The highlight of every kid’s day – taking a trip to McDonald’s.
You remember sitting in the back seat, bouncing around, waiting to see those familiar Golden Arches come into view. You couldn’t wait for your Happy Meal because it truly was the source of your joy.
And then, once the nuggets were clamoring in your stomach, you’d immediately rip into the toy, hoping it wasn’t that dumb one all your friends had.
McDonald’s is still a magical place for children. But adults? Not so much.
The growing desire to be and eat healthy doesn’t mix well with McDonald’s offerings. This fast food joint, located all over the world, is as well known as it is ostracized.
But why is that? I’ve examined essential political, economic, socio-cultural, technological, legal and environmental factors that affect the current and future success of McDonald’s. Let’s dive into this McDonald’s PESTLE analysis.
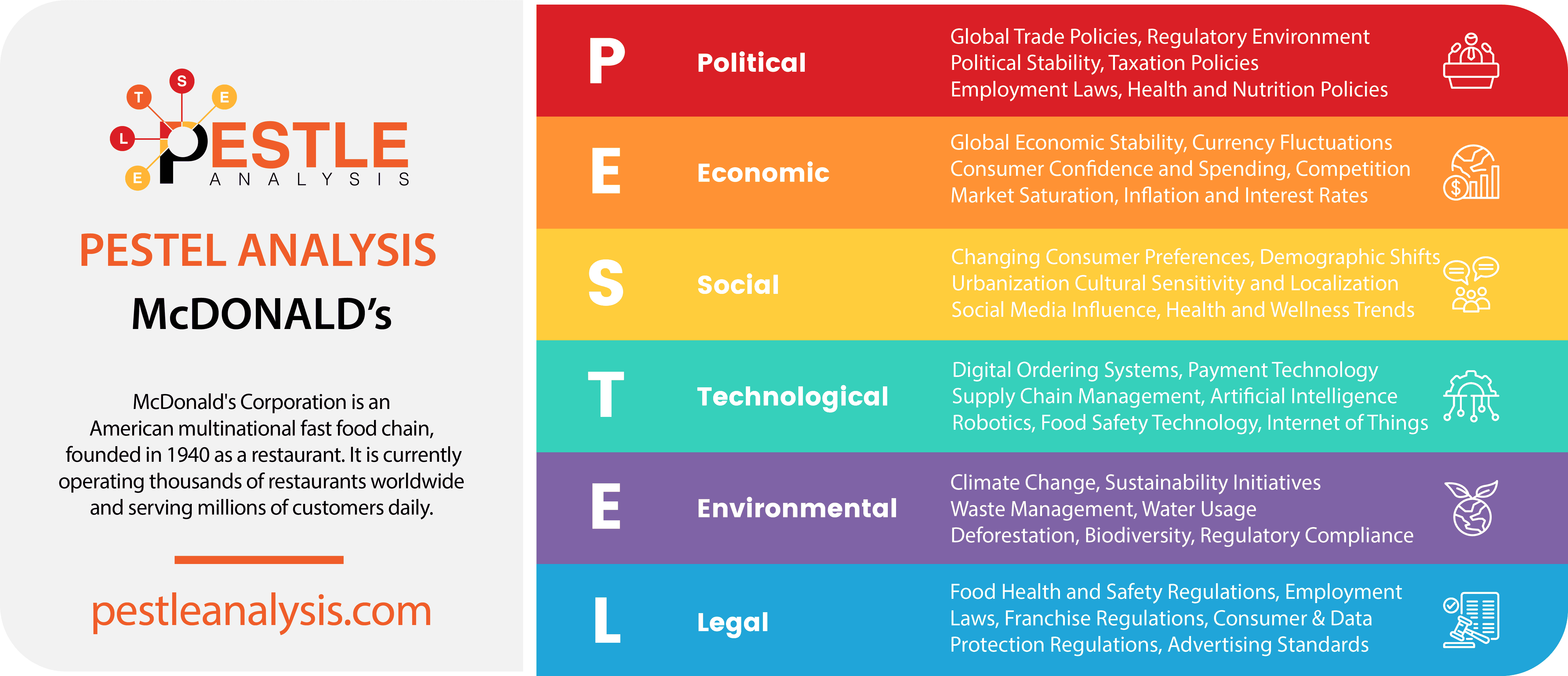
McDonald's Political Factors

Conducting a McDonald's PESTLE analysis, especially focusing on the political factors, involves looking at how political environments, policies, and governmental regulations impact its operations globally. Here are eight political factors that could influence McDonald's:
- Global Trade Policies: McDonald's operation in over 100 countries means it is highly sensitive to changes in global trade policies. Tariffs, trade barriers, and Brexit-like agreements or changes can significantly impact its supply chain costs and pricing. McDonald’s is also affected by the government tensions between countries. Even though they have restaurants located all over the world, McDonald’s is an American company. Complications amongst governmental parties could shift current trade agreements, creating a hostile environment for McDonald’s to function overseas.
