Artificial intelligence (AI) isn’t something out of sci-fi novel — it’s here, being used right this second by technology experts, businesses, and the average person like you or me. Despite moving from fantasy to everyday reality, there’s plenty of hang-ups regarding AI.
For one, people fear the power of AI.
What if it gets in the wrong hands? Can it be used nefariously? Others wonder if it’s truly better to rely on machines to do tasks humans were once responsible for.
Artificial Intelligence Strengths
Automation of Repetitive Tasks
AI can automate routine and repetitive tasks, freeing up human workers to focus on more complex and creative work.
Rather than spending hours of manpower on menial, repeatable tasks, employees can configure artificial intelligence to manage it instead. Although we’ve already used machines on the production lines before, AI allows us to manage a multitude of tasks more efficiently than before.
This is beneficial for all companies. By having technology manage everyday tasks (rather than humans), companies save money. It lowers operations costs and even noncompliance fees.
This is perfect for people who dread taking care of these tasks and would rather focus on the “big picture”. Entrepreneurs or startups who have employees wearing a lot of hats and are stretched thin will love AI for this.

Scalability
AI systems can be scaled up to handle increasing amounts of work without a proportional increase in cost or human labor, making them cost-effective for large-scale operations.
AI is now used in a variety of industries, ranging from digital marketing to healthcare. The type and sophistication of the AI needed depend on the task — you’ll need less power to automate emails than sorting through a registry of patient information, for example. It’s not just for sorting information either; we’re also seeing AI used in facial recognition and academic research too.
Personalization
Artificial Intelligence can tailor experiences and recommendations based on individual preferences and behaviors, enhancing user satisfaction in applications such as online shopping and streaming services.
Within the home, people who have smart speakers and light bulbs are using AI too. These devices make managing the home easier and can reduce the cost of electricity. You can even find AI in your car, so long as you’re buying a brand like Tesla.
In some ways, it’s strange. Only a few years ago, artificial intelligence was found only in sci-fi books, games, and movies. Now it’s commonplace, despite not reaching even its full capabilities yet.
More Strengths
- Data Analysis and Insights: AI can process and analyze vast amounts of data quickly, providing valuable insights and identifying patterns that may be missed by humans.
- Accuracy and Precision: AI systems can perform tasks with a high degree of accuracy and consistency, reducing the likelihood of human error.
- 24/7 Availability: Unlike humans, AI systems can operate continuously without the need for breaks, making them ideal for tasks that require constant monitoring or engagement.
- Predictive Capabilities: AI can use historical data to make predictions about future events, which is useful in fields like finance, healthcare, and weather forecasting.
- Natural Language Processing: AI can understand and generate human language, enabling more natural and effective interactions between humans and machines through chatbots and virtual assistants.
- Image and Speech Recognition: AI excels at recognizing and interpreting visual and auditory data, making it valuable in applications such as facial recognition, medical imaging, and voice-controlled devices.
- Adaptive Learning: AI can learn and adapt over time through machine learning algorithms, improving its performance and making better decisions as more data becomes available.
Artificial Intelligence Weaknesses
Limited Emotional Intelligence
AI lacks emotional intelligence and the ability to understand and respond to human emotions, making it less effective in roles that require empathy and interpersonal interaction.
You know by now that artificial intelligence is a form of technology. It can be a machine or an algorithm. But of course, it’s not human. And this last point remains a strength and a weakness simultaneously. As a strength, it means people working in jobs requiring a touch of “humanity” feel safe — their job isn’t up for grabs by our technological overlords quite yet.
But as a weakness, this means AI is limited. It’s a tool but not necessarily a solution. AI can communicate, but it can’t communicate emotionally. And so, although it can use information, it won’t be able to grasp or react to the complexities of human emotion.
Ethical Concerns
AI raises various ethical issues, including biases in decision-making, lack of transparency, and the potential misuse of AI for harmful purposes.
Developers are always pushing to redefine the limits of AI. Right now, it’s able to complete a task, learn, and retain information. But maybe, in the future, it’ll get to the point of improving and redesigning without human input. It’s this potential reality that makes people remember the robotic overthrowing in the movie I, Robot.
Technological experts, like Elon Musk, have warned against artificial intelligence, believing that we need to be smart about how we use it. And how do we use it?
This prompts the question of ethics. Is there a line for the ethical use of AI? Bills, regulations, and laws aren’t keeping up with the rapid development of technology. Even Congress doesn’t fully understand how the internet works, so what hope is there for the ethical use of AI?
Security Risks
AI systems can be highly vulnerable to hacking and cyberattacks, posing significant security risks.
These systems often process and store vast amounts of sensitive data, including personal information, financial records, and proprietary business information. A successful breach can lead to the unauthorized access and exploitation of this data, causing substantial harm to individuals and organizations.
Moreover, AI algorithms can be manipulated through adversarial attacks, where malicious actors subtly alter inputs to deceive the AI into making incorrect decisions. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures and continuous monitoring is essential to protect AI systems from these evolving threats.
Dependence on Infrastructure
AI technology demands a robust and sophisticated technological infrastructure to function effectively.
This includes high-speed internet, powerful computing resources, and reliable data storage solutions.
In regions with limited access to these technological amenities, deploying and utilizing AI can be challenging. The disparity in infrastructure availability can lead to a digital divide, where certain areas or communities are unable to benefit from AI advancements.
Additionally, the energy consumption required to support large-scale AI operations is significant, raising concerns about environmental impact and sustainability.
Maintenance and Updates
Maintaining and updating AI systems is a continuous and resource-intensive process. AI models need regular updates to improve accuracy, adapt to new data, and address emerging threats.
This requires a team of skilled professionals, including data scientists, engineers, and cybersecurity experts, to manage the lifecycle of AI applications. Furthermore, software updates and patches are crucial to fix vulnerabilities and enhance system performance.
Without proper maintenance, AI systems can become outdated, less effective, and more susceptible to security breaches. Organizations must invest in the necessary resources and infrastructure to ensure their AI systems remain reliable and secure over time.
High Initial Costs
Developing and implementing AI systems can be expensive, requiring significant investment in hardware, software, and specialized personnel.
Example:
In 2024, China's commercial hub, Shanghai, announced a substantial investment of 100 billion yuan ($13.79 billion) to boost its integrated circuit, biomedicine, and artificial intelligence (AI) industries.

