The banking industry plays a crucial role globally, deeply intertwined with and often regulated by governmental and economic dynamics. Banks operate under a framework of laws and regulations that significantly influence their operations, growth potential, and service offerings.
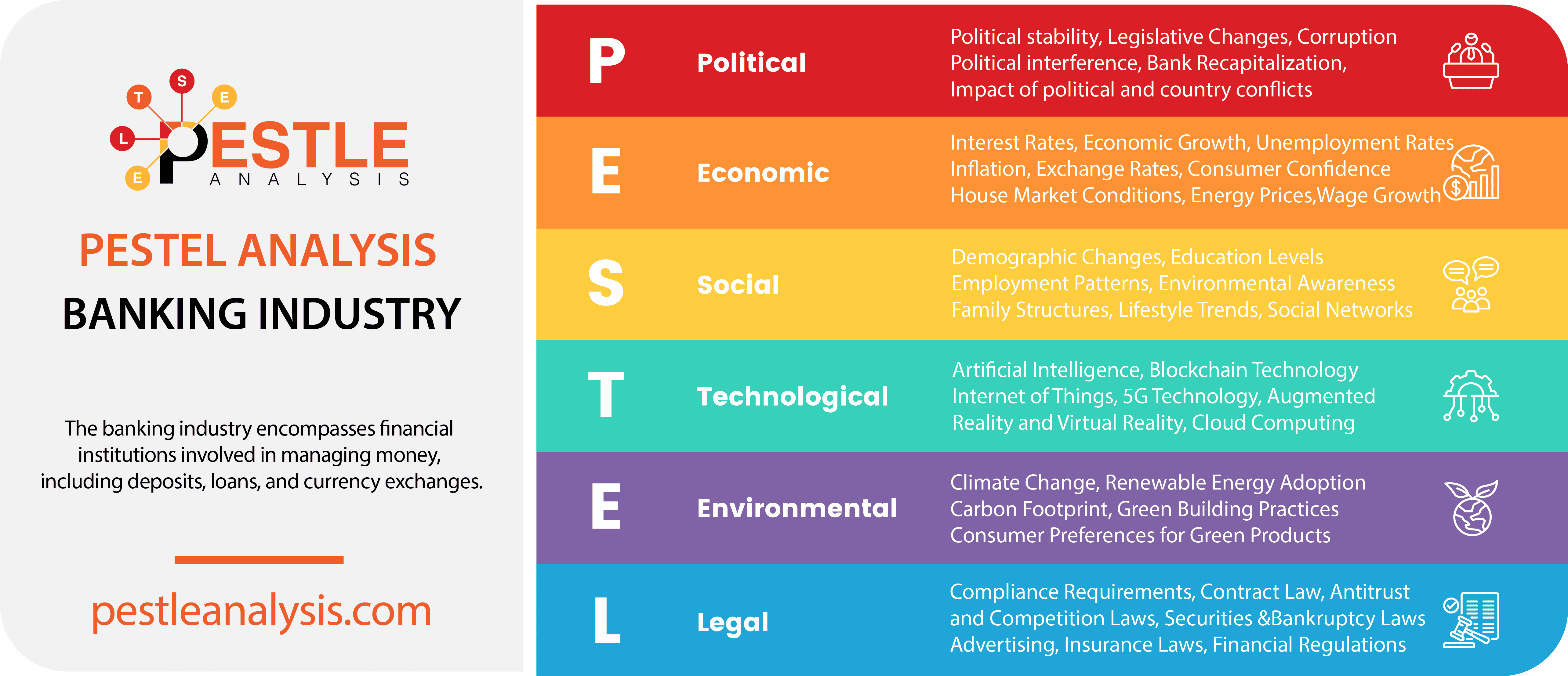
This banking industry's PESTLE analysis highlights key factors affecting the banking sector.
This analytical tool helps organizations assess various macro-environmental factors that could impact their operations, decision-making processes, and overall strategy.
Today we'll use the framework to analyze how these six external factors affect an entire industry.
Banking Industry's Political factors

The banking industry looks all powerful — but it’s susceptible to a bigger giant: the government.
Government laws affect the state of the banking sector. The government can intervene in banking matters whenever it chooses, leaving the industry susceptible to political influence. This includes corruption amongst political parties or specific legislative laws such as labor laws, trade restrictions, tariffs, and political stability.
