Automobiles have been around for more than 150 years, but it's only recently that we've noticed the industry's scary environmental ramifications. You've got to wonder: Will the market for motor vehicles survive with all this tension?
In this PESTLE analysis, we'll look at the Political, Economic, Sociocultural, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors affecting the automotive industry, in the hopes of gaining some insight into the future of this space! It will also complement our SWOT analysis of the automotive industry.
Automotive Industry's Political Factors

Here are key political factors affecting the automotive industry.
Government Regulations and Policies
Driving motor vehicles can be extremely dangerous. Although we like to think of airplanes as being unsafe, the truth is that you're significantly more likely to have a car or motorcycle accident than to be involved in a plane crash.
As a result of this, governments across the world enforce strict safety regulations around the automotive industry. Not only do these regulations govern the manufacturing of motor vehicles — providing specific build requirements, such as seatbelts, to ensure passenger safety — but they also affect those behind the wheel. This makes it more difficult to launch a new business in the automotive space, helping existing brands to maintain their place in the market.
Government regulations and policies are crucial in shaping the automotive industry. These regulations can include safety standards, environmental regulations, and fuel economy requirements. Compliance with these regulations can increase production costs but also drive innovation.
Aside from controlling the safety aspect of the automotive industry, politicians also take great interest in the environmental consequences of motor vehicles.
Almost all cars, motorcycles, and buses are powered by fossil fuels such as petroleum and diesel, which produce a number of environmental pollutants when burnt. A major concern with motor vehicles is that of carbon emissions, i.e. the amount of carbon dioxide produced by driving a vehicle.
As such, governments also have a great interest in the emissions statistics of new and existing vehicles. This, along with other environmental concerns, is yet another regulatory hoop for automotive manufacturers to jump through.
- Example: The European Union’s stringent CO2 emission standards compel automakers to innovate in electric and hybrid technologies.
Trade Policies and Tariffs
Trade policies and tariffs directly impact the automotive industry by influencing the cost of imported and exported vehicles and components. Trade agreements or disputes can lead to fluctuations in pricing and supply chain adjustments.
- Example: During the US-China trade war, tariffs were imposed on various automotive parts, which increased manufacturers' costs and impacted global supply chains.
Political Stability
Political stability in a country can affect the automotive industry's operational certainty and investor confidence. Unstable political environments can lead to disruptions in manufacturing and distribution, impacting overall productivity and profitability.
- Example: Political unrest in countries like Thailand and Brazil has interrupted automotive manufacturing and sales.
Government Incentives and Subsidies
Government incentives and subsidies for electric vehicles (EVs) and green technologies can significantly influence the automotive market. These incentives can make EVs more affordable for consumers and encourage manufacturers to invest in new technologies.
- Example: China's government offers substantial subsidies for electric vehicle manufacturers, fostering a rapidly growing EV market.
International Relations and Trade Agreements
International relations and trade agreements can facilitate or hinder the automotive industry's growth. Favorable trade agreements can open new markets and reduce costs, while adverse relations can lead to restrictive measures.
- Example: The US-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) replaced NAFTA, impacting automotive trade by setting new rules on labor and content requirements for vehicles manufactured in North America.
Automotive Industry's Economic Factors
Here are important economic factors affecting the automotive industry.
Economic Growth and Stability
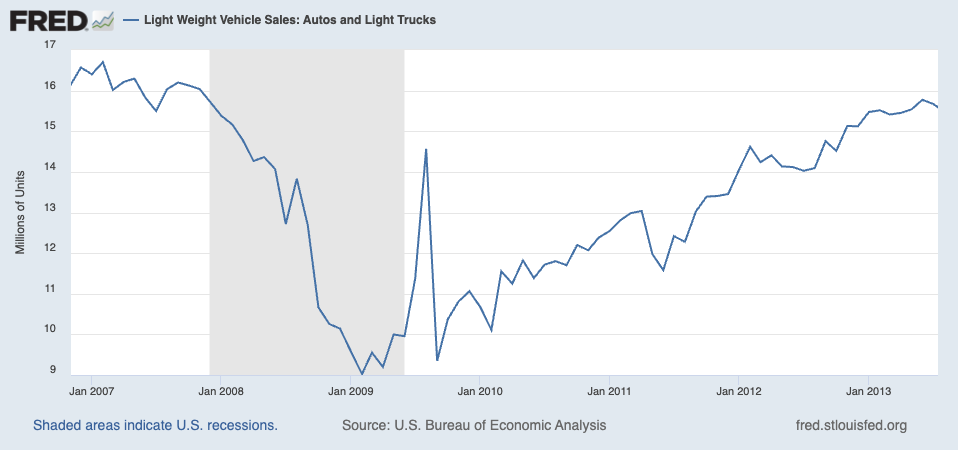
The overall economic growth and stability of a country or region have a profound impact on the automotive industry. Economic downturns can lead to reduced consumer spending on big-ticket items like vehicles, while economic booms can boost sales.
