100 years ago, Jack Cohen, a former member of the Royal Flying Corps, invested the demobilization money he received at the end of World War I to set up a shop in London. On his first day, he made a profit of £1 for £4 of sales. That was the start of Tesco - the UK's biggest supermarket. In today's Tesco SWOT Analysis, you will learn:
- Strengths: Tesco's internal advantages driving its growth.
- Weaknesses: Problems within Tesco holding it back.
- Opportunities: Situations Tesco could leverage to progress.
- Threats: External factors putting Tesco at a disadvantage.
Back in 2020, through strong leadership and management, the company transformed one of the biggest threats to Tesco into one of its greatest strengths. The year also marked the transition of leadership from Dave Lewis to Ken Murphy. What did this mean for Tesco and the industry?
Well, you can read more to find out.
SWOT Analysis of TESCO
A SWOT analysis is like mapping out a game plan for a business. It stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. By looking at these four areas, a business can get a clear picture of what’s working, what’s not, and where there are chances to shine or challenges to tackle. It’s a handy tool for making smart decisions!
Let's begin with Tesco's strengths.
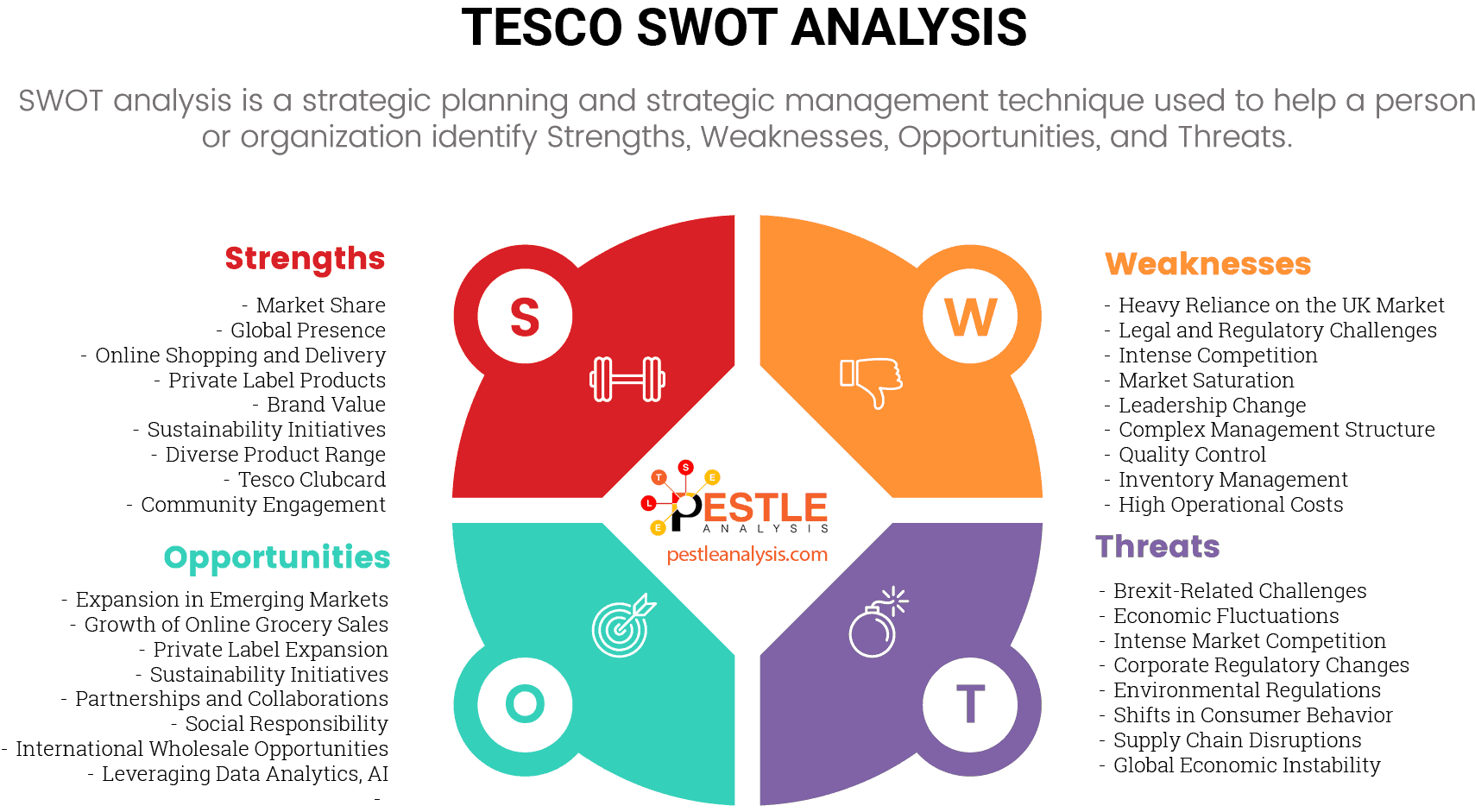
Tesco's strengths

After a devastating accounting scandal causing a £6.4 billion loss in 2015, people thought Tesco's run at the top of the supermarket chains was over. However, Tesco made a remarkable recovery. Many of Tesco's strengths come from this magnificent turnaround. Here are some of the advantages Tesco has:
- Market Share: Tesco holds a commanding position in the retail market. It's the biggest player in the UK with a significant share of the market. This position gives it a competitive advantage in terms of scale and influence over suppliers and buyers. According to Kantar, Tesco has 27.4% of the grocery market share in Great Britain. Tesco's closest competitor, Sainsbury's, has a market share of 15.3%. Thus, Tesco's dominance in the market is unchallenged.