Let's examine 7 political factors affecting the banking industry in detail:
- Political Stability: The stability of the political environment in a country is crucial for the banking sector. Political turmoil can lead to economic instability, which adversely affects the banks’ operations and profitability
- Legislative Changes: Changes in legislation can significantly impact the banking industry, from altering the competitive landscape to modifying how banks operate and deliver services to their customers.
- Corruption and Political Interference: Corruption and undue political interference in some regions can undermine the efficiency of the banking sector, leading to an unstable banking environment and reducing foreign investment appeal.
- Fiscal Policy: The fiscal decisions made by governments, such as spending and budget allocations, can indirectly impact the banking sector by influencing economic growth and interest rates, which in turn affect loan demand and savings rates.
- Bank Recapitalization: Governments sometimes step in to recapitalize banks to ensure financial stability and restore confidence in the banking system. This can occur during times of financial distress or crisis, where capital injections are needed to support the banks' balance sheets and enable continued lending activities.
- Impact of Political and Country Conflicts: Political and country conflicts can severely affect banks by leading to economic sanctions, operational risks, currency fluctuations, asset freezes, reputational damage, complex compliance issues, and investment uncertainties, ultimately impacting global banking operations and financial stability.
- Political Leadership Change: Changes in political leadership can lead to shifts in regulatory frameworks, economic policies, and market confidence, affecting everything from banking regulations and interest rate policies to foreign investment and exchange rates, thereby significantly influencing banking operations and financial stability.
Check out our complete list of political factors affecting all businesses here.
Banking Industry's Economic factors

The banking industry and the economy are tied. How income flows, whether the economy is prospering or barely surviving during times of recession, affects how much capital banks can access. Spending habits, and the reasons behind them, affect when customers borrow or spend funds at banks.
Additionally, when inflation skyrockets, the bank experiences the backlash. Inflation affects currency and its value and causes instability. Foreign investors think twice before providing their funds when a particular country’s currency value is high.
Exchange rates also affect banks globally — stable currencies such as the US dollar impact other currencies, spending habits, and inflation rates in other countries.
Let's take a closer look at 11 economic factors affecting the banking industry:
- Interest Rates: Fluctuations in interest rates can influence bank profitability as they affect the cost of borrowing and the yield on assets like loans and securities.
- Economic Growth: Strong economic growth boosts business activity, leading to more banking activity as businesses and consumers increase borrowing and saving. Conversely, recessions typically lead to reduced banking activity.
- The 2024 announcement by major U.S. banks to increase their dividends following the Federal Reserve's stress tests indicates a strong economic position and resilience against market volatility. This move reflects the banks' confidence in their financial health and ability to support sustained economic growth through continued lending and capital allocation.
- Unemployment Rates: Higher unemployment rates generally lead to higher loan defaults as more people struggle to meet financial commitments. This affects the credit quality of the bank's loan portfolio.
- Inflation: Inflation impacts the value of money and purchasing power, which can affect the real value of loans and investments. High inflation rates often lead to higher interest rates
- Exchange Rates: Banks with international operations face risks related to fluctuations in exchange rates, which can affect the value of overseas earnings and influence the competitiveness of banking services globally.
- Consumer Confidence: Consumer sentiment and confidence influence spending and saving behaviors. High consumer confidence encourages more spending and borrowing, which benefits banks, while low confidence can lead to higher savings rates, reducing consumer borrowing and spending.
- Housing Market Conditions: Changes in the housing market can significantly affect banking through mortgage lending activity and real estate financing. A robust housing market increases the demand for mortgages and home equity loans, boosting bank revenues. Conversely, a downturn can lead to higher default rates and reduced profitability for banks.
- Energy Prices: High energy prices can increase operational costs for businesses and consumers, potentially leading to reduced spending and increased loan defaults. For banks, this can mean higher credit risk. Additionally, banks that finance energy projects or loans linked to the energy sector might see fluctuations in loan demand based on energy price volatility.
- Wage Growth: Strong wage growth enhances consumer purchasing power, leading to increased spending and borrowing, which is beneficial for banks. It also reduces the risk of loan defaults as more consumers can meet their debt obligations comfortably. However, stagnant or declining wages can dampen consumer spending and increase the risk of defaults.
