customers, including startups, large enterprises, and government agencies, enabling them to run applications and store data efficiently.
- Growth in mobile commerce and related technologies: Imagine being able to do all your shopping, banking, and even schoolwork right from your smartphone. That's the essence of mobile commerce. Growth in mobile commerce and related technologies refers to the increasing use of smartphones and tablets for shopping and other online activities. For Amazon, this trend means optimizing their mobile platform to ensure a seamless shopping experience.
- Example: In 2013, Amazon reported that over 50% of their customers shopped using mobile devices. To cater to this growing trend, Amazon continuously updates its app with new features like voice search, one-click ordering, and augmented reality to help customers visualize products in their homes.
- Cybersecurity threats and the need for robust protection measures: Imagine if someone tried to hack into your personal computer and steal your photos and messages. Businesses face similar but much larger threats, known as cybersecurity threats. Cybersecurity threats involve the risk of data breaches, hacking, and other cyber attacks that can compromise sensitive information. For Amazon, protecting customer data and their systems is critical.
- Example: Announced in 2022 and made generally available in 2023, Amazon Security Lake is a centralized data lake designed specifically for handling all security-related data. It collects information from AWS environments, other SaaS providers, on-premises environments, and cloud sources, conforming to the OCSF open standard. At its launch, Amazon Security Lake integrated data from over 80 sources, including major security partners and analytics providers like CrowdStrike and Datadog. This system allows businesses to pool their security data in one place, making it easier to identify, assess, and respond to threats across their entire IT infrastructure. Amazon Security Lake enhances the visibility and response capabilities of security teams, further protecting critical business data and applications from cyber threats.
Amazon's Legal Factors

Legal factors are the fine print rules and regulations that keep businesses on their toes—think of them as the law's love letters to companies.
Curious about the legal lingo? Check out my list of legal factors that can impact a business.
- Intellectual property and patent disputes: Imagine if you invented a cool new gadget, and someone else copied your idea and started selling it as their own. Intellectual property (IP) laws are there to protect your inventions, but sometimes companies end up in disputes over these rights. Intellectual property and patent disputes involve conflicts over the ownership and use of inventions, designs, and other creations. For Amazon, these disputes can be significant, affecting their ability to innovate and compete.
- Example: One notable case was in 2019, when Amazon was sued by Vocalife LLC, a company that claimed Amazon’s Echo devices infringed on their patented microphone technology. The court battles and potential settlements in such disputes can be costly and time-consuming for Amazon.
- Global and local e-commerce regulations: Imagine if you had to follow different rules for how you could sell your homemade crafts in different states or countries. That’s what companies like Amazon face with e-commerce regulations. Compliance with global and local e-commerce regulations means that Amazon has to follow various laws and standards in every country where they operate. These regulations can affect everything from how they handle customer data to how they advertise products.
- Example: In 2020, the Indian government introduced several rules to regulate e-commerce activities, which impacted how companies like Amazon operate in the country.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Policy: Amazon had to adjust its business model to comply with India's FDI rules, which restrict how foreign-owned e-commerce platforms can sell goods. These rules prohibit platforms from having inventory of their own and selling it directly to consumers. Instead, they can only act as marketplaces for third-party sellers.
- Data Localization Requirements: India mandated that all e-commerce companies store critical data within the country. Amazon had to ensure that the personal data of Indian users is stored on local servers.
- Product Listing and Exclusivity: The regulations also prohibited exclusive deals and required that marketplaces provide a level playing field to all sellers. This meant Amazon had to ensure fair access to all sellers without preferential treatment.
- Taxation laws impacting profit margins: Imagine if your allowance or earnings from a part-time job were taxed differently depending on where you lived. For global companies, taxation laws can significantly impact their profits. Taxation laws determine how much companies like Amazon must pay in taxes in different regions. These laws can affect their overall profitability and financial strategies.
- Example: In 2017, the European Commission ordered Amazon to pay €250 million in back taxes to Luxembourg, claiming that Amazon received unfair tax advantages. Such rulings can have a significant impact on Amazon’s profit margins and financial planning, despite this specific tax dispute was ruled in favor of the Amazon company in 2023.
