The tourism industry has been growing for decades, and shows no signs of stopping.
Technological advancements have revolutionized the tourism industry, making travel more accessible and convenient than ever before. Online booking platforms, mobile travel apps, and social media influence have changed how people plan and experience their travels.
Despite these innovations, the industry faces numerous challenges and uncertainties.
Conducting a PESTLE analysis on the tourism industry helps identify the key macro-environmental factors shaping the industry, providing valuable insights for businesses and policymakers. This analysis is crucial for developing strategies that align with changing consumer behaviors and ensuring the industry's long-term success.
Political Factors

Here are the political factors affecting the tourism industry.
Government Policies
Government policies significantly impact the tourism industry. Policies regarding tourism development, infrastructure investment, and promotion of the country as a travel destination can either boost or hinder the industry.
Supportive policies, such as subsidies, grants, and tax incentives, encourage investment in tourism infrastructure and services.
Visa Regulations
Visa policies influence the ease with which travelers can enter a country. Countries with lenient visa regulations or visa-free travel agreements with other nations tend to attract more tourists.
Conversely, strict or complicated visa requirements can be a significant barrier to tourism.
Thanks to many governments' decisions to open up borders to foreigners, traveling to new countries is easier than ever. While some countries are still difficult to access (often for political reasons), the vast majority of destinations can now be visited by tourists from all over the world.
In many cases, a visa of some sort is necessary; however, the process of applying for a visa has been expedited in many countries, in part thanks to the use of technology.
Example:
- In 2024, Turkey made a significant change to its visa regulations by dropping the visa requirement for U.S. travelers. This policy shift means that American tourists no longer need to apply for an e-visa, which previously cost $51.50. This change is expected to further boost tourism to Turkey, building on the record number of American visitors in 2023. The new visa-free policy allows U.S. travelers to stay in Turkey for up to 90 days within a 180-day period, making it easier and more attractive for them to visit popular destinations like Istanbul, the ancient ruins of the Lakes Region, and the coastal areas of Bodrum.
Government stability
Political stability is a major factor in the success of tourist destinations. Travelers are naturally curious to visit all corners of the world, and they can only be swayed by the threat of danger. Most popular tourist destinations are considered safe.
However, there are a number of culturally rich destinations that would be popular tourist spots if not for political instability. Examples include Syria, Iraq, and, recently, Hong Kong.
Countries with stable political environments are perceived as safer and more appealing destinations. Conversely, political unrest, conflicts, or frequent changes in government can deter tourists and negatively affect the tourism sector.
Government Spending on Infrastructure
Government investment in infrastructure, such as airports, roads, public transport, and tourism facilities, is critical for the growth of the tourism industry. Improved infrastructure enhances accessibility and the overall experience for tourists, making a destination more appealing.
Example:
- In 2024, the Thai government is investing in two new international airports, Andaman and Lanna, set to begin construction by 2027, with a combined capacity of 40 million passengers. Additionally, Bangkok Suvarnabhumi Airport's $4.8 billion expansion aims to increase capacity to 135 million passengers, while Don Mueang International Airport's capacity will rise to 50 million, illustrating how infrastructure investments drive tourism growth.
International Relations
Diplomatic relations between countries play a crucial role in tourism. Positive international relations can lead to bilateral agreements that promote travel and tourism, such as open skies agreements, which facilitate increased air travel between nations.
Conversely, strained relations or sanctions can restrict travel and impact tourism flows.
Security Measures
Security measures and policies are essential in ensuring the safety of tourists.
Governments implement various security protocols, such as airport security checks, anti-terrorism measures, and surveillance systems, to protect travelers. While these measures are necessary for safety, they can also impact the ease and comfort of travel.
Example:
- Starting in 2024, Israel introduced a new online application system for visitors from visa-exempt countries, including the United States. Travelers now need to fill out an electronic application 72 hours before their flight and pay a 25 NIS ($7) entry fee. This new system aims to enhance security and streamline the entry process. A pilot version of this ETA-IL program was launched for U.S. and German travelers in June 2024, with full implementation for all visa-exempt countries beginning in August 2024.
Public Health Policies
Public health policies, especially in light of global health crises like the COVID-19 pandemic, have a significant impact on tourism.