- Regulatory Environment: The fast-food industry faces stringent regulations concerning food safety, public health, and operational licensing. Changes in these regulations can affect McDonald's operational efficiency and costs.
- Taxation Policies: Variations in corporate tax rates, as seen with recent U.S. tax reforms, impact McDonald’s profitability. Different countries’ tax strategies can influence where McDonald's invests and expands.
- Employment Laws: Employment regulations, including minimum wage laws, affect how McDonald's manages its labor force. For instance, rising minimum wages may increase operational costs and affect pricing strategies.
- Political Stability: McDonald’s requires stable political environments for predictable business operations. Political instability, like unrest or government upheaval in any country, could disrupt its operations and profitability. Examples include:
- Example: CEO Chris Kempczinski said in January 2024 that several markets in the Middle East were experiencing a "meaningful business impact" due to the Israel-Hamas conflict and "associated misinformation" about the brand. Eventually, in April McDonald's had to buy back 225 franchised outlets in Israel following boycotts.
- Health and Nutrition Policies: Governments are increasingly focusing on health and nutrition, influencing menu regulations and requirements for calorie and nutritional information disclosure. This affects product offerings and marketing strategies. Fast food shops are feeling governmental pressure because of the high amounts of sodium and sugar pumped into their menu. Sugar and sodium are linked to many common health diseases like type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease. Consuming too much of these foods can lead to obesity, stroke, and heart attack. As a countermeasure, McDonald’s is now offering new “healthy” addition to pre-existing food choices. For instance, you can now add additional protein to their fruit smoothies. Adding alternatives is one way to respond to changing public health agreements, but it could also increase their operating costs too.
- Environmental Regulations: Political focus on environmental impact influences regulations around packaging and waste management. This requires McDonald’s to invest in more sustainable practices, impacting its cost structure.
- Public Health Policy Changes Due to Pandemics: The COVID-19 pandemic led to shifts in public health policy, affecting operational modes, with increased emphasis on contactless delivery and hygiene standards. Future health crises could lead to similar impactful changes. McDonald’s must respond to political laws and influences in over a hundred countries. Like any other restaurant, they must comply with health and hygiene regulations. If their food doesn’t abide by a certain code, they would be shut down. Their employees must also adhere to all food and health laws while working in any given location.
These factors show that McDonald's must continuously adapt to a complex web of political influences that can vary significantly by region and over time.
McDonald's Economic Factors

For McDonald's, understanding economic factors is crucial as they influence consumer spending habits and operational costs. Here are several key economic factors to include in our McDonald's PESTLE analysis:
- Global Economic Stability: The overall health of the global economy, including economic growth rates, influences consumer spending power. In times of economic downturn, like the 2008 financial crisis when disposable income was at an all-time low while people scrambled to find new jobs, or during recessions, fast-food chains may see an increase in customers opting for lower-cost dining options, potentially benefiting McDonald's.
- Currency Fluctuations: Since McDonald's operates in multiple countries, it is exposed to currency exchange risks. Fluctuations can affect the profitability of overseas operations and impact financial reporting.
- Inflation Rates: High inflation rates can lead to increased operational costs, such as food, labor, and rent. McDonald's may need to adjust its pricing strategies to maintain margins without deterring cost-sensitive customers. Examples include:
- 2024: Some lower-income Americans are rejecting McDonald’s and opting to cook at home instead, the fast food chain’s chief financial officer said at an investor conference in March, as inflation is pushing Americans to cut back on small luxuries, such as dining out.