Amazon's Environmental Factors

Environmental factors are Mother Nature's way of reminding businesses that they need to play nice with the planet.
Want to go green? Check out my list of all the environmental factors that can impact a business.
- Initiatives for reducing carbon footprint and sustainable practices: Imagine if everyone in your neighborhood decided to reduce their carbon footprint by using less electricity and recycling more. Companies are doing the same on a larger scale to help the environment. Reducing carbon footprint and adopting sustainable practices involve efforts to minimize environmental impact through various green initiatives. For Amazon, this means implementing strategies to decrease carbon emissions and promote sustainability across their operations.
- Example: On March 20, 2025, Amazon started selling carbon credits to suppliers and firms with net-zero goals, leveraging projects like forest restoration (Reuters). I see this reinforcing its 2040 net-zero pledge, though it’s limited to residual emissions per SBTi, balancing profit with pressure to cut emissions directly.
- Climate Change: Amazon faces growing pressure from climate change, with rising global temperatures and extreme weather events disrupting its supply chain—like delayed shipments from floods or wildfires. I see the company countering this through its Climate Pledge, aiming for net-zero carbon by 2040, but its massive logistics network still churns out emissions that are tough to offset.
- Example: Irrigation projects in the Amazon basin: Peru’s $7 billion Trasvase Maranon project, part of a $24 billion plan announced March 24, 2025 (Reuters), will divert water from the Maranon River, risking Amazon basin ecosystems. I think this could clash with Amazon’s net-zero pledge, pushing it to prove sustainable sourcing.
- Waste management and packaging recycling efforts: Imagine if your family started separating all their trash into recycling bins to reduce waste. Businesses do this on a much larger scale to help the environment. Waste management and packaging recycling efforts involve strategies to reduce waste and promote recycling. For Amazon, this means finding ways to use less packaging and recycle more materials.
- Example: By 2021, Amazon had reduced the weight of its packaging by 36% and eliminated over 1 million tons of packaging materials since 2008 through its Frustration-Free Packaging program. This program encourages suppliers to create packaging that is easier to open, 100% recyclable, and designed to ship products in their original packaging without additional boxes.
- Energy consumption in data centers and logistics: Imagine if your school decided to use solar panels to power all its computers and lights to save energy. Companies do similar things on a much larger scale to be more eco-friendly. Energy consumption in data centers and logistics refers to the amount of energy used in running data centers and transporting goods. For Amazon, reducing this energy consumption is crucial for sustainability.
- Example: By 2021, Amazon had become the largest corporate purchaser of renewable energy in the world, with 274 renewable energy projects generating over 12,000 MW of electricity. These projects help power Amazon’s data centers and operations with green energy, reducing their reliance on fossil fuels and cutting down on carbon emissions.
- Environmental regulations and compliance requirements: Imagine if there were strict rules at your school about how to handle waste and use resources efficiently. Companies have to follow similar rules on a much larger scale to protect the environment. Environmental regulations and compliance requirements are laws and guidelines that businesses must follow to minimize their environmental impact. For Amazon, this means adhering to various international and local environmental standards.
- Example: Amazon has committed to meeting the goals set by the Paris Agreement by aiming to reach net-zero carbon emissions by 2040. They have also pledged to report their carbon footprint annually and take active steps to reduce it. Compliance with such international agreements requires Amazon to continually adapt and improve their sustainability practices.
PESTLE Analysis of Amazon: Template
Now that you've got a good handle on how political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors affect Amazon, it's time to dig even deeper!
To keep your research rolling, try looking up more PESTLE analysis examples - this will give you different perspectives and ideas.
Also, check out similar analyses of Amazon's competitors like Walmart, Google, and Alibaba. Seeing how these companies tackle the same challenges can give you a broader understanding of the business world.
Remember, the more you learn, the better you'll get at spotting the key factors that shape big companies' strategies!