- Global Presence: Besides the UK, Tesco operates in several countries, giving it international exposure and diversification of its business risks.
- Online Shopping and Delivery: Despite the pandemic, Tesco registered a 10.5% growth in the last three months to September 2020. The growth came from Tesco boosting its online sales. The volume of growth is clear from Tesco hiring 16,000 people to cater to the growth in demand. Especially post-pandemic, Tesco’s strong online presence and efficient delivery system have been a game changer. They’ve invested heavily in their digital platform, making shopping convenient and accessible.
- Private Label Products: Tesco offers a range of private label products that are often cheaper than branded equivalents but maintain good quality. This appeals to budget-conscious consumers.
- Innovation: Couchbase judged Tesco as winners in the EMEA region for Advanced NoSQL Architecture. The award recognizes Tesco's efforts to optimize its delivery scheme in response to COVID-19 induced shortages. According to Couchbase, Tesco ran nearly 2 billion iterations.
- Adaptability: In response to pandemic-triggered restrictions on in-store purchases, Tesco was able to double its delivery capacity to 1.5 million slots. The upgrade resulted in a profit of £551 million, which is 28.7% higher than the figures last year.
- Brand Value: Tesco has a strong brand reputation for quality and affordability, which attracts and retains customers. It’s a household name, and many people trust it for their daily shopping.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Increasingly, Tesco is focusing on sustainability, aiming to become a zero-carbon business by 2050, which improves its image and appeal, especially among environmentally conscious shoppers.
- Diverse Product Range: From groceries to electronics, Tesco offers a wide variety of products. This diversity attracts a broad customer base and meets different consumer needs under one roof.
- Tesco Clubcard: Their loyalty program, the Clubcard, is a big plus. It’s well-integrated into Tesco’s strategy, offering rewards and personalized discounts, which enhance customer loyalty and data collection.
- Community Engagement: Tesco has a strong track record of community involvement and charity work, which enhances its corporate social responsibility profile and endears it to local communities.
- Financial Turnaround: Thanks to the leadership of Dave Lewis, Tesco recovered from an annual loss of £6.4 billion in the annual report of 2015 to an operating profit of £1.9 billion in the annual report of 2020. Tesco's annual operating income for 2022 further increased to $3.511B, a 56.07% increase from 2021. Yet, Tesco's annual operating income for 2023 dropped to $1.852B.
Each of these strengths helps Tesco maintain its market leader status and offers a buffer against competitive forces. It’s like having a well-stocked toolkit; whatever the job, Tesco seems to have the right tool handy!
In light of Tesco's strengths, the reason Tesco is so successful is its management. Dave Lewis has left Ken Murphy a winning company. Let's hope Ken Murphy continues to drive Tesco's growth.
But not everything is picture-perfect. Tesco does have some internal vulnerabilities to address. Next, we will look at Tesco's weaknesses.
Tesco's weaknesses
Tesco's biggest competitors are Sainsbury's, Asda, and Morrisons. Together, the four companies are known as the Big 4. They account for 66% of the market share in Great Britain. Each of the Big 4 has its set of hurdles to overcome, here are Tesco's:
- Heavy Reliance on the UK Market: Despite its international presence, Tesco is still heavily reliant on the UK market for the majority of its revenues. This can be risky because any downturn in the UK economy or changes in consumer behavior can have a significant impact on its overall performance. Tesco has had a mixed record with its ventures outside the UK, including exiting from markets like the US, Japan, and Turkey. These exits suggest difficulties in replicating its domestic success internationally.
- Legal and Regulatory Challenges: Tesco has faced various legal and regulatory issues over the years, including a significant accounting scandal a few years back as previously mentioned. These not only affect its financials but can also tarnish its brand reputation.