- Interest Rates: Changes in interest rates can influence McDonald's cost of capital. Lower interest rates make financing expansion or new initiatives more affordable, whereas higher rates could limit growth opportunities due to higher borrowing costs.
- Consumer Confidence and Spending: Consumer confidence levels directly affect spending behaviors. High confidence boosts discretionary spending on dining out, benefiting McDonald's. Conversely, low confidence can reduce restaurant visits. Examples include:
- Example: Reuters reported in March 2024 that global businesses such as McDonald's are also wrestling with weak demand in China as employment issues, a deepening property crisis and economic uncertainties put a damper on consumer sentiment.
- Unemployment Rates: Higher unemployment generally leads to reduced consumer spending on eating out as people tighten their budgets. McDonald's, with its value-oriented offerings, might withstand the impact better than more upscale dining options. The company is known for its high turnover rate, meaning it hires and loses workers on a consistent basis. It’s a known joke that McDonald’s is “always hiring,” but this can be a glimmer of hope for locations with high unemployment rates.
- Fuel Prices: Changes in fuel prices can impact McDonald's in two ways. First, higher fuel prices reduce disposable income, potentially cutting into fast food spending. Second, they can increase operational costs related to supply chain logistics.
- Real Estate Markets: The cost and availability of suitable real estate affect McDonald’s ability to expand in desired locations. Real estate market trends can dictate where and how quickly McDonald’s can open new outlets.
By monitoring and adapting to these economic factors, McDonald's can better strategize its global and local operations, pricing, and expansion plans to remain competitive and profitable.
McDonald's Social Factors

Social factors play a critical role in shaping McDonald's business strategies, as they directly influence consumer preferences and behaviors. Here are key social factors that McDonald's needs to consider:
- Changing Consumer Preferences: There is a growing trend towards healthier eating and an increasing demand for quality food options. McDonald's has responded by introducing more salads, fruit, and low-calorie options to cater to this shift. Consumers obsessively scrutinize what they’re putting into their bodies. We’re seeing a rise in low-carb and low-sugar diets. People are jumping on the intermediate fasting bandwagon. Why? Because they’re seeking ways to strengthen their bodies without sacrificing health. Unfortunately, McDonald’s menu doesn’t comply with these demands, making them as a less desirable option for health-conscious adults. McDonald’s is trying, though. You can swap out high-sugar ingredients in their drinks for a low-calorie alternative, and they’ve recently come out with high-protein smoothies. However, consumers are still complaining about the high sugar content in these drinks.
- Demographic Shifts: Changes in demographics, such as aging populations in developed countries or younger demographics in emerging markets, affect product offerings and marketing strategies. For example, targeting millennials and Gen Z with technology-driven service options like mobile ordering and delivery.
- Urbanization: Increased urbanization has led to a rise in the number of people eating out frequently. McDonald's capitalizes on this by locating restaurants in urban centers and busy city locations, ensuring they capture the urban workforce and shoppers.
- Cultural Sensitivity and Localization: Overseas, fries and hamburgers don’t cut it. People in Asian countries, for example, are used to eating their local cuisine. Although hamburgers and fries can be nice to have once in a while, it might not be the first choice option for international audiences. While McDonald’s has offered localized menu options in countries like Japan and Canada — an opportunity they should take advantage of more often — it can be a costly endeavor for the company, too. McDonald’s adapts its menu and marketing campaigns to align with local tastes and cultural preferences. This includes special menu items that cater to regional flavors and dietary habits, like vegetarian burgers in India or teriyaki burgers in Japan.
- Social Media Influence: The impact of social media on consumer choices is significant. McDonald's leverages platforms like Twitter, Instagram, and Facebook for marketing, customer engagement, and handling customer service issues.
- Consumer Attitudes Toward Sustainability: Increasing concern about environmental issues has led consumers to favor businesses that practice sustainability. McDonald's has responded by using more environmentally friendly packaging and committing to sourcing ethically produced ingredients. Examples include:
- Example: Food packaging of a McDonald’s filet-o-fish carton in 2023 was found to contain PFAS chemicals in September according to EHN.org.
- Health and Wellness Trends: As public awareness of health issues increases, more consumers are scrutinizing the nutritional content of their food. McDonald's has made efforts to provide clearer nutritional information and offer more balanced choices.