Governments may impose travel restrictions, quarantine requirements, and health certifications to control the spread of diseases. Effective public health measures and crisis management can help restore confidence in travel during health emergencies.
Legal Framework and Regulations
The legal framework governing the tourism industry, including regulations related to business operations, labor laws, and environmental protections, affects how tourism businesses operate.
Clear and supportive regulations create a conducive environment for the growth of the tourism sector.
Cultural Policies
Cultural policies that protect and promote cultural heritage sites, traditions, and practices are important for sustainable tourism development.
Governments that invest in preserving cultural attractions and promoting cultural tourism can attract tourists interested in unique and authentic experiences.
Economic Factors
Here are the Economic factors affecting the tourism industry:
Economic Stability
The overall economic stability of a country plays a crucial role in the tourism industry. Countries with stable economies attract more tourists because they are perceived as safe and reliable destinations.
Economic stability also affects the ability of local businesses to invest in tourism infrastructure and services.
Exchange Rates
Exchange rates can significantly influence tourist flows. A favorable exchange rate makes a destination more affordable for international tourists, encouraging more travel.
Conversely, an unfavorable exchange rate can make a destination expensive and deter potential visitors.
Disposable incomes
The level of disposable income among potential tourists directly impacts their ability to travel. Higher disposable income means people can afford to spend more on travel, accommodations, and other tourism-related activities.
Economic conditions that increase disposable income, such as wage growth and low unemployment rates, are beneficial for the tourism industry.
Inflation Rates
Inflation affects the cost of travel and tourism services.
High inflation can lead to increased prices for accommodation, food, transport, and other tourism-related expenses, making a destination less attractive to budget-conscious travelers. Stable and low inflation rates help maintain reasonable pricing and attract more tourists.
Interest Rates
Interest rates impact the cost of borrowing money for both tourism businesses and consumers.
Lower interest rates make it cheaper for businesses to invest in tourism infrastructure and for consumers to finance their travel plans. Conversely, higher interest rates can reduce investment in the tourism sector and decrease consumer spending on travel.
Employment Levels
Employment levels in both the destination country and the tourists’ home countries affect tourism.
High employment rates in the home countries of tourists lead to higher disposable incomes and more travel. Similarly, high employment levels in the destination country ensure that there are enough workers to provide quality services to tourists.
Economic Growth
Economic growth in both the destination and source markets stimulates the tourism industry.
Rapid economic growth increases disposable income and boosts consumer confidence, leading to more travel spending. Economic growth also enables governments to invest in tourism infrastructure, improving the overall tourist experience.
Global Economic Trends
Global economic trends, such as recessions or booms, impact the tourism industry.
During economic downturns, people tend to cut back on discretionary spending, including travel. Conversely, during periods of economic growth, travel spending typically increases.
Cost Efficiency & Market Competition
The sharing economy is the business trend in which individuals exchange goods and services directly with one another using facilitating services such as Uber and Airbnb.
As you may have noticed from those two examples, the rise of the sharing economy is changing the way we travel. With services like Uber offering a reliable way for tourists to catch rides around the world, and Airbnb offering a cheaper alternative to traditional travel accommodation (mainly hotels and hostels), the sharing economy is making travel more economical.
These services introduce more competition into the market, potentially driving down prices and improving service quality in traditional sectors like hotels and local taxi services.
Taxation Policies
Taxation policies, including VAT, sales taxes, and tourism-specific taxes, can impact the cost of travel. Higher taxes increase the overall cost for tourists, which can deter travel.
Conversely, tax incentives and reductions can make a destination more attractive and boost tourism.
In many countries, tourists can claim a tax refund on products purchased during their trip upon departure. Although these tax incentives are rarely the only reason for a tourist to visit, they are certainly an "incentive" for all tourists!
Example:
- In 2024, Cambodia introduced significant tax incentives to support the tourism sector, which had been severely impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic. These incentives include exemptions from monthly tax payments (excluding VAT and accommodation tax), exemption from income tax for 2023, and suspension of tax audits for the fiscal years 2020 to 2023. These measures target registered tourism enterprises such as hotels, guesthouses, restaurants, and travel agencies operating in major tourist areas.
Tourism Demand and Supply
The balance of demand and supply in the tourism market influences prices and the availability of services.