- Commodity Prices: Fluctuations in commodity prices can impact banks in several ways. Banks involved in financing commodity trading or providing loans to commodity-dependent sectors (like agriculture or mining) can experience changes in loan demand and repayment capabilities based on commodity price volatility.
- Public Debt Levels: High public debt can influence macroeconomic stability and economic growth, affecting bank operations indirectly. High debt levels may lead to higher taxes or reduced public spending, which can dampen economic growth and increase loan defaults. Moreover, if public debt leads to inflation or currency devaluation, it can affect the entire financial sector, including interest rates and the cost of funding for banks.
General economic factors affecting all industries can be found here.
Banking Industry's Social Factors

Cultural influences, such as buying behaviors and necessities, affect how people see and use banking options. People turn to banks for advice and assistance for loans related to business, home, and academics. Consumers seek knowledge from bank tellers regarding saving accounts, bank-related credit cards, investments, and more.
Consumers desire a seamless banking experience. And technology is developing to allow consumers to buy products easier, without requiring assistance directly from banks.
Here are 7 social factors affecting the banking industry in more detail to include in PESTLE analysis:
- Demographic Changes: Shifts in population structure, such as aging populations or increasing youth demographics, can affect banking needs. Older customers might focus more on savings and retirement products, while a younger demographic could increase demand for tech-savvy banking solutions like mobile banking and online services.
- Education Levels: Higher education levels typically correlate with a greater use of banking services, as educated individuals are more likely to engage in complex financial products such as investments, insurance, and loans. Educated populations also tend to have higher incomes, which increases their banking needs and potential for wealth management services.
- Employment Patterns: Changes in employment patterns, such as shifts from full-time employment to gig or freelance work, can influence how individuals use banking services. Banks may need to adjust their products to cater to people with fluctuating incomes or those who need faster access to financial services.
- Environmental Awareness: As public concern for the environment grows, consumers increasingly prefer to do business with eco-friendly companies. Banks can attract these customers by promoting green banking practices, sustainable investments, and supporting eco-friendly projects and businesses.
- Family Structures: Changes in family structures, such as an increase in single-parent households or multi-generational living situations, can alter banking needs. Products like joint accounts, child savings accounts, and estate planning services may see changes in demand based on these trends.
- Lifestyle Trends: Shifts in lifestyle, such as an increased preference for digital nomadism or remote work, necessitate flexible banking solutions that are accessible from anywhere. This includes mobile banking, global transaction services, and digital-first customer service.
- Social Networks: The rise of social media has transformed customer service and marketing strategies in banking. Banks use social networks to engage with customers directly, address their concerns in real-time, and market new products effectively. Additionally, the spread of financial advice and opinions through these networks can influence public perceptions and behaviors related to banking.
Here is our complete list of social factors affecting businesses and industries.
Banking Industry's Technological factors
Once, it was expected to visit the local bank to make changes to financial accounts. But not anymore.
Technology is changing how consumers handle their funds. Many banks offer a mobile app to witness accounts, transfer funds, and pay bills on smartphones.
Smartphones can scan cheques, and the bank can process them from their end, at their location. This change helps to save paper and the need to drive directly to the branch to handle these affairs.
Debit cards are also changing. Chips have been implemented, requiring users to insert their cards into debit machines rather than swiping them. Other countries, such as Canada, have implemented a “tap” option — tapping the debit card onto the device, requiring no PIN, for a transaction to complete. These changes make it easier for the user to make purchases without required intrusion from banks.
Even banks themselves are utilizing technology within the workplace. Telecommunicating through virtual meetings is being embraced. It replaces the need for in-person meetings.