This massive fund highlights the scale of financial commitment needed to support fields such as intelligent chips, software, autonomous driving, and intelligent robots. Such investments are crucial to support original innovation and accelerate the emergence of globally competitive enterprises, underscoring the high initial costs associated with advancing AI technology.
More Weaknesses
- Limited Understanding and Context: AI systems often lack the deep understanding and contextual awareness that humans possess, leading to potential misinterpretations or inappropriate responses in complex situations.
- Data Dependency: AI performance heavily relies on the quality and quantity of data. Poor quality data or insufficient data can lead to inaccurate results and flawed decision-making.
- Lack of Creativity: AI can process existing information and make predictions based on patterns, but it struggles with creativity and innovative thinking, which are inherently human traits.
- Job Displacement: The automation of tasks through AI can lead to job losses and economic displacement, particularly in sectors where repetitive tasks are common.
Artificial Intelligence Opportunities
And yet, despite the fear caused by AI, it does come with a fair share of opportunities.
Combining AI with newer forms of tech
Artificial intelligence is connected to other new forms of technology, including machine learning, deep learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT). It’ll likely be adopted into programming, enabling developers to reverse problem solve. This allows for enhanced responses to problems, which may benefit other industries, like customer service.
Transportation and Logistics
AI can improve logistics and transportation through route optimization, predictive maintenance, and autonomous vehicles. AI-driven systems can enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and minimize environmental impact.
Right at this moment, we’re seeing the adoption of Artificial Intelligence in the automobile market.
Tesla car models use it to self-drive on the highway and park without human assistance. Obviously, this is something straight out of a science fiction novel (aka cool as heck) but it’s also beneficial for people who have disabilities and has impacted their driving ability.
Enhanced Healthcare
AI has the potential to revolutionize healthcare by improving diagnostics, personalizing treatment plans, and enabling predictive analytics for disease prevention.
AI-driven tools can analyze medical images, process large datasets to identify trends, and support decision-making for medical professionals.

Innovative Business Models
AI enables the creation of new business models and services.
From predictive maintenance in manufacturing to personalized marketing in retail, AI can drive innovation and create competitive advantages for businesses.

Financial Services
AI can improve financial services through fraud detection, risk assessment, and personalized financial advice. AI algorithms can analyze transaction patterns to identify fraudulent activities and help investors make informed decisions.
Example:
In 2024, JPMorgan Chase began rolling out a generative AI product, enabling employees in its asset and wealth management division to use a large language model called LLM Suite for tasks such as writing, idea generation, and summarizing documents.

Similarly, Morgan Stanley partnered with OpenAI to introduce a GenAI-powered chatbot, providing financial advisors with quick access to the bank's intellectual capital. These implementations highlight AI's potential to enhance productivity and innovation in financial services.

Agricultural Advancements
AI can support precision agriculture by analyzing soil conditions, predicting crop yields, and optimizing irrigation and fertilization. This can lead to increased productivity, reduced resource use, and improved food security.