High demand for tourism can lead to higher prices and greater investment in tourism infrastructure. Conversely, low demand can result in lower prices and reduced investment.
Social Factors

Here are the Social factors affecting the tourism industry.
Changing Lifestyle Trends
Modern lifestyles and the increasing emphasis on experiences over material possessions have driven more people to travel.
Trends such as wellness tourism, adventure tourism, and eco-tourism are becoming more popular as people seek unique and fulfilling travel experiences.
Cultural Diversity and Appeal
Different cultures and unique experiences attract tourists seeking to explore new traditions, foods, festivals, and lifestyles. Destinations known for their rich cultural heritage and vibrant local customs often draw more visitors.
Impact of Globalization
Globalization has made travel more accessible and appealing.
The ease of obtaining information about foreign destinations, increased availability of international flights, and the proliferation of global tourism brands contribute to the growth of tourism.
Demographic Shifts
The age, income, and social status of potential tourists influence tourism patterns. For instance, the growing middle class in emerging markets and the increasing number of retirees with disposable income in developed countries contribute to higher travel demand.
Example:
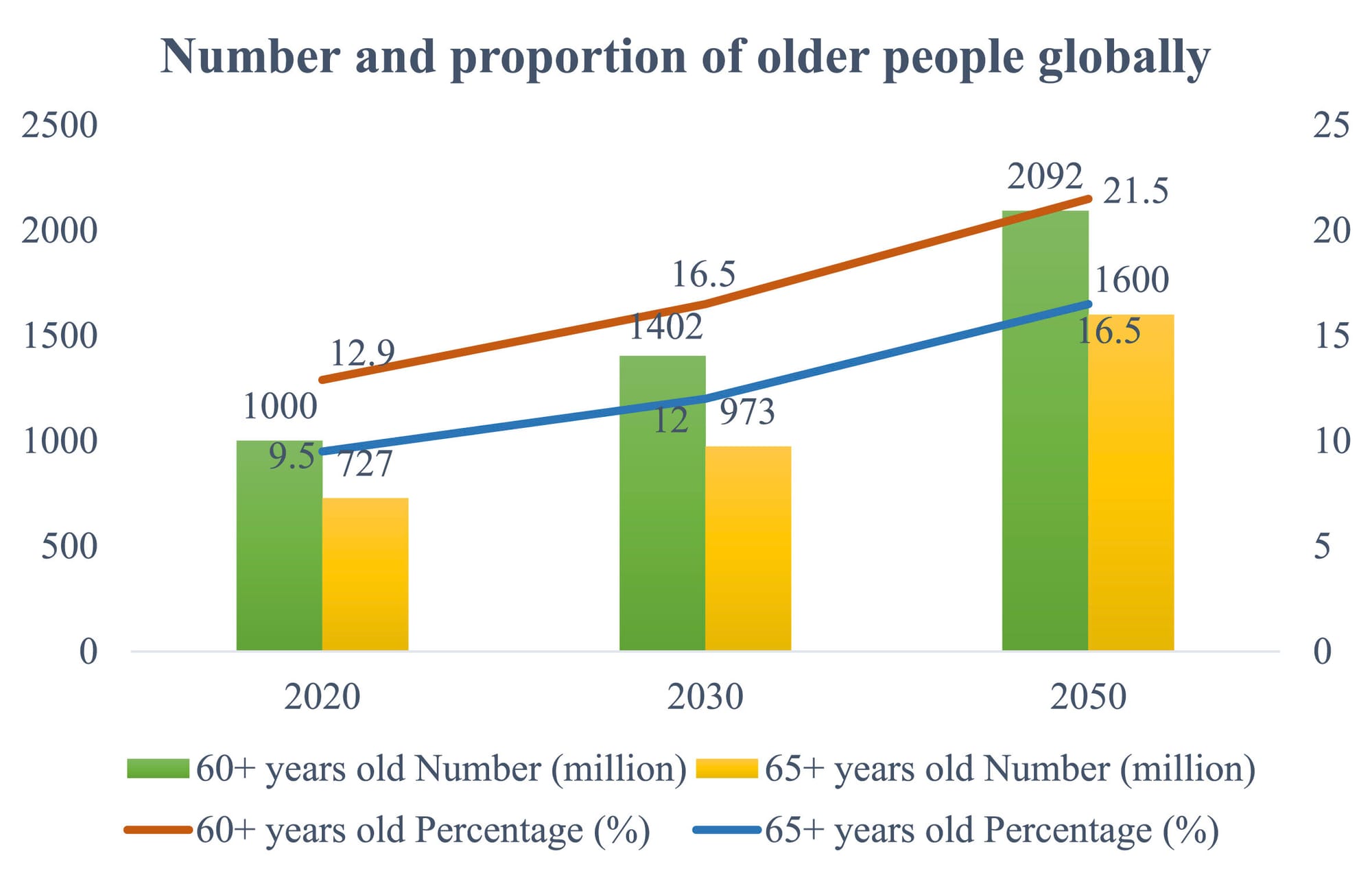
- With an aging global population, there is also a greater focus on making tourism more inclusive and accessible, according to Phys.org. This includes training frontline service employees to better interact with elderly tourists and those with specific health conditions. Enhancing accessibility and providing tailored services for senior tourists not only improves their travel experiences but also taps into a lucrative market segment.