- Workforce Diversity: Social attitudes towards diversity and inclusion affect McDonald's employment policies and practices. McDonald’s promotes diversity in its workforce, recognizing that a diverse team can better serve an equally diverse customer base.
By staying attuned to these social factors, McDonald's can adapt its strategies to meet changing consumer expectations and societal norms, which is crucial for maintaining its market position and brand reputation globally.
McDonald's Technological Factors
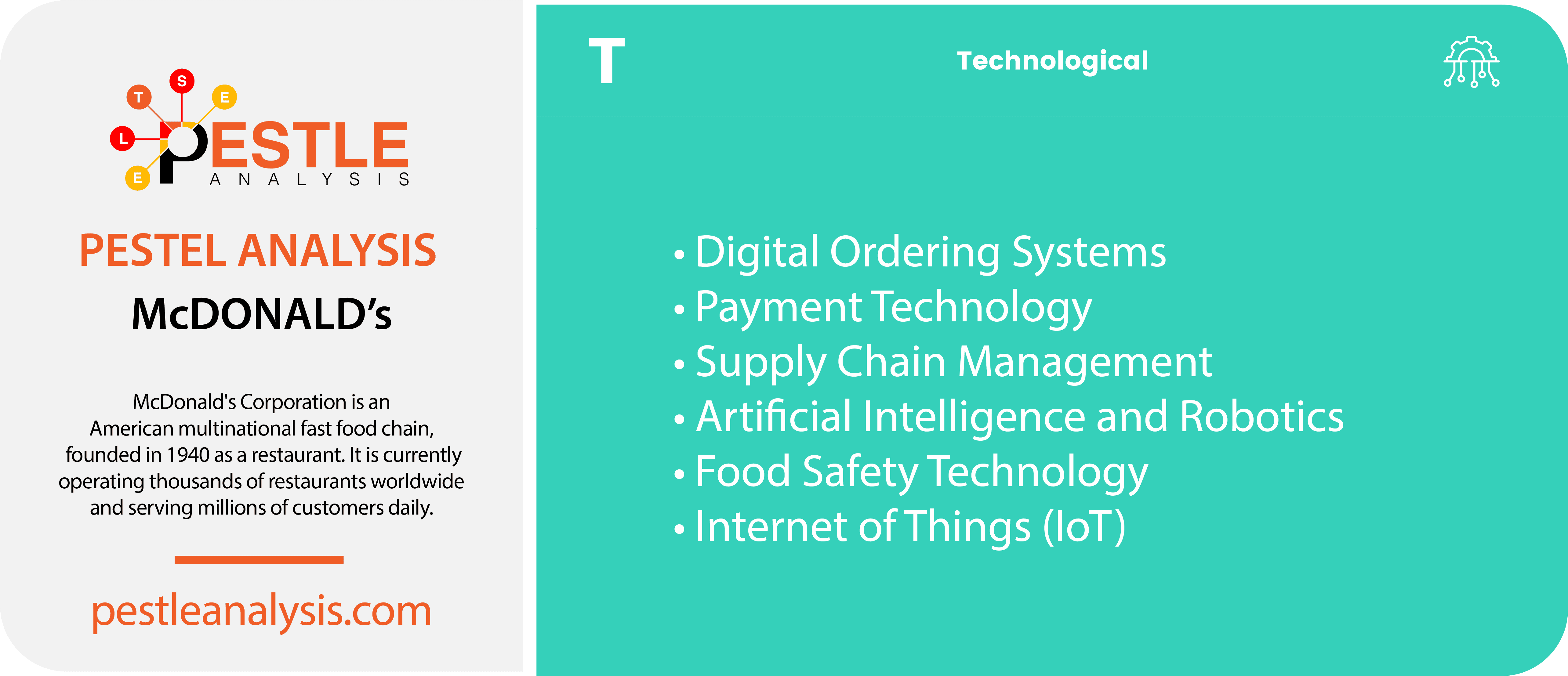
Technological factors are pivotal in shaping McDonald's operational efficiency and customer engagement strategies. Retail giants, like Amazon, designed their business structure for internet use only. Compared to these, it doesn’t seem McDonald’s has a strong need for technology. But that’s not true. The tech they use is necessary to improve staff productivity and communication amongst teams and produce food as quickly as their customers expect. Here are several key technological factors to consider in a McDonald's PESTLE analysis:
- Digital Ordering Systems: The introduction of digital ordering through mobile apps and self-service kiosks has revolutionized how customers interact with McDonald's, reducing order times and improving customer experiences. This technology also allows for data collection that can drive personalized marketing and improve service. McDonald’s has upgraded their menus with flashy television screens hanging from the ceiling behind their cashiers. They also use their website to showcase nutritional information. In some locations, you can order your food online, allowing you to stroll in and grab your meal without waiting in line. Examples include:
- Example: Technology can act both as an ally and a foe. In March, 2024, McDonald’s suffered a system failure that left customers in UK, US, Australia and Japan unable to order food according to CNBC.