- Example: During the 2008 financial crisis, global car sales plummeted as consumers and businesses cut back on spending.
Consumer Income and Purchasing Power
The income levels and purchasing power of consumers are crucial in determining the demand for automobiles. Higher disposable incomes typically lead to increased sales of new vehicles, while economic hardship can push consumers toward the used car market or delay purchases.
As a general trend, individuals around the world are earning more and more money every year.
This means they have more money to spend on luxury items such as electronics and, of course, automobiles! It comes as no surprise, then, that demand for motor vehicles is slowly but surely growing.
This is especially true in developing regions—such as some African states—where recent economic developments have only recently made it possible for poorer households to afford their own cars. Ultimately, this growing demand for motor vehicles means that more cars will be sold, and the automotive industry will become even more profitable for its participants.
- Example: Rising middle-class incomes in emerging markets like India and China have led to a surge in passenger vehicle demand.
Interest Rates
Interest rates, set by central banks, affect the cost of financing vehicles. Lower interest rates make car loans more affordable, encouraging consumers to purchase new vehicles, whereas higher interest rates can deter buyers due to increased loan costs.
- Example: The Federal Reserve's interest rate cuts in the US following the COVID-19 pandemic helped sustain car sales by lowering borrowing costs.
Fuel Prices
Fuel prices directly influence the cost of vehicle ownership and can shift consumer preferences toward more fuel-efficient or alternative-fuel vehicles. Volatile fuel prices can lead to changes in the types of vehicles consumers prefer, such as a shift from SUVs to compact cars.
- Example: The rise in oil prices in the early 2000s drove demand for hybrid and more fuel-efficient vehicles.
Exchange Rates
Exchange rates can impact the cost of importing and exporting vehicles and parts. A stronger domestic currency can make exports more expensive and imports cheaper, affecting the competitiveness of automakers in the global market.
- Example: A strong Japanese yen can make cars produced in Japan more expensive for overseas buyers, affecting sales.
Employment Rates and Job Security
Employment rates and job security influence consumer confidence and spending power. High employment and job security encourage consumers to make significant purchases like cars, while high unemployment rates can suppress demand.
- Example: The rise in unemployment during the COVID-19 pandemic led to a decline in car sales as consumers faced financial uncertainties.
Automotive Industry's Social Factors

Here are 5 Social factors affecting the automotive industry:
Changing Consumer Preferences
Consumer preferences are evolving rapidly, driven by lifestyle changes, technological advancements, and environmental concerns. There is a growing demand for electric vehicles (EVs), hybrids, and other environmentally friendly transportation options. Additionally, preferences are shifting towards connected and autonomous vehicle features.
- Example: The increasing popularity of Tesla and other EVs reflects a shift in consumer demand towards sustainable and innovative vehicle technologies.
Urbanization and Demographic Shifts
There's no doubt that, from a Sociocultural perspective, the popularity of driving is growing.
It's becoming commonplace for families around the world to own one or more motor vehicles; in fact, owning one or more motor vehicles is already the norm in developed countries such as the United States, Canada, and much of the European Union.
Part of this is a cultural phenomenon: it's not like many of us can't get away with bicycles and buses, but instead, we choose to drive motor vehicles simply because that's what is expected of us.
Urbanization and demographic changes, such as the growth of urban populations and the aging population in many regions, impact the automotive industry. Urban dwellers often prefer smaller, more fuel-efficient cars or public transportation, while an aging population might prioritize comfort and ease of use in their vehicle choices.
- Example: The rise in urban populations in cities like New York and London has led to increased demand for compact cars and alternative transportation options such as car-sharing services.
Health and Environmental Awareness
Increased awareness of health and environmental issues influences consumer behavior and regulatory policies. Consumers are becoming more conscious of the environmental impact of their vehicles, leading to greater demand for low-emission and fuel-efficient cars.
- Example: The global push for reducing carbon footprints has resulted in higher sales of hybrid and electric vehicles and the adoption of stricter emissions standards by governments.