More Opportunities
- Improved Education: AI can transform education through personalized learning experiences, intelligent tutoring systems, and administrative automation. It can help identify students' strengths and weaknesses, adapt teaching methods to individual needs, and free up educators' time for more personalized interactions.
- Environmental Protection: AI can contribute to environmental sustainability by optimizing resource use, improving energy efficiency, and supporting conservation efforts. For example, AI can be used to monitor wildlife populations, predict natural disasters, and manage renewable energy sources.
- Smart Cities: AI can enhance urban living by improving traffic management, waste management, and public safety. Smart city technologies can analyze data from various sources to optimize infrastructure and provide better services to residents.
- Customer Service: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide efficient and scalable customer service. They can handle routine inquiries, resolve issues quickly, and offer personalized support, enhancing customer satisfaction and reducing operational costs.
- Scientific Research: AI can accelerate scientific discoveries by analyzing large datasets, simulating complex systems, and generating new hypotheses. In fields such as genomics, materials science, and climate research, AI can help scientists uncover new insights and advance knowledge.
Artificial Intelligence Threats
And although there are plenty of opportunities for AI, this technology has just as many (or more) threats.
Job Displacement
The automation of tasks through AI can lead to significant job losses, particularly in industries where repetitive tasks are common. This can result in economic displacement and increased unemployment rates.
People believe the adoption of artificial intelligence will lead to job loss. And honestly, this is happening on a small scale. Think about those self-checkouts at Walmart. There’s several of them and only one or two employees stepping in whenever a customer has a problem.
No more humans working the cashier is a viable future for corporations. This is one example of AI taking over simple human tasks, but also taking away job opportunities. To combat this, the job market will need to evolve. Rather than being replaced, humans will need to work alongside AI. Whether this is a viable future is yet to be determined.
Example:
According to this 2024 news story, Walmart plans to potentially, Walmart plans to potentially spend $200 million on self-driving forklifts as part of broader efforts to automate its warehouse operations. The world's largest retailer aims to use autonomous forklifts to move pallets of goods in its distribution centers, which replenish Walmart stores. This initiative includes the possible purchase of hundreds of forklifts from Fox Robotics, with a $25 million investment already made in the Austin-based startup.
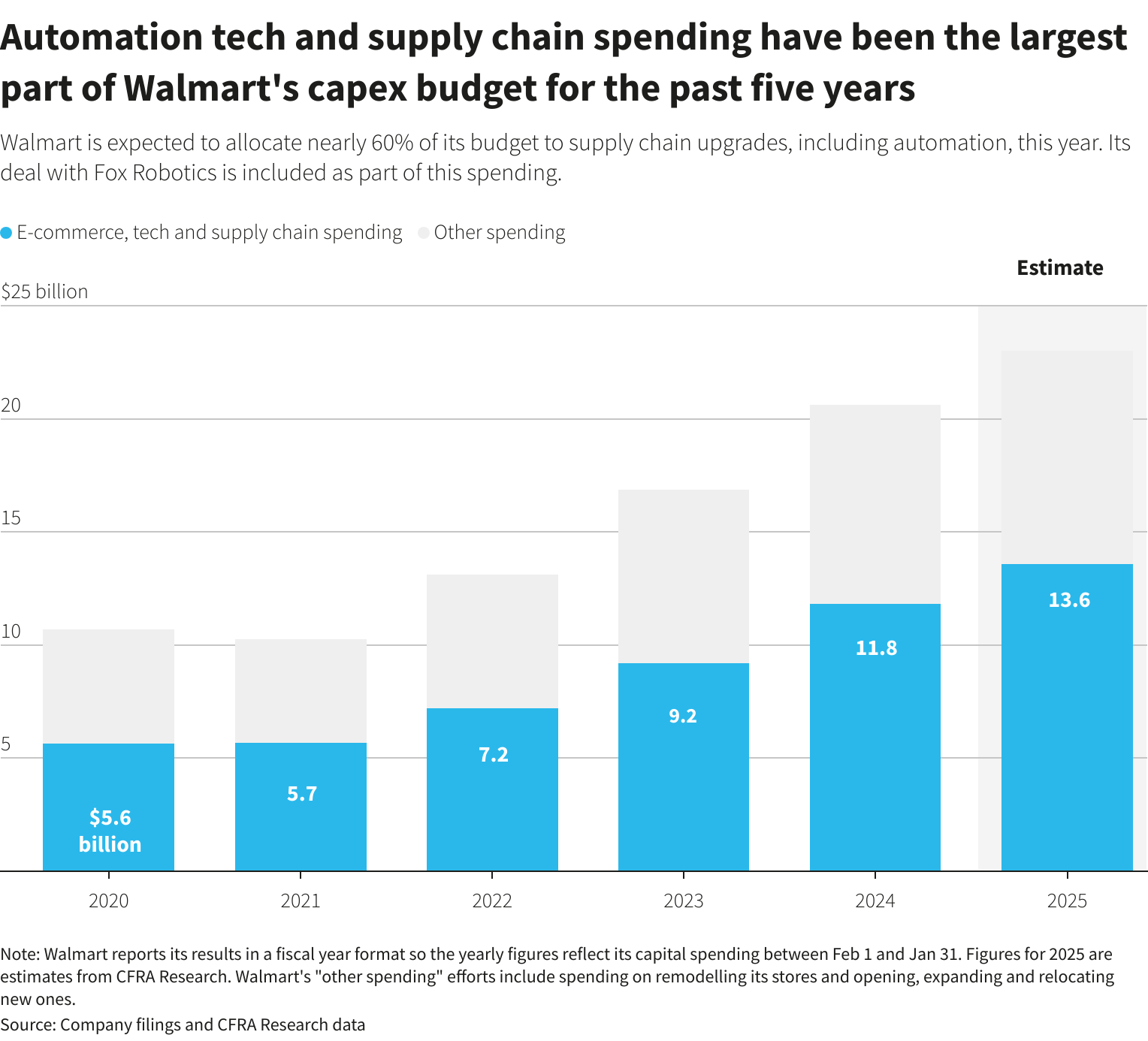
The rollout, which could occur in stages over several years, underscores Walmart's strategy to enhance efficiency, reduce labor costs, and increase profit margins. A single human operator can manage up to six autonomous forklifts at a time, potentially saving up to 40% on labor costs. While Walmart maintains that people will always be part of its warehouse operations, the increasing automation signals a shift toward less dependence on human labor. This move towards robotics and automation highlights the potential for significant job displacement in the future as companies seek to streamline operations and cut costs.
Loss of Control
As AI systems become more autonomous, there is a risk of losing control over their actions. This can be particularly concerning in critical areas such as military applications and autonomous vehicles.