- Payment Technology: Adoption of various payment technologies, including contactless and mobile payments, enhances the convenience for customers. This is crucial in maintaining competitiveness, especially in markets where digital payments are becoming the norm.
- Supply Chain Management: Advanced supply chain management systems are essential for McDonald's to ensure efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Technologies that track inventory in real-time, predict demand, and optimize delivery schedules are vital in managing their extensive global supply chain.
- Artificial Intelligence and Robotics: McDonald's has been exploring AI for various uses, such as predictive analytics in sales and customer service (e.g., AI-powered chatbots). Robotics in the kitchen for routine tasks like frying and flipping burgers are also being tested, potentially transforming operations.
- Sustainability Technology: In response to environmental concerns, McDonald's invests in technologies that reduce waste and energy consumption. Examples include energy-efficient appliances, LED lighting, and systems to recycle water and heat.
- Food Safety Technology: Implementing advanced food safety technologies helps McDonald's maintain high standards. This includes everything from temperature tracking sensors in food transport vehicles to AI systems that monitor the cleanliness and safety procedures in kitchens.
- Marketing and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems: Leveraging big data analytics and CRM software, McDonald's can tailor marketing efforts and promotions to individual customer preferences, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty. McDonald’s is also active on social media. They use Facebook and Instagram ads to nab their customers' attention with their new or returning offerings, like their summer hit, the McCafe Vanilla Chai Frappuccino.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices are integrated into McDonald's operations to streamline processes and improve quality control. For instance, IoT can be used in equipment to alert maintenance teams about potential issues before they become critical.
By effectively integrating these technological advancements, McDonald's can not only enhance operational efficiencies and customer service but also drive future growth by staying ahead of industry trends and expectations. Although McDonald’s is incredibly well-known (and needs a little introduction), not capitalizing on social technology will only give their competition, like Wendy’s, known for their witty and hilarious Twitter conversations, an advantage.
McDonald's Legal Factors

Legal factors significantly impact McDonald's operations, affecting everything from how they conduct business to how they manage employee relations and customer interactions. Here are key legal considerations that McDonald's needs to address:
- Food Safety and Health Regulations: McDonald's must comply with strict local and international food safety standards, which regulate everything from food handling to kitchen cleanliness. Compliance is monitored by various health agencies, and failure to adhere can result in fines, closures, or worse, damage to reputation.
- Example: In October 2024, an E. coli outbreak linked to McDonald’s Quarter Pounder hamburgers resulted in one death and dozens of illnesses across 10 U.S. states, primarily Colorado. Following the incident, McDonald’s proactively removed slivered onions and beef patties from stores in affected states and is cooperating with the CDC’s ongoing investigation. This outbreak caused a 6% drop in the company’s shares, underscoring the critical need for strict food safety compliance. Legal actions may follow, similar to past incidents in the fast food industry, reminding McDonald’s and others of the heavy costs of any lapse in safety protocols.
- Employment Laws: These include minimum wage requirements, working conditions, anti-discrimination laws, and benefits entitlement. As a global employer, McDonald's must navigate a complex web of employment legislation in every country it operates in, ensuring fair treatment and legal compliance. Examples include:
- Example: Reuters reported in March, 2024 that McDonald's must face a proposed class action claiming it violated antitrust laws by prohibiting franchisees from poaching employees from other McDonald's restaurants, after the U.S. Supreme Court declined to take up the case.
- Franchise Regulations: Since much of McDonald's global operations are franchised, the company must adhere to specific laws that govern franchising activities. This includes how franchises are awarded, overseen, and how ongoing relationships are managed.