Social Mobility and Lifestyle Changes
Social mobility and changing lifestyles, including the rise of the gig economy and remote work, affect transportation needs and vehicle usage patterns. Flexible work arrangements and the gig economy can alter the types of vehicles in demand, such as increased interest in multi-purpose or delivery vehicles.
- Example: The increase in remote work due to the COVID-19 pandemic has led to changes in vehicle usage patterns, with some consumers delaying car purchases or opting for different types of vehicles.
Brand Loyalty and Cultural Influences
Brand loyalty and cultural influences play a significant role in automotive purchasing decisions. Cultural perceptions of car ownership and brand reputation can drive consumer loyalty and affect market dynamics. Additionally, social media and online reviews have become crucial in shaping consumer opinions and preferences.
- Example: German car manufacturers like BMW and Mercedes-Benz benefit from strong brand loyalty and a reputation for high-quality engineering, which influences consumer choices globally.
Automotive Industry's Technological Factors
Here are 7 technological factors affecting the automotive industry:
Advancements in Electric Vehicle (EV) Technology
Electric vehicle technology is rapidly evolving, with improvements in battery life, charging infrastructure, and overall vehicle performance. These advancements are crucial for reducing the carbon footprint of the automotive industry and meeting regulatory standards for emissions.
- Example: Tesla's advancements in battery technology, such as the development of the 4680 battery cell, have significantly increased the range and efficiency of their electric vehicles.
Autonomous Driving and AI
Without a doubt, the biggest Technological shift impacting the automotive industry is the advance of self-driving technology. With some automotive brands, such as Tesla, already offering nearly completely autonomous motor vehicles, there is a huge change to the way we commute on the horizon.
This isn't necessarily a good or bad thing for the automotive industry, but it may mean that conventional car manufacturers have to change their business strategy to stay relevant.
The development of autonomous driving technologies and artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming the automotive industry. Self-driving cars and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) are becoming more prevalent, offering enhanced safety, convenience, and efficiency.
- Example: Waymo, a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc., has made significant strides in developing fully autonomous vehicles, aiming to revolutionize personal and commercial transportation.
Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
Aside from the advent of self-driving cars, another big Technological advancement in the automotive industry is, generally speaking, the safety of motor vehicles.
It was only in the 1980s that wearing seat belts became a requirement; similarly, it took lower-end automotive brands until the early 2000s to begin rolling out airbags across their models. Not only are standards improving across the industry, but so is the underlying technology.
Most recently, automotive manufacturers have begun introducing emergency brake assist systems to their vehicles, vastly reducing the likelihood of front-end collisions.
One of the most significant technological factors that have profoundly enhanced safety standards in the automotive industry is the development and implementation of Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS). These systems use a combination of sensors, cameras, radar, and software to provide real-time information and automated responses, thereby increasing vehicle safety and reducing the likelihood of accidents.
- Example: Tesla's Autopilot and Mercedes-Benz's DISTRONIC systems use Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) to enhance highway driving safety.
- Example: Subaru's EyeSight and Honda Sensing systems offer Lane Departure Warning (LDW) and Lane Keeping Assist (LKA) to prevent unintentional lane departures.
- Example: Volvo's City Safety system, which is standard in many of its models, can prevent or mitigate frontal collisions.
Connectivity and the Internet of Things (IoT)
The integration of connectivity and IoT in vehicles allows for smarter, more connected driving experiences. Features like real-time traffic updates, vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication, and remote diagnostics are becoming standard, enhancing safety and convenience.
- Example: General Motors' OnStar service provides connected safety and security solutions, enabling real-time assistance and vehicle tracking.
Advanced Manufacturing and Automation
Technological advancements in manufacturing, such as automation and robotics, are revolutionizing vehicle production. These technologies increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improve the precision and quality of manufacturing processes.
- Example: BMW's use of collaborative robots (cobots) in their assembly lines has improved production efficiency and worker safety.
Lightweight Materials and Fuel Efficiency
The development of lightweight materials, such as carbon fiber and advanced composites, is critical for improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. These materials help create lighter, more fuel-efficient vehicles without compromising safety or performance.
- Example: The widespread adoption of aluminum and carbon fiber in vehicle bodies, as seen in models like the Ford F-150, significantly reduces vehicle weight and enhances fuel efficiency.
Cybersecurity
As vehicles become more connected and reliant on software, cybersecurity becomes a critical concern. Protecting vehicles from hacking and ensuring the security of data and communication systems is essential for maintaining consumer trust and safety.