People wonder — will AI become so intelligent, humans can’t control it any longer? This seems like a far off fear, but it may be closer than you think.
IBM has a supercomputer named Watson, who appeared on and won more than $5 million on the game show Jeopardy back in 2011. Watson is hooked up to the cloud and uses machine learning and analytical software. It proved to be smarter than humans (at least in finding, using, and retaining information quickly) on the show eight years ago — and this is when artificial intelligence was “new”.
Is it possible for Watson (or similar supercomputers) to eventually become sentient? It’s too soon to tell, and this is the threat people feel.
Dependence on Technology
Increasing reliance on AI systems can create vulnerabilities if these systems fail or are compromised. This dependence can lead to disruptions in critical services and infrastructure.
AI is used in the diagnosis of medical conditions. In fact, it’s been known to find diagnoses quicker than humans.
But what if the computer gets it wrong? Or if the technology is corrupted by a virus and changed? The repercussions of premature or completely wrong diagnoses could lead to fatalities.
See, the biggest threat to AI is the “what if” of it all. Since technology is constantly tested and advanced, we don’t know the limits. And that’s both exciting and terrifying.
More Threats
- Bias and Discrimination: AI systems can perpetuate and even amplify existing biases present in the training data. This can lead to unfair treatment and discrimination in areas such as hiring, lending, and law enforcement.
- Privacy Concerns: AI systems often require large amounts of data, raising concerns about privacy and data security. The collection and use of personal data by AI systems can lead to unauthorized access and misuse of sensitive information.
- Security Vulnerabilities: AI systems can be targeted by cyberattacks, leading to data breaches and manipulation of AI algorithms. Adversarial attacks can deceive AI systems into making incorrect decisions, posing significant security risks.
- Ethical Dilemmas: The use of AI in decision-making processes raises ethical questions about accountability and transparency. There is a risk of AI systems making decisions that lack human empathy and ethical consideration.
- Economic Inequality: The benefits of AI may not be evenly distributed, potentially exacerbating economic inequality. Wealthy individuals and organizations may have greater access to AI technologies, widening the gap between different socioeconomic groups.
- Misuse of AI: AI technology can be used for malicious purposes, such as creating deepfakes, enhancing cyberattacks, or developing autonomous weapons. The misuse of AI can have serious implications for security and societal stability.
- Regulatory Challenges: The rapid advancement of AI technology poses challenges for regulation and governance. Developing appropriate legal and ethical frameworks to manage AI's impact on society is complex and requires international cooperation.
Final thoughts on the SWOT Analysis of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence is here and it isn’t going anywhere. The possibilities are endless, and this drives experts to keep advancing it. However, some of the public worries — about the future of jobs, and even of humankind.

AI isn’t evil though — it takes over mundane tasks to free up our time. It’s ported into various forms of technology, like smart bulbs, to reduce electricity use and emissions. It’s also helping to diagnose conditions early in healthcare — in the right hands, AI has the ability to increase our quality of life.
We just need to keep an eye (and hand) on it.