- Intense Competition: The retail sector is fiercely competitive. Tesco has to constantly fend off rivals like Sainsbury's, ASDA, and discount supermarkets like Aldi and Lidl. These competitors often engage in price wars, putting pressure on Tesco’s profit margins.
- Market Saturation: In its key markets, particularly in the UK, Tesco faces the issue of market saturation. There's limited room for growth in already heavily served areas, which might force Tesco to seek expansion in less familiar or more competitive markets.
- Leadership Change: Ken Murphy took the reins as CEO from Dave Lewis in September 2020. According to the Retail Gazette, the change heralds a new chapter in Tesco's story. Maintaining the well-oiled machine, which Dave left behind while accelerating the massive push online would be no easy task.
- Complex Management Structure: As Tesco is such a large company, its management structure is quite complex. This can sometimes slow down decision-making or dilute accountability, making it hard to implement changes swiftly.
- Quality Control: Tesco boasts rigorous quality control measures, but a disturbing complaint from a customer indicates room for improvement. Although Tesco apologized for selling chicken with partially digested feed, the incident should not have occurred in the first place.
- Food Safety Issues: Given the range of food products Tesco sells, lapses in adhering to food safety guidelines have major consequences. For instance, Tesco issued urgent food recalls after discovering safety issues and defects that endanger customers.
- Shortage of Products: To prevent shortages due to panic buying during COVID-19, Tesco was rationing a few of its items. However, Tesco assured customers they are adequately stocked to cater to normal buying patterns.
- Inventory Management: Tesco paid £175,000 in fine for displaying products 15 days past their expiry date. On hearing about the issue, Tesco removed the items and put in place systems to avoid similar problems.
- High Operational Costs: Running a vast network of physical stores involves high costs, from staffing to utilities and maintenance. With the shift towards online shopping, maintaining profitability in physical stores is increasingly challenging.
Some of Tesco's weaknesses, such as shortage of products or change in leadership, are temporary. The long-standing ones remain problems associated with quality control and inventory management.
By acknowledging and addressing these weaknesses, Tesco can work on strategies to mitigate these risks and improve its overall resilience. Think of it like a football team figuring out its defensive weaknesses to avoid letting goals in!
What’s unique about Tesco is its core value: "No one tries harder for customers." Based on this core value, Tesco will address its weaknesses over time.
Having completed the first two parts of our SWOT analysis, we have now concluded analyzing the internal factors that affect the grocery retailer.
Now, let's move on to Tesco's opportunities.
Tesco's Opportunities

The supermarket industry was one of the few industries to hold its own during the COVID crisis. This once-in-a-century crisis marked a permanent shift in the way people conduct business. And this new world brought new opportunities. Here are some of Tesco's opportunities.
- Expansion in Emerging Markets: While Tesco has faced challenges internationally, there remains significant potential for expansion in emerging markets where retail sectors are still growing. Countries with rising middle-class populations offer new customer bases and the opportunity for substantial growth.
- Growth of Online Grocery Sales: Measures to prevent the spread of COVID-19 also prevented people from stepping out as much as they used to. The restrictions popularized buying groceries online. That's why Ocado benefited from a 76% rise in online sales. Tesco can and should leverage the trend. The shift towards online shopping is accelerating, and there's room for Tesco to further enhance its e-commerce platform. Investing in technology to streamline the online shopping experience and expanding its delivery options can attract more customers.
- Private Label Expansion: Tesco’s private label products are already a strength, but there’s still room to grow. Developing new private label items that compete directly with national brands could improve profit margins and customer loyalty.
- Sustainability Initiatives: There's a growing demand for sustainable and ethically sourced products. Tesco can lead the market by expanding its range of eco-friendly products and adopting more robust sustainability practices, which can also improve its public image. Tesco can diversify its product offerings to include more premium products or expand into new categories like health and wellness, which are gaining popularity. This can help attract different customer segments and increase basket sizes. As consumers become more health-conscious, Tesco could further capitalize on this trend by offering more healthy, ready-to-eat options that cater to busy lifestyles. The plant-based protein market size was £4.1 billion in 2020 and is estimated at USD 13.3 billion in 2023, while projected to reach USD 19.2 billion by 2028. Switching to meat alternatives also promotes sustainable business. It's in light of this opportunity Tesco is committing to a 300% increase in sales of meat alternatives by 2025.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: Collaborating with technology companies, for instance, to enhance data analytics or improve supply chain logistics, can help Tesco stay competitive and innovative.
- Community Engagement and Social Responsibility: By intensifying its community engagement and social responsibility efforts, Tesco can strengthen its local presence and customer loyalty, which is crucial in competitive retail landscapes. Social supermarkets stockpile unsold inventory that's within its use-by date. Then, the supermarket sells the inventory at very affordable rates, preventing wastage and food poverty. Tesco is passionate about both causes and should actively participate in this initiative.