- Example: The automotive industry has seen initiatives like the Auto-ISAC (Automotive Information Sharing and Analysis Center) to enhance cybersecurity awareness and collaboration among manufacturers.
Automotive Industry's Legal Factors

Here are 4 Legal factors affecting the automotive industry:
Emission and Environmental Regulations
Stringent emissions and environmental regulations significantly impact the automotive industry.
Governments around the world are implementing strict standards to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. Compliance with these regulations often requires substantial investment in new technologies and can affect production processes and costs.
- Example: The European Union's Euro 6 emission standards impose strict limits on the emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter from vehicles, pushing manufacturers to develop cleaner engines and exhaust systems.
Safety Standards and Regulations
Automotive manufacturers must adhere to various safety standards and regulations designed to protect passengers, pedestrians, and other road users. These regulations cover aspects such as crashworthiness, airbag deployment, seatbelt design, and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
- Example: The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the United States enforces safety standards, such as the requirement for all new vehicles to be equipped with rearview cameras to improve visibility and reduce accidents.
Intellectual Property Rights
Interestingly, the issue of copyright also affects the automotive industry.
Certain features of a car — from its branding to even its shape — can be protected by copyright, trademark, or patent laws. It's uncommon to hear about legal showdowns in the automotive space, but they do happen.
In recent decades, a rising issue has been that of Chinese automobile manufacturers blatantly stealing the designs of Western counterparts. For example, Chinese brand Geely has created some oddly similar copies of the Rolls Royce Phantom, resulting in some conflict. It's unclear what net effect this copying has on the industry, but it's definitely present.
Intellectual property rights (IPR) are crucial in protecting innovations in the automotive industry. Patents, trademarks, and copyrights safeguard technological advancements and brand identity, enabling companies to maintain a competitive edge. However, the industry also faces challenges related to patent infringement and counterfeit parts.
- Example: Tesla has numerous patents related to battery technology, electric powertrains, and autonomous driving systems, which help protect its innovations and maintain its market position.
Labor Laws and Regulations
Labor laws and regulations affect the automotive industry's workforce management, including working conditions, wages, health and safety standards, and union relations. Compliance with these laws ensures fair treatment of employees but can also influence operational costs and flexibility.
- Example: The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) in the United States sets minimum wage, overtime pay, and child labor standards, impacting how automotive companies manage their workforce and payroll.
Automotive Industry's Environmental Factors

Here are 8 Environmental factors affecting the automotive industry:
Climate Change
Climate change is a significant driver for the automotive industry, influencing both consumer behavior and regulatory frameworks. The push to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat global warming has led to stricter environmental regulations and increased demand for sustainable vehicle technologies.
As touched upon earlier, carbon dioxide is one of the most serious Environmental pollutants generated by the automotive industry. It plays a large role in global climate change, by means of the greenhouse effect.
Over the last few years, the issue of carbon emissions has gained global attention. We continue to drive motor vehicles on a daily basis, but it's unclear whether governments will be forced to take greater action to stop global warming — and that might involve a complete ban on production or usage of motor vehicles, or at least a switch towards electric vehicles.
- Example: The Paris Agreement has set global targets for reducing carbon emissions, prompting automakers to accelerate the development of electric and hybrid vehicles.
Resource Scarcity
The availability and sustainability of raw materials, such as lithium for batteries and rare earth elements for electronic components, are critical issues for the automotive industry. Resource scarcity can lead to increased costs and supply chain challenges.
- Example: The growing demand for lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles has highlighted the need for sustainable mining practices and recycling programs to manage limited resources.
Energy Consumption
The energy consumption of manufacturing processes and the overall fuel efficiency of vehicles are key environmental considerations. Reducing energy use not only lowers costs but also minimizes the environmental impact of production.
- Example: Automotive companies are investing in energy-efficient manufacturing techniques, such as using renewable energy sources and improving factory efficiency, to reduce their carbon footprint.
Waste Management
Proper waste management, including the disposal and recycling of automotive parts and materials, is crucial for minimizing environmental impact. The industry must address the lifecycle of vehicles from production to end-of-life disposal.
- Example: Programs like "end-of-life vehicle" (ELV) directives in the European Union require manufacturers to ensure that a significant percentage of a vehicle's materials are recyclable.
Air Quality
The automotive industry significantly impacts air quality through vehicle emissions. Reducing emissions of pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter is vital for public health and environmental protection.