Increasing Racial Acceptance
Another positive social factor for the tourism industry is the growing racial acceptance.
People worldwide are becoming more accepting of different races and religions, making travel a more comfortable experience for tourists. This increased acceptance reduces concerns about being profiled or targeted based on skin color, faith, or other personal traits, encouraging more people to travel freely and confidently.
Social Media and Influencer Impact
Social media platforms play a crucial role in the tourism industry. Travelers frequently share their experiences on social media, influencing their followers' travel decisions.
Individuals now maintain a constant online presence and often travel to create impressive content for their social media profiles. This social popularity of travel motivates people to embark on trips they might have otherwise skipped, providing a significant boost to the tourism industry.
Additionally, influencer marketing has become a powerful tool for destinations and brands to reach wider audiences. Engaging content and authentic reviews from influencers can drive interest and bookings.
Travelers often rely on social media reviews, travel blogs, and influencer endorsements to choose destinations and plan their trips. User-generated content and viral travel trends can boost a destination’s popularity.
Events and Festivals
Major events, festivals, and cultural celebrations attract tourists from around the world. Destinations that host internationally renowned events, such as the Olympics, World Cups, or music festivals, experience significant boosts in tourism.
Language and Communication
The ability to communicate effectively in the destination country affects tourists' experiences. Destinations that offer multilingual support and have locals proficient in widely spoken languages like English are more likely to attract international visitors.
Education and Awareness
Increased global awareness and education about different regions and cultures have expanded people’s horizons, encouraging them to explore new destinations. Educational tourism, where people travel for learning and cultural exchange, is also on the rise.
Family Structure and Travel Patterns
Changes in family structures, such as the rise of single-parent families, childless couples, and multi-generational travel groups, affect tourism trends.
Travel packages and destinations that cater to diverse family needs and preferences are becoming more popular.
Work-Life Balance and Leisure Time
The balance between work and leisure time significantly impacts tourism.
In societies where work-life balance is prioritized, people are more likely to take vacations and short breaks. Paid leave policies and flexible work arrangements also encourage travel.
Technological Factors

Here are the Technological factors affecting the tourism industry.
Online Booking Systems
The advent of online booking systems has revolutionized the tourism industry. Websites and mobile apps allow travelers to book flights, hotels, and tours with ease and convenience.
This technology has not only streamlined the booking process but also provided customers with a plethora of options and competitive pricing at their fingertips.
Smart Transportation Systems
One of the biggest technological factors influencing the tourism industry is the development of transport.
Not only do travelers have more transportation options than ever before, but they are also cheaper (and faster!). Buses, trains, and planes are also more comfortable and feature new amenities such as WiFi connectivity or charging ports.
Technological advancements in transportation, such as high-speed trains, autonomous vehicles, and ride-sharing platforms, are enhancing the connectivity and efficiency of travel. These innovations reduce travel time, improve safety, and offer convenient options for tourists, making travel more accessible and enjoyable.
Mobile Technology
Mobile technology is integral to the modern travel experience. Travelers rely on their smartphones for everything from navigation to booking accommodations on the go.