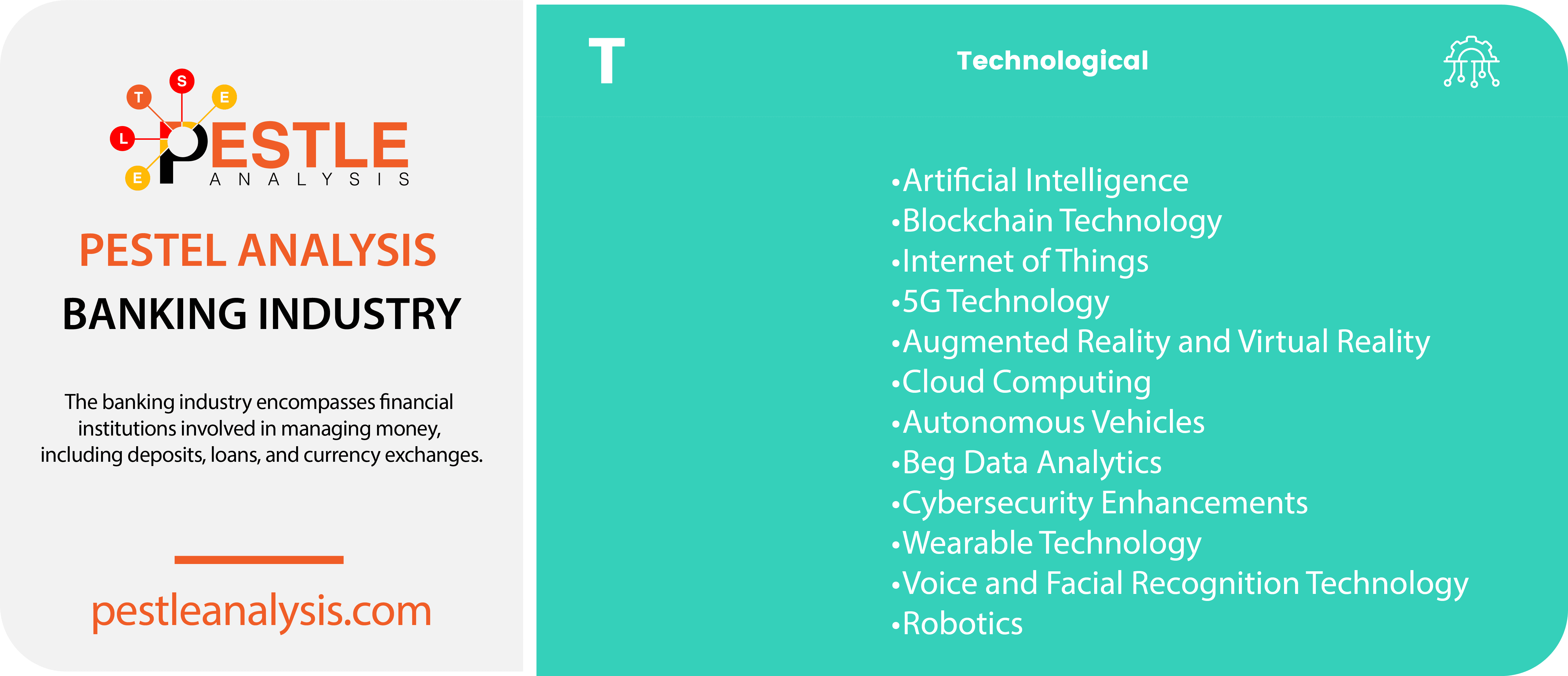
Here's a list of 12 technological factors for our PESTLE analysis affecting the banking industry:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI can revolutionize banking through personalized customer service via chatbots, enhanced fraud detection systems, and more efficient back-office operations. It can also help in credit scoring and risk management by predicting loan defaults more accurately.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain offers banks enhanced security and transparency for transactions. It can reduce fraud, streamline payment processes, and lower operational costs by eliminating intermediaries in processes such as international money transfers.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT technology can help banks improve customer experience and security. For instance, connected devices can enable seamless and secure biometric-based banking transactions and personalized banking services based on customer location and behavior.
- 5G Technology: 5G will enhance the speed and efficiency of mobile banking services, allowing banks to offer more reliable and faster services, including real-time data processing and enhanced mobile banking experiences.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): These technologies can transform customer interactions with banks by offering virtual branches and immersive experiences for exploring complex financial products or services through virtual reality platforms.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud technology enables banks to reduce IT costs, improve scalability, and enhance the flexibility of their operations. It supports the deployment of digital banking solutions that can scale quickly to meet customer demands.
- Autonomous Vehicles: As autonomous vehicle technology advances, banks might explore new financing models and insurance products tailored to autonomous vehicles' unique needs and usage patterns.
- Big Data Analytics: Big data allows banks to gain deeper insights into customer behaviors and preferences, enabling personalized product offerings, improved customer service, and optimized risk management strategies.
- Cybersecurity Enhancements: As cyber threats evolve, banks invest in advanced cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive financial data and maintain customer trust, ensuring compliance with increasingly stringent regulations.
- Wearable Technology: Wearables can integrate banking more seamlessly into customers' daily lives, enabling transactions and financial monitoring directly from smartwatches and other devices.