- International Wholesale Opportunities: Tesco can leverage its brand and expertise in retail to expand its wholesale operations internationally, supplying products to other retailers in various markets.
- Leveraging Data Analytics, AI and Machine Learning: Utilizing advanced data analytics to understand customer preferences and shopping behaviors can help Tesco personalize marketing and enhance customer satisfaction. Supermarket chain Morrisons partnered with TCS, a leading IT consulting company, to improve operations and productivity. Using AI and machine learning to predict and deliver street-level requirements could be a game-changer.
These opportunities, if pursued, can help Tesco maintain its leadership position and navigate the evolving retail environment. It’s like spotting open spaces on the soccer field—knowing where to run can make all the difference in scoring goals or defending well!
At present, Tesco's best opportunity is to bolster its presence in the online space. If Tesco gets this right, it will ensure its reign at the top for many years to come.
But Tesco should not take things for granted and should masterfully navigate through a changing landscape. We'll talk about Tesco's threats next.
Tesco's Threats
Back in 2020, the UK was going through a political crisis, a health crisis, and an economic crisis. And one of Tesco's main rivals was making a comeback. So, Tesco must watch out for these threats. Here are the details:
- Brexit-Related Challenges: For Tesco, as a UK-based company, Brexit has brought about trade uncertainties and potential tariffs on imported goods, additional customs checks, and quotas, which could increase costs and complicate operations.
- Economic Fluctuations: Being a dominant player in the retail sector means Tesco is sensitive to economic downturns. Recessions or financial instability can reduce consumer spending power, impacting sales at Tesco stores. Ken Murphy, the new CEO of Tesco, forecasts tough times during the holiday season. Economic recession and the resultant drop in purchasing power are the main reasons for concern. Also, rising unemployment adds another layer of financial uncertainty for Tesco's patrons.
- Intense Market Competition: The competition in the retail market is fierce. Tesco is up against traditional rivals like Sainsbury's and ASDA, as well as budget retailers like Aldi and Lidl, which have been expanding rapidly. A few years ago, the ownership of Asda changed hands from Walmart to the billionaires Issa brothers. The new owners sought to bring Asda to their 6000 forecourts across 10 countries. The revival of Asda posed a serious threat to Tesco's market share. There's also growing pressure from online giants like Amazon entering the grocery market.
- Corporate Regulatory Changes: Changes in retail and labor regulations, such as minimum wage increases or changes in food safety and labeling requirements, can lead to higher operational costs for Tesco.
- Environmental Regulations: Increasingly strict environmental regulations could impose additional operational costs on Tesco, particularly in areas like packaging, waste management, and carbon emissions.
- Shifts in Consumer Behavior: Consumer preferences are continually evolving. There’s a trend towards local and organic products and an increased awareness of health and sustainability issues. Tesco must adapt to these changes to stay relevant and maintain customer loyalty.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Events like natural disasters, pandemics, or political instability can disrupt supply chains. This can lead to shortages and increased costs, affecting Tesco’s ability to provide products consistently at competitive prices. Brexit affected 80% of the imported food sold in supermarkets. With Brexit imposing restrictions at the port of entry, the stymied flow of imported goods from the EU to the UK will negatively impact Tesco's supply chain.
- Global Economic Instability: International operations expose Tesco to global economic risks, including currency fluctuations and differing economic conditions in other countries where it operates.
By staying vigilant and responsive to these threats, Tesco can better navigate potential challenges. Think of it like a goalie in hockey; being aware of where the puck might be shot helps in making effective saves!
Opportunities and threats are external factors affecting the grocery retailer. To study more external factors affecting the business environment of Tesco, make sure to check out our PESTLE analysis of Tesco, which compliments today's analysis.
Recommendations based on our Tesco SWOT Analysis
Tesco's strengths are unique to Tesco. However, its weaknesses are common to other players in the supermarket industry. So, Tesco will continue to reap the benefits of robust leadership and management practices that make it stand tall among its rivals.
Also, by tackling the ongoing challenges Brexit and COVID impose, Tesco has shown its resilience by reinventing itself to cater to the rise in online grocery sales. Tapping this vein could be very profitable for Tesco.
The main takeaway from Tesco's SWOT analysis is that strong leadership can turn any crisis around. It can also transform a perilous situation into a training ground for reinvention and growth.
Expanding our study to include a SWOT analysis of Tesco's competitors can provide a more comprehensive view and help us understand the broader retail landscape. By examining the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats facing other key players in the market, we can better identify Tesco's relative advantages and areas for improvement. Check these out below:
- SWOT Analysis of Sainsbury's
- SWOT Analysis of Aldi
- PESTLE Analysis of Asda