Mobile apps tailored to travel needs, such as those for language translation, local attraction guides, and transport services, enhance the overall convenience and enjoyment of the travel experience.
Cybersecurity
With the increasing reliance on digital platforms, cybersecurity is a critical concern in the tourism industry.
Protecting customer data, ensuring secure transactions, and safeguarding against cyber threats are paramount to maintaining trust and confidence among travelers. Advanced cybersecurity measures and protocols are essential to mitigate risks and protect sensitive information.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning technologies are increasingly being used to personalize travel experiences.
AI-powered chatbots provide 24/7 customer service, assisting with inquiries and bookings. Machine learning algorithms analyze user preferences and behaviors to offer tailored recommendations for destinations, accommodations, and activities.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
VR and AR technologies are transforming how destinations and attractions are marketed. Virtual tours and AR-enhanced guides allow potential travelers to explore destinations and experiences before they book, providing a taste of what to expect.
This technology can significantly influence travel decisions and enhance on-site experiences with interactive and immersive content.
Big Data and Analytics
Big data analytics enable tourism businesses to gain valuable insights into customer preferences, travel trends, and market demands.
By analyzing large datasets, companies can make informed decisions about marketing strategies, pricing models, and service improvements. This data-driven approach helps in creating personalized experiences and optimizing operational efficiency.
Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT technology enhances the travel experience through interconnected devices. Smart hotels utilize IoT to offer personalized room settings, such as lighting, temperature, and entertainment preferences.
Additionally, IoT-enabled devices in transportation, like connected cars and smart luggage, improve safety and convenience for travelers.
Innovation and Accessibility
The integration of technology in services like Uber and Airbnb has revolutionized how tourists plan and manage their trips, offering real-time information, easy booking processes, and cashless transactions.
Legal Factors
Here are some of the legal factors affecting the tourism industry.
Regulations and Compliance
Travel regulations are essential, encompassing international, national, and local travel laws.
These include visa requirements, customs regulations, and health and safety standards, all of which must be adhered to by tourism businesses and travelers alike. Additionally, environmental laws play a significant role, with regulations designed to protect natural resources impacting tourism activities.
For example, there might be restrictions on wildlife tours, specific eco-tourism guidelines to follow, and stringent waste management practices to ensure minimal environmental impact.
Furthermore, local zoning laws dictate where hotels, resorts, and other tourist facilities can be established and operated, which directly influences business planning and development in the tourism sector.
Employment Laws
Employment laws are critical in shaping the working conditions within the tourism industry.
Labor laws, which include regulations regarding wages, working conditions, hours, and employee rights, must be strictly followed to ensure fair treatment of workers. This is particularly relevant in a sector that often relies on seasonal employment, necessitating legal requirements for hiring temporary workers, including the necessary visas and permits for foreign employees.
Health and Safety Regulations
Health and safety regulations are paramount in the tourism industry.
Public health policies set the standards for food safety and hygiene in accommodations, ensuring that tourists' well-being is prioritized.
Safety standards for various activities, such as adventure sports, transportation, and accommodation facilities, are enforced to protect tourists and provide a safe travel experience.
Consumer Protection Laws
Protecting tourists from fraudulent practices is essential, which is where fair trading laws come into play. These regulations ensure that advertising is truthful and pricing is transparent, safeguarding consumers' rights.
Additionally, travel insurance regulations require businesses to offer insurance that covers cancellations, medical emergencies, and other unforeseen events, providing tourists with a safety net.
International Agreements and Policies
International agreements and policies can significantly influence tourism. Bilateral agreements between countries may facilitate easier travel through relaxed visa rules and air travel agreements.
Additionally, global health regulations, especially those relevant during pandemics like COVID-19, require strict compliance to ensure safe and healthy travel conditions.
Licensing and Permits
Obtaining the necessary licenses and permits is crucial for operating tourism businesses. This includes operational permits for hotels, travel agencies, tour companies, and other related businesses.
Special permits may also be required for specific activities, such as wildlife tours, visiting historical sites, or engaging in adventure sports.
Environmental Factors

Here are the environmental factors affecting the tourism industry.
Climate and Weather
The climate and weather conditions of a destination significantly influence tourism.