- Consumer Protection Laws: These laws safeguard consumers against unfair practices and ensure that McDonald's markets its products truthfully. Adhering to these laws involves providing accurate information about products, especially in advertising and labeling.
- Environmental Laws: Increasingly stringent environmental laws affect how McDonald's manages its waste, packaging, and overall environmental footprint. Compliance includes everything from reducing packaging waste to handling the disposal of cooking oils and food waste.
- Data Protection and Privacy Laws: With the rise of digital ordering and loyalty programs, McDonald's collects vast amounts of customer data. Laws such as the GDPR in Europe dictate how this data must be handled, stored, and protected against breaches.
- Intellectual Property Laws: Protecting its brand and trademarks is crucial for McDonald’s. This includes the logo, brand name, and proprietary information like recipes and operational techniques. Infringements can lead to legal battles and require constant vigilance.
- Advertising Standards: McDonald's must comply with national and international advertising standards that regulate the accuracy and fairness of the information presented in their marketing materials, especially those targeted at children.
Navigating these legal factors is essential for maintaining McDonald's operational integrity and public trust. Failure to comply can result in legal actions, financial penalties, and a damaged reputation, all of which can significantly impact their bottom line.
McDonald's Environmental Factors

Environmental factors are increasingly important in the operational and strategic decisions of global corporations like McDonald's. Here’s how various environmental factors impact McDonald's:
- Climate Change: Shifts in climate can affect McDonald's supply chain, potentially disrupting the availability of agricultural products like beef, potatoes, and vegetables. Adapting to these changes requires McDonald's to engage in sustainable sourcing practices and possibly diversify their suppliers.
- Sustainability Initiatives: There is growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible business practices. McDonald's has responded by implementing programs to reduce their environmental footprint, such as using renewable energy sources, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and improving energy efficiency in restaurants.
- Waste Management: Fast food generates significant waste, including food and packaging waste. McDonald's has been working on initiatives to reduce waste, increase recycling, and innovate in packaging to make it more sustainable, which is crucial for regulatory compliance and customer approval.
- Water Usage: The conservation of water is critical in many regions where water scarcity is an issue. McDonald's employs water-saving technologies and practices in its restaurants and throughout its supply chain to mitigate its impact on local water resources.
- Deforestation: As a large purchaser of beef, McDonald's is implicated in global supply chains that can contribute to deforestation, particularly in the Amazon. McDonald's commits to sourcing beef from suppliers that do not contribute to deforestation, aligning with global efforts to preserve forests.
- Biodiversity: Operations can impact local wildlife and ecosystems, especially when expanding into new areas. McDonald's must consider ecological impacts, engaging in responsible site selection and construction practices to minimize environmental disruption.
- Regulatory Compliance: Environmental regulations vary by country but generally include emissions, waste management, and resource usage. Compliance is not just about avoiding fines; it's also about aligning with public and governmental expectations to maintain a positive brand image.
- Public Perception and Corporate Responsibility: As environmental concerns become a higher priority for consumers, McDonald's corporate responsibility in this area heavily influences its brand reputation. Transparent and genuine efforts in environmental sustainability can greatly enhance customer loyalty and attract environmentally conscious consumers.
By addressing these environmental factors identified in our PESTLE analysis, McDonald's can not only reduce its operational risks and costs but also enhance its corporate reputation and appeal to a broader base of consumers who are increasingly aware of and concerned about environmental issues.