- Voice and Facial Recognition Technology: These technologies enhance security and user experience in banking by enabling biometric authentications for accessing banking services, thus reducing fraud and simplifying the login processes.
- Robotics: In banking, robotics can streamline operations by automating routine tasks such as data entry and compliance checks, thus reducing costs and improving service speed and accuracy.
Visit our list of technological factors that affect every kind of industry.
Banking Industry's Legal Factors

The banking industry follows strict laws regarding privacy, consumer laws, and trade structures to confirm frameworks within the industry. Such structures are required for customers in the allocated country and for international users.
Let's see 13 legal factors affecting the banking industry in our PESTLE analysis below:
- Compliance Requirements: Banks must adhere to a complex array of local, national, and international regulations that govern their operations. Compliance affects nearly every aspect of banking operations, including capital requirements, customer interactions, and reporting standards.
- Labor Laws: These govern employment practices within banks, affecting hiring, wages, working conditions, and layoffs. Compliance with labor laws is crucial to avoid legal disputes and ensure a fair working environment.
- Consumer Protection Laws: Banks must comply with laws designed to protect consumers from fraud, ensure fair lending, and transparent disclosure of loan terms and bank fees. Violations can lead to significant fines and reputational damage.
- Environmental Laws: While banks are not typically heavy polluters, their investment policies and lending practices to industries such as mining or manufacturing can be subject to environmental scrutiny. Banks may need to assess the environmental impact of their financing activities.
- Data Protection and Privacy Laws: These are particularly critical for banks as they handle significant amounts of sensitive financial information. Regulations such as GDPR in Europe or CCPA in California dictate how banks must protect customer data and respond to breaches.
- Contract Law: Governs the agreements banks make with customers, vendors, and partners. It's essential for enforcing loan agreements, service contracts, and resolving disputes legally.
- Antitrust and Competition Laws: These laws prevent monopolistic behaviors and ensure fair competition. Banks must navigate these laws when planning mergers, acquisitions, or partnerships.
- Securities Law: Critical for banks involved in investment banking, securities laws regulate how securities are issued, traded, and managed. Compliance is crucial to avoid legal penalties and ensure market integrity.
- Bankruptcy Laws: Influence how banks deal with insolvent individuals or corporations. Understanding these laws is crucial for managing credit risk and making decisions about loan extensions.
- Advertising Laws: Banks must comply with regulations that govern the accuracy and fairness of their advertising. This includes how they represent financial products and services to avoid misleading consumers.
- Financial Regulations: These are the broadest category of laws affecting banks, covering everything from how much capital banks must hold to how they report financial activities and manage risk.
- Insurance Law: For banks that offer insurance products or invest in insurance companies, understanding and complying with insurance regulations is essential to operate legally and effectively.
- Cyber Law: With the increasing threat of cyberattacks, banks must follow laws that protect against digital fraud and theft. This includes implementing robust cybersecurity measures and reporting breaches as required by law.
Check out more legal factors that affect the business environment in this article.
Banking Industry's Environmental Factors

With the use of technology — particularly with mobile banking apps — the use for paper is being reduced. Additionally, the need to drive directly to a branch to handle affairs is minimized as well.
Many issues are taken care of through mobile apps and online banking services. Consumers can apply for credit cards online, buy cheques online, and have many of their banking questions answered online or by phone. Thus, reducing individual environmental footprints.
In the final part of our PESTLE analysis of the banking industry, we examine 10 environmental factors:
- Climate Change: Banks are increasingly assessing the risk climate change poses to their loan portfolios, particularly in sectors like agriculture, real estate, and insurance. This includes considering the physical risks to assets from extreme weather and the transition risks associated with shifting towards a low-carbon economy.
- Renewable Energy Adoption: As renewable energy technologies become more prevalent, banks are finding opportunities in financing projects related to solar, wind, and other renewable energy sources. This not only helps in portfolio diversification but also enhances the bank's image as a socially responsible entity.
- Carbon Footprint: Regulatory pressures and societal expectations are driving banks to reduce their own carbon footprints and to finance projects that aim to reduce carbon emissions. This includes initiatives like green bonds and other sustainable financial products.