Favorable weather attracts tourists, while extreme weather conditions like hurricanes, heavy rainfall, or extreme heat can deter visitors. Seasonal variations also play a role, with peak tourist seasons often aligning with the most pleasant weather.
Sustainability Practices
There is a growing emphasis on sustainable tourism practices.
Tourists are increasingly seeking destinations that prioritize environmental conservation and sustainable practices. This includes eco-friendly accommodations, responsible wildlife tourism, and initiatives to reduce carbon footprints.
Natural Disasters
Natural disasters such as earthquakes, tsunamis, floods, and wildfires can have devastating impacts on tourism. These events can cause immediate harm to infrastructure and long-term damage to a destination’s reputation as a safe place to visit.
Environmental Regulations
Governments and international bodies impose environmental regulations that affect the tourism industry. These regulations might include restrictions on certain activities to protect natural resources, waste management requirements, and guidelines for sustainable tourism development.
Biodiversity and Natural Attractions
The presence of unique biodiversity and natural attractions like national parks, wildlife reserves, beaches, and mountains draw tourists. Efforts to protect and promote these natural assets can enhance a destination's appeal.
Pollution Levels
Pollution, including air, water, and noise pollution, can significantly deter tourists. Destinations with high levels of pollution are less attractive, and efforts to improve environmental quality can enhance their appeal.
Climate Change
Climate change poses long-term challenges and opportunities for tourism. Rising sea levels, changing weather patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events can alter tourist destinations. Conversely, destinations might benefit from new tourism opportunities due to changing climates in other regions.
Water Scarcity
Water scarcity can impact tourism, especially in regions heavily reliant on water-intensive activities like golf courses, swimming pools, and luxury resorts. Sustainable water management practices are essential to ensure the long-term viability of tourism in these areas.
Eco-tourism Demand
There is an increasing demand for eco-tourism, where tourists seek environmentally responsible travel experiences. This includes activities like hiking, bird watching, and staying in eco-lodges that minimize environmental impact.
Waste Management
Effective waste management practices are crucial in maintaining the environmental integrity of tourist destinations. Poor waste management can lead to pollution and damage the natural beauty that attracts tourists.
Energy Consumption
The tourism industry’s energy consumption patterns affect its environmental impact. The use of renewable energy sources and energy-efficient practices in accommodations, transportation, and tourist facilities can reduce the carbon footprint and appeal to environmentally conscious travelers.
Wildlife Conservation
Wildlife conservation efforts are important in preserving the natural attractions that draw tourists. Destinations that actively engage in protecting their wildlife and natural habitats are more likely to attract eco-conscious tourists.
Green Certifications
Green certifications for hotels, tour operators, and other tourism-related businesses signal a commitment to sustainable practices. These certifications can attract tourists looking for environmentally responsible options.
Infrastructure Development
The development of environmentally sustainable infrastructure, such as green buildings and eco-friendly transport options, can enhance a destination's appeal and reduce its environmental impact.
PESTLE Analysis of the Tourism Industry: Final Thoughts
As I wrap up our PESTLE analysis of the tourism industry, it’s clear that a variety of factors play significant roles in shaping its future. Politically, I’ve seen how government policies, visa regulations, political stability, and international relations can make or break a destination’s appeal. Economically, things like economic stability, exchange rates, disposable incomes, and global economic trends greatly influence how and where people choose to travel.
On the social front, it’s fascinating to see how changing lifestyle trends, cultural diversity, social media influence, and demographic shifts are driving new travel behaviors. Technological advancements, such as online booking systems, mobile apps, AI, big data, and IoT, are revolutionizing the industry, making travel more convenient and personalized.
Legally, I’ve noted the importance of staying compliant with regulations, employment laws, consumer protection measures, and international agreements to ensure safe and fair operations. Environmentally, I’m particularly interested in how sustainability practices, climate change, pollution levels, and conservation efforts are becoming crucial as more travelers seek eco-friendly options.
Understanding these factors helps me—and hopefully you too—see the bigger picture of what makes the tourism industry tick.
Now, feel free to check out the following types of analysis of key industries related to tourism:
- PESTLE Analysis of the Hotel Industry
- PESTLE Analysis of the Food and Beverage Industry
- PESTLE Analysis of the Airline Industry