Recommendations based on the PESTLE Analysis of McDonald's
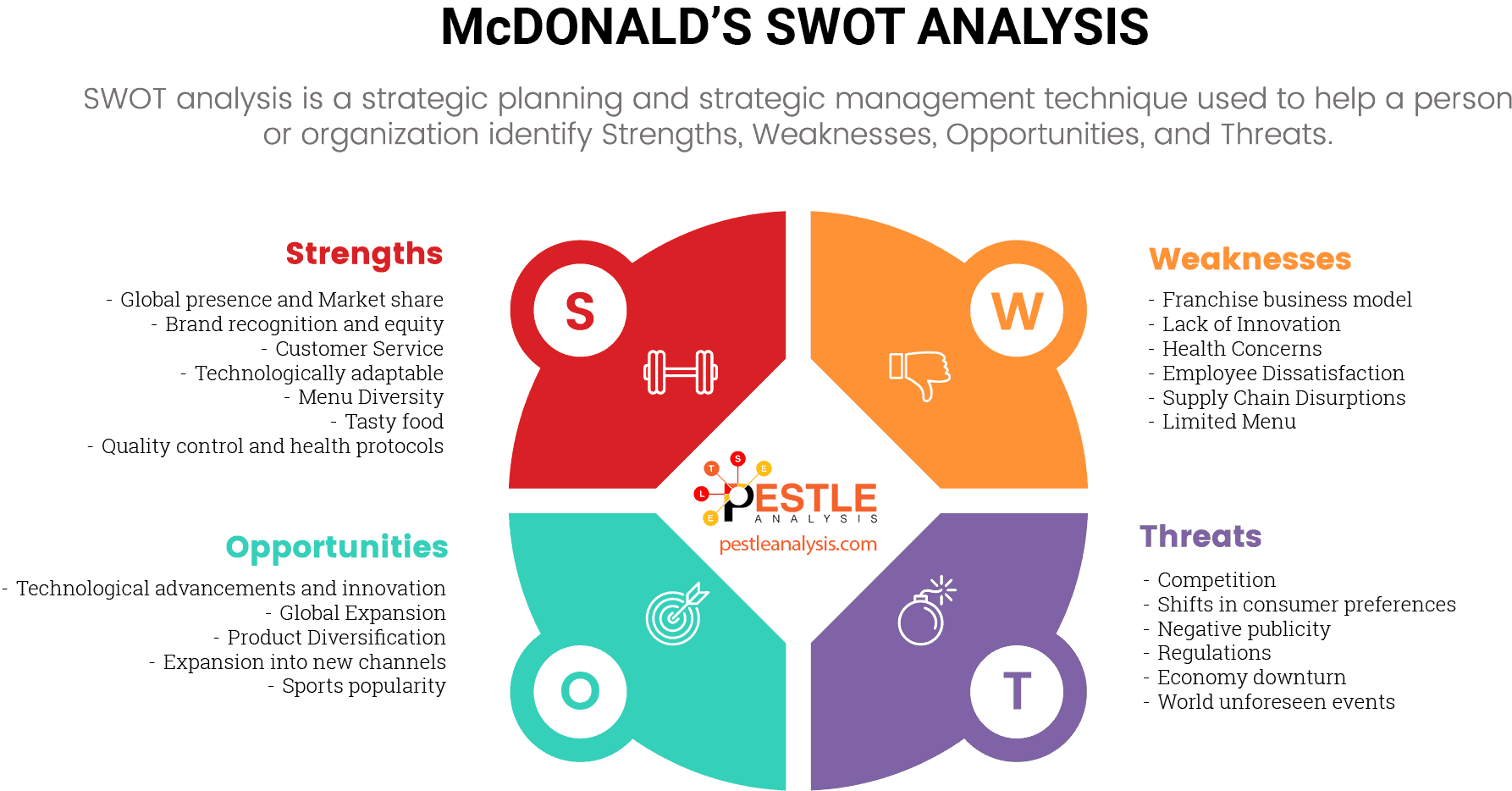
McDonald’s needs to shed its unhealthy image to move forward with the growing food trends. It won’t be easy. But it’s necessary if they want to survive among other fast food companies who are reshaping their menu for their customers.
In conclusion, McDonald's operates within a complex and dynamic environment shaped by a myriad of political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors. Each of these dimensions presents its own set of challenges and opportunities, influencing McDonald's strategic decisions and operational practices globally. Understanding these factors is crucial for maintaining McDonald's competitive edge and ensuring its long-term sustainability and profitability.
For businesses looking to conduct similar analyses or for students studying corporate strategy, comparing McDonald's PESTLE factors with those of its competitors can provide deeper insights. Make sure to check out the following analysis of McDonald's competitors:
- PESTLE analysis of Subway
- PESTLE analysis of KFC
- PESTLE analysis of Starbucks
- SWOT analysis of Chipotle
- SWOT analysis of Burger King
- SWOT analysis of Wendy's
We encourage you to explore our full guide on PESTLE analysis, where we dive deeper into each factor with comprehensive examples from various industries. This guide will not only enhance your understanding of how global corporations like McDonald's strategize and adapt but also equip you with the analytical tools to explore the business environments of other major players.