- Green Building Practices: Banks involved in financing construction projects are increasingly incorporating green building standards into their lending criteria, promoting environmentally friendly construction practices.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Banks providing loans to the agricultural sector are increasingly considering sustainable practices as part of their lending criteria to mitigate environmental risks and promote sustainable development.
- Energy Efficiency Regulations: Compliance with energy efficiency regulations can influence the bank's operations directly through their own energy use and indirectly by affecting the types of projects they are willing to finance.
- Consumer Preferences for Green Products: This trend is influencing banks to develop and offer green financial products such as eco-friendly loans or mortgages that offer better rates for energy-efficient homes or businesses.
- Corporate Sustainability Practices: As banks adopt more sustainable practices, they not only reduce their environmental impact but also appeal to environmentally conscious investors and customers, enhancing their brand reputation and customer loyalty.
- Environmental Advocacy: Pressure from environmental groups can lead banks to reconsider their investment strategies, particularly in divesting from fossil fuels and other industries harmful to the environment.
- Green Technology Innovations: The emergence of green tech provides new business opportunities for banks in terms of financing innovative technologies that address environmental challenges.
Again, a complete list of environmental factors affecting industries can be found in this post.
Recommendations and Further Study Based on the Banking Industry PESTLE Analysis
The banking industry is held accountable by the government. What and how they offer services is determined by politics and current governmental laws. Additionally, banks are at the whim of the economy — inflation rates can devastate banking prospects as it affects the value of currency. Banks can:
- Enhance Regulatory Compliance and Adaptability: Given the influence of political leadership changes and legislative shifts, banks should invest in robust compliance frameworks that are agile enough to adapt to new regulations swiftly. This involves enhancing their monitoring systems and regulatory technology (RegTech) to ensure they can quickly adjust to changes such as new financial regulations or anti-money laundering (AML) standards.
- Strengthen Economic Resilience: In light of economic factors like interest rate fluctuations, inflation, and economic cycles, banks should build resilient financial models that can withstand economic downturns. This includes diversifying income streams, maintaining strong capital buffers, and developing risk assessment models that consider various economic scenarios. Banks should also focus on strengthening their credit risk management to mitigate potential losses from loan defaults during economic downturns.
- Leverage Technology for Competitive Advantage: Economic and political stability can be enhanced through technological adoption. Banks should continue to invest in technology such as AI, blockchain, and big data analytics to improve operational efficiencies, enhance customer service, and offer innovative products. This can help them stay competitive in a rapidly changing market, respond more effectively to consumer demands, and manage risks associated with cyber threats and technological disruptions.
Technology is helping consumers spend and save money with readily available apps and online services. For many daily transactions, it isn’t required for users to visit their branch anymore. This, in turn, saves the use of paper and gas spent from driving to and from banking locations. Legally, banks regard consumer laws, trade agreements, and privacy laws. They also must have top-notch cyber security with the growing use of technology with banking transactions. Banks can also:
- Embrace Social Responsibility and Inclusion: Given the evolving social factors like demographic changes and increasing social mobility, banks should focus on inclusive banking to cater to a broader spectrum of the population. This includes offering products tailored to underserved communities, enhancing financial literacy programs, and ensuring that banking services are accessible to all societal segments. Initiatives such as microfinancing and tailored loan programs for small businesses in economically diverse areas can help build community trust and expand customer bases.
- Develop Green Banking Initiatives: In response to growing environmental awareness and consumer preference for sustainable practices, banks should increase their offerings of green financial products. This could include green bonds, sustainable investment funds, and eco-friendly mortgages that offer incentives for energy-efficient home improvements. By doing so, banks not only align with environmental conservation efforts but also attract environmentally conscious customers.
- Enhance Reporting and Transparency on Sustainability: Banks should improve their transparency in environmental and social governance (ESG) efforts by publicly reporting their progress and impact. This could involve detailed reporting on carbon footprint reduction, investments in sustainable projects, and contributions to social causes. Enhanced transparency will not only comply with increasing regulatory demands but also bolster the bank's image as a responsible and trustworthy institution in the eyes of investors and customers.
If you enjoyed this PESTLE analysis and want to learn more, you can now jump over to our dedicated page on this strategic planning tool. But feel free to check out analysis we've done for some of the most popular banks worldwide:
- SWOT Analysis of JPMorgan
- SWOT Analysis of Bank of America
- SWOT Analysis of Wells Fargo
- Porter's Five Forces Analysis of Barclays