- Example: The introduction of low-emission zones in cities like London restricts the use of high-polluting vehicles, encouraging the adoption of cleaner alternatives.
Water Usage
Water usage in the manufacturing process and its conservation are important environmental factors. Efficient water management practices can help reduce the environmental impact and operational costs.
- Example: Automotive manufacturers are implementing water recycling and treatment systems in their production facilities to minimize water consumption and pollution.
Sustainable Sourcing
The ethical and sustainable sourcing of raw materials and components is increasingly important for the automotive industry. Ensuring that supply chains are free from environmentally damaging practices and human rights abuses is critical.
- Example: Companies like BMW and Volvo are focusing on sourcing materials from suppliers that adhere to stringent environmental and ethical standards, including conflict-free minerals and sustainable mining practices.
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with environmental regulations and standards is mandatory for the automotive industry. These regulations govern emissions, waste management, and the use of hazardous materials, among other factors.
- Example: The Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) standards in the United States mandate specific fuel efficiency targets for automakers, influencing vehicle design and technology.
Key Takeaways and Recommendations Based on our PESTLE Analysis of the Automotive Industry
The motor vehicle has become a part of everyday life for many of us. Not only can we afford to buy and fuel our cars more than ever before, but we're also implicitly expected to use automobiles. However, the environmental consequences of driving are serious, and it looks like we might have to think about making the switch to electric vehicles to save our planet.
Adoption of ADAS Technologies
Why Important: The integration of Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) is crucial for enhancing vehicle safety. These systems significantly reduce the risk of accidents by providing real-time alerts and automated responses to potential hazards.
Recommendation: Automotive companies should prioritize the development and widespread implementation of ADAS technologies, ensuring that these features are available across a wide range of vehicle models.
Compliance with Emission and Environmental Standards
Why Important: Adhering to stringent emission and environmental regulations is essential for meeting legal requirements and reducing the environmental impact of vehicles. Compliance helps in mitigating climate change and promotes the adoption of cleaner technologies.
Recommendation: Invest in research and development to create cleaner and more efficient technologies, such as electric and hybrid vehicles, to meet and exceed regulatory standards.
Enhancing Connectivity and IoT Integration
Why Important: Leveraging connectivity and IoT features enhances the driving experience, improves safety, and opens up new service opportunities. Connected vehicles can provide real-time traffic updates, remote diagnostics, and other valuable services.
Recommendation: Develop and integrate IoT and connectivity features into vehicles, focusing on improving the overall user experience and safety.
Prioritizing Cybersecurity
Why Important: As vehicles become more connected and reliant on software, ensuring robust cybersecurity measures is critical to protect against hacking and data breaches. Maintaining consumer trust and vehicle safety is paramount.
Recommendation: Implement comprehensive cybersecurity protocols and continuously update them to protect vehicle systems and user data from potential threats.
Compliance with Safety Regulations
Why Important: Meeting or exceeding safety standards is crucial for legal compliance, consumer trust, and overall vehicle safety. Continuous innovation in safety features ensures that vehicles remain safe and competitive in the market.
Recommendation: Ensure that all vehicles comply with current safety regulations and invest in developing advanced safety features to stay ahead of regulatory changes.
Consumer Education on ADAS and Safety Features
Why Important: Educating consumers on the benefits and proper use of ADAS and other safety features maximizes their potential and enhances overall vehicle safety. Informed drivers are more likely to use these systems effectively.
Recommendation: Implement comprehensive consumer education programs, including user manuals, online tutorials, and dealership training sessions, to ensure that customers understand and utilize safety features correctly.
By focusing on these six critical areas, the automotive industry can enhance vehicle safety, comply with regulatory standards, and meet consumer expectations for advanced and secure vehicles.
Further Reading
The automotive industry is influenced by a myriad of factors across political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental dimensions as this PESTLE analysis demonstrated.
By understanding and strategically addressing these factors, automotive companies can navigate the complexities of the market, enhance their safety standards, and sustain growth and innovation.
To delve deeper into how these factors specifically impact major automotive companies, I encourage you to explore the following PESTLE analyses of key automotive players. These analyses will provide more detailed insights into the strategies and challenges unique to each company, helping you gain a comprehensive understanding.
- PESTLE Analysis of Tesla
- PESTLE Analysis of Mercedes-Benz
- PESTLE Analysis of Toyota
- PESTLE Analysis of Ford
- PESTLE Analysis of BMW
- PESTLE Analysis of Volkswagen
- SWOT Analysis of General Motors
- SWOT Analysis of Honda






